HSZ80 Array Controller ACS Version
Page
Japan USA
Page
Chapter
Creating Storagesets
CLI Commands
Vii
Viii
Appendix a
Page
Figures
Xii
Tables
Xiii
Xiv
Getting Help
Compaq Website Telephone Numbers
Component Precaution
Precautions
Electrostatic Discharge Precautions
Xvi About This Guide
Maintenance Port Precautions
Vhdci Cable Precautions
Xvii
Typographical Conventions
Conventions
Xviii About This Guide
Special Notices
Xix
Required Tools
Xx About This Guide
Related Publications
Xxi
Revision History
Xxii About This Guide
General Description
Typical Installation
2General Description
Basic Building Block
Basic Building Blocks List
4General Description
Summary of HSZ80 Features
Summary of Controller Features
6General Description
HSZ80 Array Controller
Bridging the Gap Between the Host and Its Storage Subsystem
8General Description
HSZ80 Array Controller
HSZ80 Array Controller
Description of Parts
10General Description
Description of Parts
Parts of the Optional Maintenance Port Cable
12General Description
Operator Control Panel
EMU PVA
Maintenance Port
14General Description
Utilities and Exercisers
Fault Management Utility
Virtual Terminal Display
Code Load and Code Patch Utility
Configuration Utility
Disk Inline Exerciser
Clone Utility
Change Volume Serial Number Utility
Field Replacement Utility
Device Statistics Utility
Cache Module
Cache Module Memory Configurations
18General Description
Location of Cache Module Parts
Read-Ahead Caching
Caching Techniques
Read Caching
20General Description
Write-Through Caching
Write-Back Caching
Cache Policies Resulting from Cache Module Failures
Fault-Tolerance for Write-Back Caching
Nonvolatile Memory
22General Description
Cache Policies and Cache Module Status
24General Description
Failover to controller B
Resulting Cache Policies and ECB Status
26General Description
Through caching to its units Less than
28General Description
External Cache Battery
10 ECB Capacity Based on Memory Size
11 Location of Parts
30General Description
Charging Diagnostics
Battery Hysteresis
Page
Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
2Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Configuration Rules
Introduction
Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Few Tips
4Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Configuring a Single Controller
Location of Parts for a Single Controller Configuration
6Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
SET Thiscontroller HOSTFUNCTION= ID, Mode
8Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Connecting a Single Controller to the Host
10Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Location of Parts for Transparent Failover
12Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
SET Failover Copy = Thiscontroller
Restart Othercontroller Restart Thiscontroller
14Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Connecting in Transparent Failover Mode to the Host
16Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Location of Parts for Multiple-Bus Failover
18Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
SET Multibusfailover Copy = Thiscontroller
Restart Othercontroller Restart Thiscontroller
20Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Connecting in Multiple-Bus Failover Mode to the Host
Optional Steps
22Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Change the CLI prompt
Set the maximum data-transfer rate
24Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
UPS Support
Setting the PVA Module ID Switch
26Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Establishing a Local Connection to Controller
PC/Terminal to Maintenance Port Connection
28Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
This Controller and Other Controller
Selecting a Failover Mode
Using Transparent Failover Mode
Using Multiple-Bus Failover Mode
30Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Selecting a Cache Mode
Enabling Mirrored Write-Back Cache
Fault-Tolerance
32Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Setting Scsi Target ID Numbers
Host Scsi Bus
34Configuring an HSZ80 Array Controller
Device Scsi Bus
Using Preferred ID Numbers
Page
Creating Storagesets
2Creating Storagesets
Disk drives
Planning and Configuring Storagesets
4Creating Storagesets
Creating a Storageset and Device Profile
Creating Storagesets
Type of Storageset
Determining Storage Requirements
8Creating Storagesets
Choosing a Storageset Type
A Comparison of Different Kinds of Storagesets
For Disk Array Technology
Using Stripesets to Increase I/O Performance
Considerations for Planning a Stripeset
10Creating Storagesets
Distribute Members across Ports
Using Mirrorsets to Ensure Availability
12Creating Storagesets
Considerations for Planning a Mirrorset
Mirrorsets Maintain Two Copies of the Same Data
14Creating Storagesets
First Mirrorset Members on Different Buses
Using RAIDsets to Increase Performance Availability
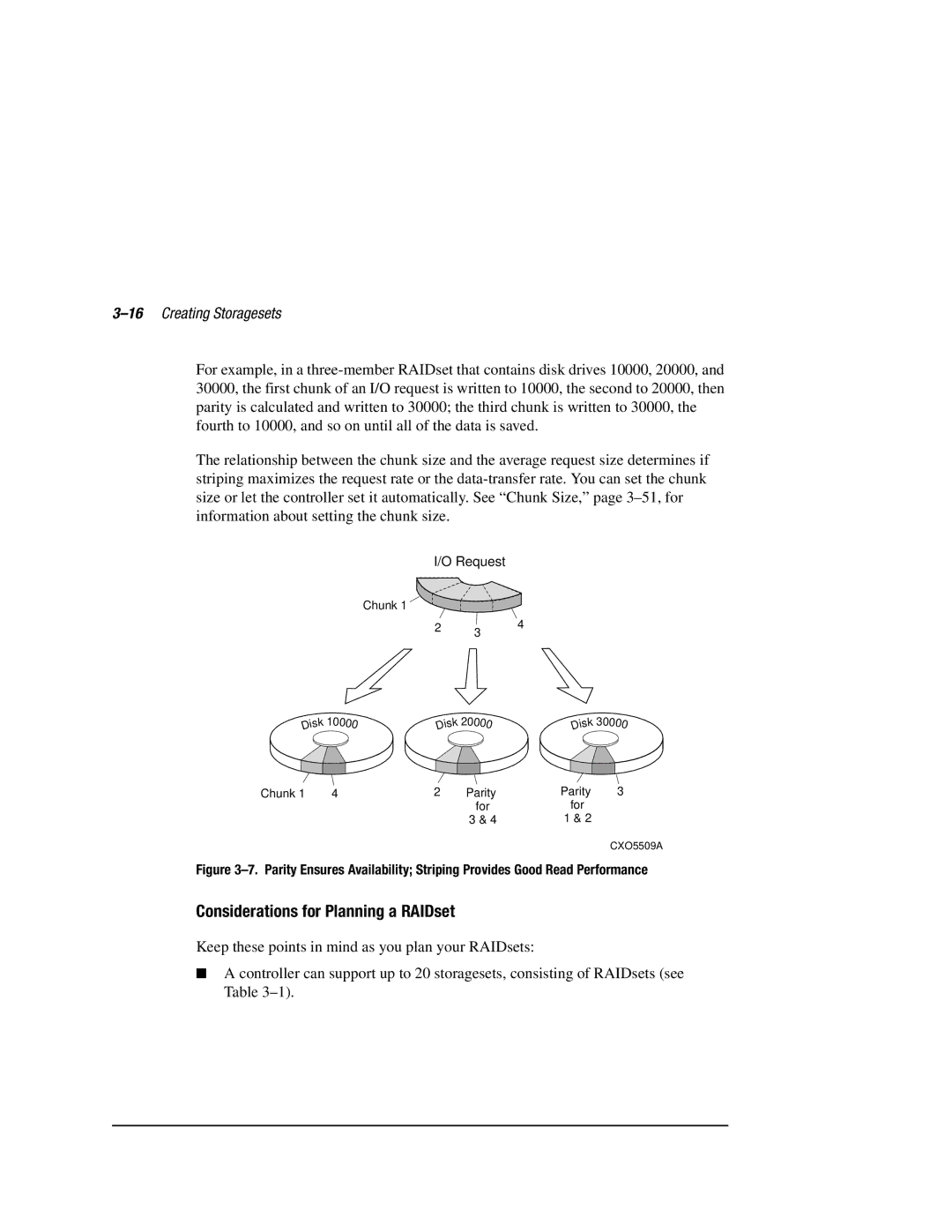
Considerations for Planning a RAIDset
16Creating Storagesets
Page
18Creating Storagesets
Striping and Mirroring in the Same Storageset
Considerations for Planning a Striped Mirrorset
Cloning Data for Backup
20Creating Storagesets
Clone Steps for Duplicating Unit Members
Example
22Creating Storagesets
Use available device DISK20400size=832317 for member
24Creating Storagesets
DISK20000size=832317 y,n y ? y
Backing Up Your Subsystem Configuration
Saving Subsystem Configuration Information to a Single Disk
Saving Subsystem Configuration Information to a Storageset
26Creating Storagesets
Displaying the Status of the Save Configuration Feature
Controller
28Creating Storagesets
Cache
Notransportable
Restoring Node IDs
Node IDs
30Creating Storagesets
Page
Assigning Unit Numbers for Host Access to Storagesets
32Creating Storagesets
Unit Numbering Examples
LUN
Creating a Storageset Map
34Creating Storagesets
10. Storageset Map
36Creating Storagesets
Device PTL Addressing Convention within Controller
Locate devicename
11. PTL Naming Convention
38Creating Storagesets
Device port numbers Target Numbers
13. Locating Devices using PTLs
Defining a Partition
Planning Partitions
40Creating Storagesets
Guidelines for Partitioning Storagesets Disk Drives
Changing Switches
Choosing Switches for Storagesets Devices
Enabling Switches
42Creating Storagesets
Replacement Policy
RAIDset Switches
Reconstruction Policy
Membership
44Creating Storagesets
Mirrorset Switches
Read Source
Copy Speed
46Creating Storagesets
Disaster Tolerance Support
Transportability
Device Switches
48Creating Storagesets
Device Transfer Rate
50Creating Storagesets
Local/Remote
Dtsupport
Initialize Switches
Chunk Size
Increasing the Request Rate
52Creating Storagesets
Increasing the Data Transfer Rate
16. Chunk Size Smaller than the Request Size
Maximum Chunk Sizes for a RAIDset
Increasing Sequential Write Performance
Maximum Chunk Size for RAIDsets
54Creating Storagesets
Save Configuration
Considerations for Saving the Configuration
56Creating Storagesets
Destroy/Nodestroy
Unit Switches for Storagesets
Unit Switches
58Creating Storagesets
Configuring Storagesets
Adding Disk Drives
2Configuring Storagesets
ADD Disk DISKnnnn ptl-location switchvalue
Adding One Disk Drive at a Time
Configuring a Stripeset
ADD Mirrorset mirrorset-name DISKnnnn DISKnnnn switch
Configuring a Mirrorset
4Configuring Storagesets
Initialize mirrorset-name switch
ADD Unit unit-number mirrorset-name switch
Show mirrorset-name
ADD Raidset RAIDset-name DISKnnnn DISKnnnn DISKnnnn switch
Configuring a RAIDset
6Configuring Storagesets
Initialize RAIDset-name switch
Show RAIDset-name
Configuring a Striped Mirrorset
ADD Stripeset stripeset-name mirrorset1 mirrorset2
8Configuring Storagesets
Configuring a Single-Disk Unit
ADD Unit unit-number DISKnnnn switchvalue
10Configuring Storagesets
Partitioning a Storageset or Disk Drive
Initialize storageset-name switch
Show storageset-name
12Configuring Storagesets
Adding a Disk Drive to the Spareset
Removing a Disk Drive from the Spareset
14Configuring Storagesets
Enabling Autospare
Delete unit-number
16Configuring Storagesets
Deleting a Storageset
Delete storageset-name
Changing RAIDset and Mirrorset Switches
Changing Switches for a Storageset or Device
Displaying the Current Switches
Changing Device Switches
Changing Unit Switches
Changing Initialize Switches
18Configuring Storagesets
Configuring with the Command Console LUN
Enabling and Disabling the CCL
20Configuring Storagesets
SCSI-2 Mode
SCSI-3 Mode
Finding the CCL Location
Troubleshooting with the CCL
Adding Storage Units with the CCL
22Configuring Storagesets
Configuring Units with Multiple Hosts
Host Modes
24Configuring Storagesets
IBM AIX
Setting Host Modes
26Configuring Storagesets
Transparent Failover Mode
Designating the Port
Accessing Units on a Given Port
28Configuring Storagesets
Designating the Host Scsi ID Number
Scsi ID
30Configuring Storagesets
Designating the Port and Designating the Host Scsi ID Number
SET this PORT1ID = SET this PORT2ID =
Multiple-Bus Failover Mode
32Configuring Storagesets
Assigning Units through Multiple Host Adapters
34Configuring Storagesets
Moving Storagesets
Moving a Storageset from one Subsystem to Another
Delete disk-name
36Configuring Storagesets
Locate disk-name
ADD Disk disk-name PTL-location
ADD storageset-name disk-name disk-name
ADD Unit unit-number storageset-name
38Configuring Storagesets
Move disk drives to their new location
CLI Commands
2CLI Commands
Using the CLI
Command Overview
CLI Overview
Getting Help
Entering CLI Commands
SET Thiscontroller ?
4CLI Commands
Recall and Edit Command Keys
Unit Naming
Unit Number
Command parameter Switches
Command Syntax
6CLI Commands
Changing the CLI Prompt
Syntax
ADD Disk
Parameters
Transportable
Switches
8CLI Commands
Remote
TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED=10MHZ TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED=5MHZ
TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED=20MHZ Default
TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED=ASYNCHRONOUS
ADD Disk DISK40200 4 2 0 Transportable
Initialize DISK20000 2 0 ADD Unit D199 DISK20000
10CLI Commands
See also
ADD Disk DISK200 2 0 0 Remote
ADD Mirrorset
COPY=FAST
Dtsupport Nodtsupport
12CLI Commands
POLICY=BESTPERFORMANCE Default
POLICY=BESTFIT
READSOURCE=disk-name READSOURCE=LEASTBUSY Default
READSOURCE=ROUNDROBIN
ADD Mirrorset MIRR1 DISK10000 DISK20100 DISK30200
14CLI Commands
Initialize MIRR1 ADD Unit D104 MIRR1
Initialize Mirror Reduce
ADD Disk ADD Unit
Show Mirrorsets Show Storagesets Unmirror
Parameter
16CLI Commands
ADD Passthrough
ADD Passthrough passthrough-name scsi-port-target-lun
ADD Passthrough TAPE20300 2 3 ADD Unit P100 TAPE20300
Show Devices Show Passthrough
18CLI Commands
Show passthrough-name
ADD Raidset
RAIDset-name
RECONSTRUCT=NORMAL Default
20CLI Commands
RECONSTRUCT=FAST
ADD Raidset RAID9 DISK10000 DISK20100 DISK30200
Noreduced Default
Reduced
Initialize RAID8
ADD Raidset RAID6 DISK10300 DISK20400 DISK30200 Reduced
22CLI Commands
ADD Unit D70 RAID8
SET Raidset Show Raidset
Delete Spareset Show Spareset Show Storagesets
ADD Spareset
ADD Spareset DISK20200 ADD Spareset DISK30300
Disk-name
Stripeset-name
24CLI Commands
ADD Stripeset
Container-name1 container-name2 container-nameN
ADD Stripeset STRIPE1 DISK10000 DISK20100 DISK30200
Initialize STRIPE1 ADD Unit D103 STRIPE1
ADD Unit ADD Mirrorset
26CLI Commands
Initialize Show Storageset Show Stripeset
ADD Unit unit-number container-name
ADD Unit
Unit-number
ADD Unit Switches for Storagesets
28CLI Commands
Page
Nopreferredpath Default
30CLI Commands
MAXIMUMCACHEDTRANSFER=32 Default MAXIMUMCACHEDTRANSFER=n
PARTITION=partitionnumber
Noreadcache
Readcache Default
Readaheadcache Default
Noreadaheadcache
Nowriteprotect
32CLI Commands
Norun
Nowritebackcache
ADD Unit D102 DISK10000 PREFERREDPATH=THISCONTROLLER
Delete unit-number SET unit-number
34CLI Commands
Createpartition
Show Units
Clearerrors CLI
Clearerrors CLI
Clearerrors CLI
Clearerrors Clearerrors Clearerrors Clearerrors
36CLI Commands
Clearerrors controller Invalidcache
Controller
Examples
Clearerrors DISK30000 Unknown
Clearerrors device-nameUNKNOWN
38CLI Commands
Device-name
See also
40CLI Commands
Clearerrors unit-numberLOSTDATA
Clearerrors D103 Lostdata
See also
Clearerrors D103 Unwriteabledata
Clearerrors unit-number
42CLI Commands
Unwriteabledata
See also
Configuration Reset
Configuration Reset
44CLI Commands
Configuration Restore Configuration Save Initialize
Configuration Restore
Configuration Restore
46CLI Commands
Configuration Reset Configuration Save Initialize
Configuration Save
Configuration Reset Configuration Restore Initialize
Createpartition container-name SIZE=percent
48CLI Commands
Createpartition
SIZE=percent
CAPACITY= CYLINDERS= HEADS= SECTORSPERTRACK=
50CLI Commands
Destroy Partition Show
Delete DISK10000
Delete STRIPE1
Delete Failedset Delete Spareset Unmirror
52CLI Commands
Delete RAID9
Delete Failedset DISK20200
Delete Failedset
SET Failedset Show Failedset
Delete Spareset DISK20300
Delete Spareset
54CLI Commands
ADD Spareset Show Spareset
Delete unit-number
Delete D103
ADD Unit Clearerrors Lostdata
56CLI Commands
Delete Failedsets Delete Sparesets Destroypartition
Destroypartition container-name PARTITION=partition-number
Destroypartition
Partition-number
58CLI Commands
Delete D102 Destroypartition RAID9 PARTITION=2
Directory
Directory
RUN
Help
60CLI Commands
Help
Help
SET ?
Your options are
Initialize
62CLI Commands
Initialize container-name
CHUNKSIZE=DEFAULT Default CHUNKSIZE=n
Saveconfiguration
64CLI Commands
Destroy Default
Nosaveconfiguration Default
Initialize DISK10000 Saveconfiguration
Show Devices Full
66CLI Commands
Reduce DISK40400 Initialize DISK40400 Nodestroy
Locate parameter
Cancel
Locate
ALL
PTL SCSI-location
68CLI Commands
Disks
Units
Locate D102
Locate DISK10000 Locate Cancel
Locate Disks
Mirror
70CLI Commands
Mirror disk-name mirrorset-name
Nopolicy Default
POLICY=BESTFIT POLICY=BESTPERFORMANCE
72CLI Commands
ADD Mirrorset Reduce Show Mirrorsets Unmirror
Battery on
Poweroff
74CLI Commands
Overridebadflush
Poweroff Switch Settings
SECONDS=nn
76CLI Commands
Poweroff SECONDS=10
Reduce
Reduce disk-name1 disk-name2 disk-name3
78CLI Commands
Disk-name1 disk-name2 disk-name3
Show STRIPE1
Show Mirrorsets
ADD Mirrorset RUN Clone Show Mirrorset
80CLI Commands
SET mirrorset-name
Old-container-name
Rename
Rename old-container-name new-container-name
New-container-name
82CLI Commands
Rename DISK10000 Mydisk Show Disks
Noignoreerrors Default
Ignoreerrors
Restart controller
Restart Thiscontroller
84CLI Commands
Immediateshutdown
Restart Othercontroller
Retryerrors unit-number
Retryerrors D103 Unwriteabledata
RUN program-name
86CLI Commands
RUN
Program-name
Page
88CLI Commands
RUN Dilx
Selftest controller
Selftest controller
Selftest Thiscontroller
90CLI Commands
Selftest Othercontroller Ignoreerrors
Restart controller Shutdown controller
SET controller
SET controller Switches
Thiscontroller
92CLI Commands
Allocationclass
CACHEFLUSHTIMER=n CACHEFLUSHTIMER=10 Default
Nocacheups Default
Cacheups
Nocommandconsolelun Default
94CLI Commands
Commandconsolelun
HOSTFUNCTION=mode HOSTFUNCTION=ID,mode
NODEID=nnnn-nnnn-nnnn-nnnn checksum
NOPORT2ID
96CLI Commands
NOPORT1ID
Mirroredcache
Page
NOPORT1PREFERREDID
98CLI Commands
NOPORT2PREFERREDID
SCSIVERSION=SCSI-3
SCSIVERSION=SCSI-2 Default
TERMINALSPEED=baudrate TERMINALSPEED=9600 Default
TERMINALPARITY=ODD TERMINALPARITY=EVEN
100CLI Commands
Maximum SCSI-Bus Lengths for Given Data Transfer Rate
SET Thiscontroller PORT1ID=2,5
101
SET Othercontroller PROMPT=CONTROLLER B
Show Thiscontroller Show Othercontroller
102CLI Commands
SET device-name
103
SET DISK10300 Transportable
104CLI Commands
SET DISK20000 TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED=5MHZ
SET DISK10300 Remote
105
SET EMU
SET EMU
FANSPEED=AUTOMATIC Default
EMU Set Point Temperatures
106CLI Commands
FANSPEED=HIGH
SET EMU SENSOR2SETPOINT=34
107
SET EMU FANSPEED=HIGH
SET Failedset
108CLI Commands
SET Failedset
Autospare Noautospare
Init DISK10000
109
SET DISK10000 Transportable
SET Failedset Autospare
SET Failover
110CLI Commands
Thiscontroller Othercontroller
SET Failover COPY=THISCONTROLLER
111
SET Multibusfailover SET Nofailover SET Nomultibusfailover
112CLI Commands
SET mirrorset-name
113
MEMBERSHIP=number-of-members
REMOVE=disk-name
114CLI Commands
REPLACE=disk-name
115
116CLI Commands
SET MIRR1 POLICY=BESTFIT
SET MIRR1 REPLACE=DISK30200
117
SET MIRR1 REMOVE=DISK30000
ADD Mirrorset Reduce Show Mirrorset Unmirror
118CLI Commands
SET Multibusfailover
119
SET Failover SET Nofailover SET Nomultibusfailover
SET Nofailover
120CLI Commands
Nodestroyunflushabledata Default
Destroyunflushabledata
SET Nofailover
121
SET Failover SET Multibusfailover SET Nomultibusfailover
122CLI Commands
SET Nomultibusfailover
SET Nomultibusfailover Destroyunflushabledata
123
SET Failover SET Multibusfailover SET Nofailover
124CLI Commands
SET RAIDset-name
125
SET RAID9 POLICY=BESTFIT
126CLI Commands
SET RAID9 REMOVE=DISK10000
SET RAID9 REPLACE=DISK20100
127
ADD Raidset Show Raidsets
128CLI Commands
SET unit-number
129
130CLI Commands
MAXIMUMCACHEDTRANSFER=n MAXIMUMCACHEDTRANSFER=32 Default
131
132CLI Commands
ERRORMODE=NORMAL ERRORMODE=FAILSAFE
133
134CLI Commands
135
SET D102 Writeprotect Noreadcache
Show controller Show device-name Show device-type
136CLI Commands
Show
Show EMU
EMU
137
Device-type
Storageset-name
138CLI Commands
Full
139
Show MIRR1
140CLI Commands
Show Mirrorset Full
141
Show Thiscontroller Full
142CLI Commands
Show EMU
Shutdown controller
143
Shutdown Thiscontroller
144CLI Commands
Restart controller Selftest controller
145
Unmirror
Unmirror DISK10300
146CLI Commands
ADD Mirrorset Reduce RUN Clone
System Profiles
Device Profile
2System Profiles
Storageset Profile
Reduced Membership
Enclosure Template
4System Profiles
Controller Specifications
Physical and Electrical Specifications for Controller
2Controller Specifications
Environmental Specifications
Optimum Operating Environmental Specifications
Table B-4 Maximum Nonoperating Environmental Specifications
Table B-3 Maximum Operating Environmental Specifications
4Controller Specifications
Glossary
GL-2Glossary
Bit
CSR
GL-4Glossary
Data striping
Dual-simplex
See ECB
GL-6Glossary
FD Scsi
IBR
GL-8Glossary
Operation
Mist
GL-10Glossary
Normal member
PCM
GL-12Glossary
PTL
RAIDset
GL-14Glossary
RFI
SCSI-P cable
GL-16Glossary
Storage subsystem
GL-17
Synchronous
GL-18Glossary
Vhdci
GL-19
Page
ADD Stripeset stripeset-name container- nameN
ADD Passthrough passthrough-name scsi-port-target-lun,5-16
ADD Raidset RAIDset-name container- nameN
ADD Unit unit-number container-name,5-27Adding
2Index
Batteryoff Poweroff Batteryon Poweroff
AUTOSPARE, 4-15SET Failedset
Chunksize Initialize
Cacheups
Capacity CREATEPARTITION, 5-49INITIALIZE
Lostdata
4Index
SET MULTIBUSFAILOVER, 5-118SET Nofailover
Page
Copy
6Index
Cylinders CREATEPARTITION, 5-49INITIALIZE
Destroyunflushabledata SET Nofailover SET Nomultibusfailover
Dilx
Disableaccesspath ADD Unit
8Index
Disks
Errormode
Enableaccesspath ADD Unit
ECB
Index
Saveconfiguration
Nosaveconfiguration
ADD Disk
Membership
PTL SCSI-location,5-68unit-number,5-68UNITS
Maximumcachedtransfer ADD Unit
SET mirrorset-name,5-113Membership
INVALIDCACHE, 5-36NODTSUPPORT
Nooverridebadflush Poweroff Noautospare SET Failedset
Nodeid
Nopolicy ADD RAIDSET, 5-20NOPORT1ID
Nopreferredpath
Overridebadflush Poweroff
NOPORT2TRANSFERRATEREQUEST ED
Noreadcache
PORT1ID
Show device-type,5-137Path
PORT2ID
Prompt
Preferredpath
SET controller, 5-98Protocol
Rename old-container-name new-container
SET mirrorset-name,5-114
SET RAIDset-name,5-125
SET mirrorset-name,5-116
RUN program name
PORT2PREFERREDID PORT2TRANSFERRATEREQUESTE D
PORT1PREFERREDID PORT1TRANSFERRATEREQUESTE D
WRITEPROTECT, 5-133WRITEBACKCACHE
Passthrough
Show storageset-name,5-137SHOW storageset-type,5-137
Size Createpartition
TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED, 3-49TRANSPORTABLE
SET controller, 5-99Tip, defined, xix Tools, xx Topology
Time
TRANSFERRATEREQUESTED, 3-49ADD Disk
Vtdpy
Writeprotect