Termination Units
Copyright E 2000 Paradyne Corporation All rights reserved
Contents
Initial Startup and Configuration
Transferring Code and Configurations Using Tftp
Configuration Options
Glossary Index
Contents
Document Purpose and Intended Audience
About This Guide
Document Summary
Product-Related Documents
About the Hotwire 8747, 8777, Termination Units
Sdsl and HDSL2 Overview
Hotwire 87xx Termination Unit Features
Model Has eight Eight
Customer Premises CP
Network Configuration
CO Site
Management Information Base MIB Support
Snmp Management Capabilities
Snmp Trap Support
User Interface Access
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
Management Serial Port Settings
Login
Logging In to the Hotwire Dslam
Initiating an ATI Session
Select
Screen
Area
Main Menu
Main Status Test Configuration Control
Screen Work Areas
Input
Fields
Keys
Keyboard Keys
Navigating the Screens
Press
Screen Function Keys
For the screen function Select Press Enter to
Switching Between Screen Work Areas
Example
Ending an ATI Session
Exiting From the Dslam Session
Using the Asynchronous Terminal Interface
Initial Startup and Configuration
Overview
Main Menu → Control → Change
Entering Identity Information
Identity
Configuration Options
Configuring the Unit
Configuration Option Area Description
Accessing and Displaying Configuration Options
Main Menu → Configuration Load Configuration From
Load Configuration from
If you select Then
Select To Access To Configure
Configuration Edit/Display
Configuration EDIT/DISPLAY
Saving Configuration Options
Save Configuration
Resetting the Device
Restoring Access to the User Interface
Select Configuration → DSL Cards → Reset Slot
Resetting AutoRate
Main Menu → Configuration →
Main Menu → Control → Reset AutoRate
Disabling AutoRate
Cross-Connecting Ports
Determining the Configuration
CROSS-CONNECT Mode
Setting the Cross-Connect Modes
Mode
Assigning Time Slots
TS01
Following example shows the configuration for DSX-1 Port
Assign Time Slots
CROSS-CONNECT Mode
Configurations Not Running IP Conservative Software
All Configurations
IP Addressing
Selecting an IP Addressing Scheme
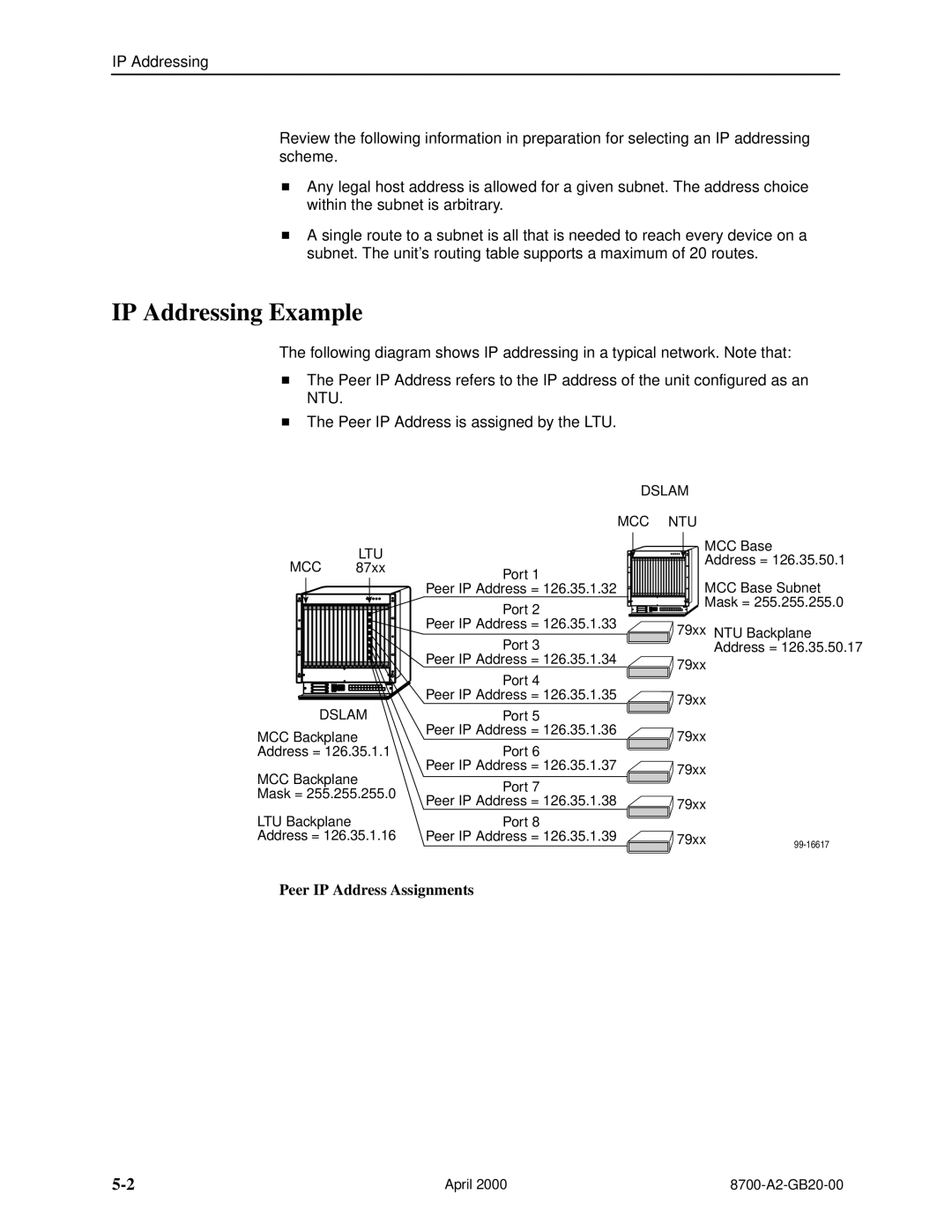
IP Addressing Example
Peer IP Address Assignments
Security
ATI Access Levels
Administer Logins
Creating a Login
Login Entry
Deleting a Login
On the Login Entry screen, for Enter
Assigning Snmp Community Names and Access Types
Controlling Snmp Access
Main Menu → Configuration → Management → Security Menu
Security
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
What to Monitor
Viewing System and Test Status
Health and Status SELF-TEST Results Test Status
Health and Status Messages
Yyyyyyyy
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
NTU/LTU
Call your service
Self-Test Results Messages
Test Status Messages Meaning
Test Status Messages
Re presentative for assistance
Device Messages
Device Messages 1 What Message Indicates What To Do
Device Messages 2 What Message Indicates What To Do
Main Menu → Status → Performance → Network Error Statistics
Viewing Network Error Statistics
Network Error Statistics
This Field Contains
Viewing Network Performance Statistics
Network Performance Statistics
This Field Contains
Viewing DSX-1 Performance Statistics
Performance Statistics
This Field Contains
Viewing G.703 Performance Statistics
Main Menu → Status → Performance → Statistics
This Field Contains
System
Viewing LED Status
DSL Loop
Display LEDs Screen Type Label Value is Indicating
System
Front Panel LEDs
LED is Indicating
Changing the Meaning of the Ports LEDs
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 1 Symptom Possible Cause Solutions
Troubleshooting 2 Symptom Possible Cause Solutions
Configuration Options , for
Testing
Accessing the Test Menu
Main Menu →
Test
Network & DSX-1 Tests
Running Network Tests
Network & G.703 Tests
8700-A2-GB20-00 April
Network Line Loopback
Repeater Loopback
DTE Loopback
Remote Send Line Loopback
Send and Monitor
Device Tests
Lamp Test
Main Menu → Test → Device Tests
Device Tests
Ending an Active Test
Telco-Initiated Tests
Telco-Initiated Line Loopback
Telco-Initiated Payload Loopback
Telco-Initiated Remote Line Loopback
Download Code
Transferring Code Configurations Using Tftp
Main Menu → Control → Download Code
Applying the Download
Configuration Loader
Main Menu → Configuration → Configuration Loader
Configuration Loader
DSL1
Completed successfully
Configuration Options
Configuration Options in , Initial Startup and Configuration
Main Menu → Configuration → Current Configuration → Network
Network Interface Options Menu
Table A-1. Network Interface Options 1
Port Status
Table A-1. Network Interface Options 2
Table A-1. Network Interface Options 3
Transmit Attenuation
DS0 Cross Connect Line Framing Model 8777, LTU only
Circuit Identifier
DSL
Maximum Line Payload Time Rate Kbps Slots
Main Menu → Configuration → Load Configuration From → DSX
DSX-1 Interface Options
Table A-4. DSX-1 Interface Options 1
Line Coding Format
Line Framing
Table A-4. DSX-1 Interface Options 2
Primary Clock Source
Main Menu → Configuration → Load Configuration From → G
Interface Options
Table A-5. G.703 Interface Options 1
Framing
Table A-5. G.703 Interface Options 2
Line Coding
Main Menu → Configuration → Load Configuration From → Copy
Copy Ports Options
Table A-6. Copy Ports Options
From Port n
System Options
Main Menu → Configuration → Load Configuration From →
Table A-7. System Options 1
Table A-7. System Options 2
Telco Initiated Loopback
Remote Telco Line Loopback
Line Termination
System Clock
System Clock
Figure A-1. System Timing
Figure A-2. System Clock Configuration Examples
Primary System Clock Reference
Table A-8. System Clock Options
Secondary System Clock Reference
CROSS-CONNECT Configuration
Main Menu → Configuration → Load Configuration From → Cross
Cross-Connect
Set Cross-Connect Mode
Table A-9. Cross-Connect Mode Options
Assign Time Slots
Following screen is displayed for a DSX-1 port
TS01 01 d
Assign Time Slots DSL
Table A-10. Assign Time Slots Options 1
8700-A2-GB20-00 April
Telnet Session Options
Management and Communication Options Menu
Telnet Session Options
Table A-11. Telnet Session Options
General Snmp Management Options
General Snmp Management Options
Name 1 Access
Name 2 Access
Table A-12. General Snmp Management Options
Snmp Management
Snmp NMS Security Options
Snmp NMS Security Options
NMS
Table A-13. Snmp NMS Security Options
Access Type
NMS IP Validation
Snmp Traps Options
Snmp Traps Options
Table A-14. Snmp Traps Options 1
Snmp Traps
Link Traps Possible Settings Disable, Up, Down, Both
Table A-14. Snmp Traps Options 2
Enterprise Specific Traps
Link Traps Interfaces
Standards Compliance for Snmp Traps
Snmp Traps
IfIndex
IfIndex
WarmStart
AuthenticationFailure
Snmp Trap Description Possible Cause
LinkUp and linkDown
LinkUp/Down variable bindings
LinkUp/Down variable bindings
Enterprise-Specific Traps
Snmp Trap Description Possible Cause
Page
Standards Compliance for Snmp Traps
Connector Pin Assignments
Connector Pin Assignments
Table C-2. Rear Connector Pinouts
Port Connector Pins Tip, Ring
Connector Pin Assignments
Technical Specifications
Specifications Criteria
Technical Specifications
Using the Worksheets
Cross-Connection Worksheets
Port Connection Diagram
DSX-1 Time Slot Assignments
Time Slot Assignments DSX-1 Port
Time Slot Assignments DSX-1 Port
Time Slot Assignments DSX-1 Port
Time Slot Assignments DSX-1 Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
TS01 TS02 TS03 TS04 TS05 TS06 TS07 TS08
TS24 TS25 TS26 TS27 TS28 TS29 TS30 TS31
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments G.703 Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Time Slot Assignments DSL Port
Glossary
511
Bridged tap
COM port
EIA-530-A
Ethernet
Factory defaults
Frame
Framer
Frame relay
Reset
Loopback
Receiver
Router
Yellow Alarm
Telnet
Transceiver
Transmitter
GL-6
Index
IN-1
IN-2
IN-3
IN-4
IN-5

![]() 79xx
79xx![]() 79xx
79xx![]() 79xx
79xx ![]() 79xx
79xx![]() 79xx
79xx