FCD-IPM
Page
International Headquarters RAD Data Communications Inc
FCD-IPM
Limited Warranty
Please observe the following precautions
General Safety Instructions
Connection of AC Mains
General Safety Practices
Connection of DC Mains
Connection of Data and Telecommunications Cables
Ports Safety Status
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Measures
Conventions
Page
To install FCD-IPM
Installing and Operating FCD-IPM
Quick Start Guide
Contents
Setup Menu
Configuration
View Menu
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Routing Tables Menu Bridge Table
FCD-IPM Main Menu
Firewall Rules Menu
View Menu Outline
Interface Routing Bridging Mode Menu
56. E1 Setup Menu
41. T1 Setup Menu
WAN Economy Menu Outline
Interval Parameters
Link Settings
Device Security Identity
Versions
Overview
E1/T1 over fiber optic links with interfaces
Applications
Backup
Features
Functional Description
Physical Description
FCD-IPM Functional Block Diagram
Main Link and Sublink Characteristics
AWG line
IO Data Channel Interfaces
System Timing Considerations
E1 over Shdsl
IP Router
Time Slot Handling
Integrated Router
Bridging
Management
Protocols
Management Using Dedicated Time Slot DTS
Framing Options
Compliance ITU G.703, G.704, G.706, G.732 Diagnostics
Zero Suppression
Unbalanced interface Two BNC coaxial
Range
Type Wire unconditioned dedicated line Line Coding
Impedance 135Ω Connector RJ-45 Protection ITU K.21, UL1950
For direct connection to a 2-wire telephone
Routing
WAN Protocols
Types
RED alarm red T1 only
Interface Options Nm LED Nm laser diode Connectors
Power indicator green
Link error red
Supply voltage
Power consumption 12W
General
RM-34 for 19-inch Rack
Introduction Technical Specifications
Site Requirements & Prerequisites
Enable free airflow
Installation and Setup
Package Contents
Equipment Needed
Location of Internal BAL/UNBAL Jumpers
Fuses
E1/T1 Link Connections
Interfaces and Connections
IO Data Channel Connections
Control Port Connection
Connecting the Power
AC Power Connection
DC Power Connection
Installation and Setup
Front Panel Indicators
Indicators
Introduction
Object Description Function
Front Panel Indicator Functions
Normal Indications
Rear Panel Indicators
Operating Instructions
Turning On
Operation
Turning Off
Connecting to the Ascii Terminal
Fault Indications
Connecting the Terminal Emulator
Press Enter several times
Password Protection
To setup the terminal
To initiate the login message
Main Menu has the following options
Chapter Configuration
To choose an option from the Main Menu
Quick Setup Menu
To access the Quick Setup Menu
Main Menu
To enter new information
Quick Setup Parameters
To configure the setup parameters
To view the options
Parameters Type Options
Quick Setup Parameters
Quick Setup for T1 PPP, IP
Quick Setup Menu Examples
Quick Setup
3shows the Quick Setup menu for E1
Quick Setup for E1 PPP, IP + Isdn Backup, 128K, PPP, IP
Set this parameter for the WAN configuration
WAN Settings
WAN Parameters
PPP
Default PPP
RFC-1490
Set the parameters in this section for each LAN connection
LAN Settings
LAN Parameters
Setting up the IP Mask
Dlci Number
Isdn Settings
Frame Relay Settings
Isdn Settings
V.24 Async Settings
Async Settings
Security Settings
Two settings that must be made
To access the Security Setup Menu
Security Setup Menu
Security Setup options are described below
Changing Login Password
Device Access Restriction
Enabling Telnet Access
Enabling Snmp Access
Firewall Option
Supervisor Access
To set a Monitor Supervisor Password
From the Main menu, select option 2, Security Setup
Firewall
To define the Solid Firewall rules
Select interface LAN Select direction outbound
Configuring Firewalls
Firewall Rules
IP Address Translation NAT
Transparent PAT Port Address Translation
IP Address Translation NAT Settings
Main Menu, press Advanced Menu appears refer to Figure
Advanced Setup Menu
Setup Menu
To access the Advanced Menu
Device Control Menu
To access the Device Control menu
Options in the Device Control menu are described below
Select this option to download a new software version
Software Download
To download a new software version via Tftp server
Download from Tftp Server
Select option 1 from the Software Download menu
Upload Device Parameters to Tftp Server
Xmodem via Control Port Boot Manager
To upload device parameters
To download device parameters
Reset Options
Download Device Parameters from Tftp Server
Terminal Type
View Menu
To access the View Menu
24. View Menu
Configuration
O1 FXS O2 FXS
SHDSL+SUB
Options in the Routing Tables menu are described below
Interface Connections
Routing Tables
Select this option to display different routing tables
Details the routing interfaces information
Bridge
IP Interfaces
IP Routing
NET RIP
IPX Routing
Select this option to display information on IPX routing
IPX NET IPX Node Type Hops Ticks Ageing Interface
IPX Services
Ospf Related Information
IP Address Pool Dhcp
Area ID Type LS-ID Orig RTR SEQ NUM AGE Cksum
IP Address Prio State
F7FD
Displaying the Shdsl Status
To access the Shdsl Status screen
Statistics
Shdsl Status and Statistics
Shdsl Status Screen Parameters
Data mode
Display Description
Displaying the Shdsl Statistics
Shdsl Statistics Parameters
To display statistics for specific intervals
T1 Diagnostics
E1/T1 Diagnostics
To refresh or clear statistics
10. Interval Parameters
Interval Parameters
Interface Type Status Days Hours MIN SEC
E1/T1 Alarms Log File
Select this option to display the E1/T1 Alarms Log file
E1/T1 Alarms
To access the Diagnostic Tools menu
Diagnostic Tools Menu
49. Ping Terminal Screen
To ping another host
Advanced Menu, press Setup menu appears refer to Figure
To access the Setup menu
Options in the Setup menu are described below
Host Parameters Menu
To access the Host Parameters menu
Host Parameters
Device ID
Device ID
Options in the Host Parameters menu are described below
Tftp Radius
Device ID Parameters
IP Host
Current NEW
IP Host Parameters
Snmp Manager Table
Default Gateway
Tftp Parameters
Tftp Trivial File Transfer Protocol
11. Radius Menu
Radius Authentication and Billing
Radius Menu Parameters
Select this option to enter FCD-IPM routing information
To access the Routing/Bridging menu
Setup menu, press Routing/Bridging menu appears
Routing/Bridging Menu
Options in the Routing/Bridging menu are described below
Interface Routing/Bridging Mode
PPP
Slip Cslip
Interface Routing/Bridging Mode Menu Parameters
BOD
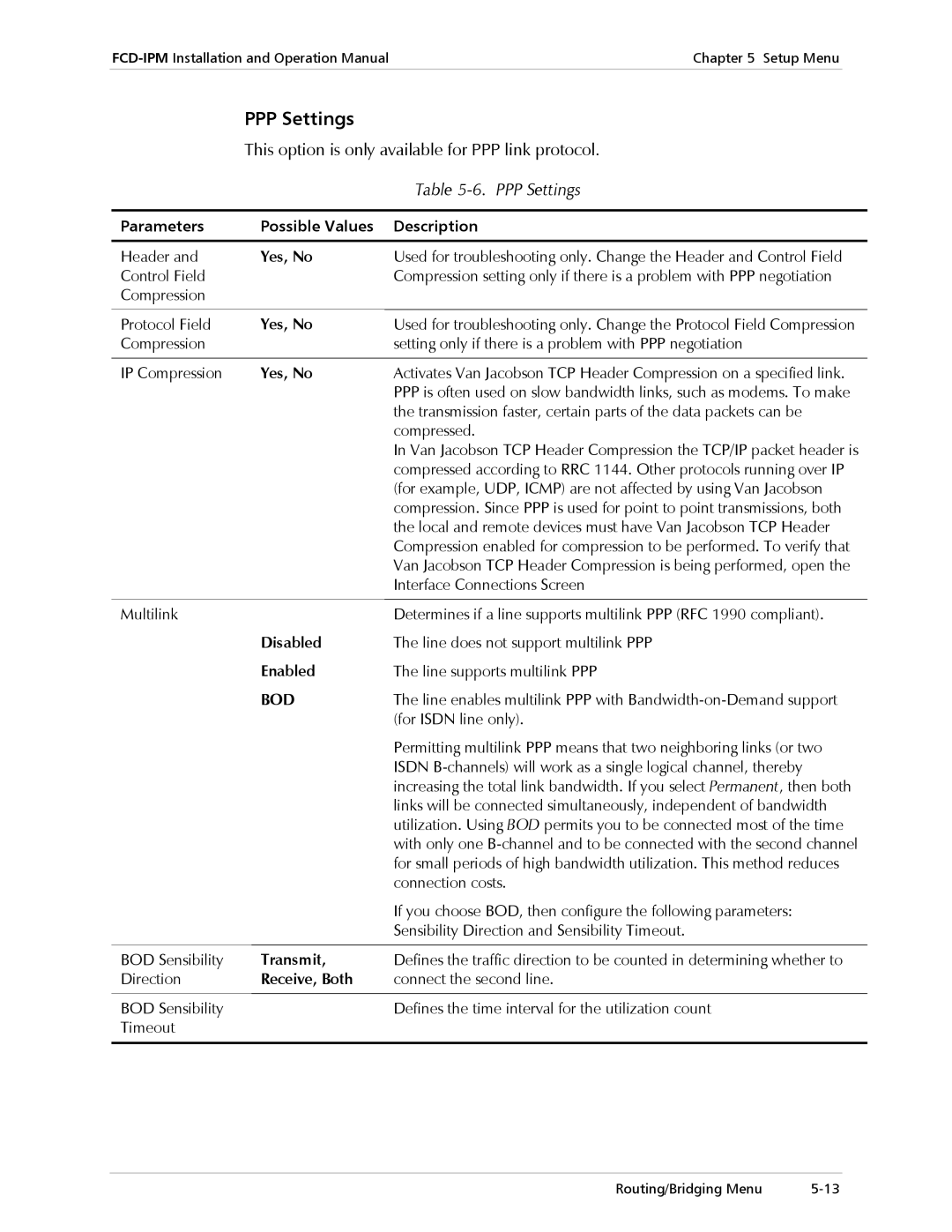
PPP Settings
PPP Settings
This option is only available for PPP link protocol
Static Stations and Nets
Static Stations and Nets
Does not remove static entries from the routing tables
Can be defined in 4 ways see Table
16. Router 2 set to Next Hop in FCD-IPM
Interface Address
IP Routings Settings
Dhcp Relay
IP Address Pool Setting Dhcp
Routing Protocol
Maximum Transmit Unit
Dhcp
FCD-IPM supports all these mechanisms simultaneously
IP Address Pool
Select this option to define IP address information
10. IP Address Pool Settings
PC Remote Access
Static Only RIP Only Static & RIP
Ospf Settings
FCD-IPM
Nothing
Link 1/CH1
Interfaces Area ID
Link 1/CH2
Stub
12. Ospf Areas Setup
Ospf Summaries Setup
Normal
13. IPX Routing Settings
IPX Routing Settings
IPX router
LAN RIP/SAP
RIP/SAP Mode
29. Station Aging Menu
Station Ageing
Setup menu, press Interface Parameters menu appears
To access the Interface Parameters menu
Interface Parameters Menu
31. Interface Parameters
Link Settings Menu
Answer & Originate
14. Link Settings
ON, Ignore
Odd
Shdsl Settings
Even
STU-C
To configure the Shdsl parameters
Shdsl Parameters
15. Shdsl Parameters
Shdsl Loops
To access the Shdsl Loops menu
16. Shdsl Loops
Loopback
E1/T1 Settings
38. FCD-IPM with an E1/T1 Interface
E1 Features
T1 Features
O2 SUB T1 FIX SUB T1
T1 Setup Menu
17. T1 Setup Parameters
O1 SUB T1
Time Slots Mapping
TS3
T1 Time Slots Mapping Link
TS1 Data LINK1
TS2 Data LINK1
Loopback options are
Disabled
Loopback
45. Remote Analog Loopback for T1 and Sub T1 Links
49. Local Analog Loopback for T1 and Sub T1 Links
48. Local Analog Loopback
B8ZS
T1 Link Parameters
ESF
B7ZS
Additional Cards Parameters
T1 Parameters Link1 Parameters
Voice Parameters
Voice
Fix Voice O1Voice O2 Voice
FCD-IPM has optional voice capabilities
Bit
FXO Voice Interface
52. FXO Voice Interface
Ring Detection to T1 On
This parameter specifies the interface type
This parameter is set to
Voice Interface
Type
Time Slots for Voice Ports
Typical screen is shown in Figure
AIS
Management Time Slot Number
Management Host IP Address
Select this parameter to set a unique IP address
O1 SUB E1
E1 Setup Menu
This section describes the parameters in the E1 Setup menu
19. E1 Setup Parameters
Time Slots Mapping
TS5 O1 Voice
TS2 FIX SUB-VOICE
TS3 FIX SUB-DATA
TS4 O1 Voice
59. Remote Analog Loopback
60. Remote Analog Loopback for E1 and Sub E1 Links
E1 Link Parameters
Select this option to configure the parameters that follow
Ccitt
20. E1 Link1 Parameters
Coding Law
TX/RX Gains
Law coding for E1 links
On/off hook from the E1 on
Default Abcd to the E1
On/off hook to the E1 on
Law coding for E1 links On/off hook from the E1 on
65. FXO Voice Interface
Out of Service Method
Signaling Feedback
Ring Detection to E1 on
Interface Type
RX/TX Gains
Refer to Table Typical screen is shown in Figure
Law Coding for E1 links Signal from the E1 on
67. E1 Time Slots Mapping Link1 Screen Alarms Filter
Management Time Slot Number
Isdn Settings Menu
Management Host IP Address
To activate the Isdn line Choose the Isdn protocol
Isdn has the following features
21. Dialing Mode Parameters
22. Answering Mode Parameters
70. Dialback Phone Number
23. Local Number for Dialback
Link Dlci State CIR Excess Throughput
Frame Relay Dlci Settings
73. Frame Relay Options in the Advanced Menu
Implementing Frame Relay
Enquiry frames in a sliding monitored events window
24. Frame Relay Link Parameters
74. Polling Intervals
25. Frame Relay Dlci Parameters
Frame Relay Dlci Parameters
Dlci
To access the Access Control menu
Access Control Security Menu
Select this option to perform security operations
79. External Access Security Menu
78. Access Control Menu
Radius
26. External Access Security Parameters
FCD IPM
Device Security Identity PPP only
Current Script for Link
Login Script Setup
Security Host/Guest PPP only
Link Host
Command codes are described in Table
Command Code
28. Command Codes
29. Example of Argument
Argument
Code to wait/send Control Sequence
WAN Economy Menu
To access the WAN Economy menu
Options in the WAN Economy menu are described below
Filters
86. Action of a Quick Filter
Forwarding
Blocking
Multiple Filters
Quick Filters
No Filters
To configure the broadcast control
Factory default Block Propagation
Toggle between Block and Forward
Add Filters Menu
Advanced Filters
Choose Advanced Filter
True-False Menus
30. Add Filters Menu Terms
Advanced Filter Parameters 31. Advanced Filter Parameters
WWW
MAC
NET
FTP
Icmp
Saving Filter Parameters
UTP
TCP
91. Connection On Demand Menu
Connection on Demand
32. Connection On Demand Parameters
You need to configure Start Connection Terminate Connection
Example
Following examples demonstrate how COD can be used
93. Any Frame Starts a Connection
94. Limiting Access to a Specific PC
95. Manual Connection
Spoofing
33. IP/IPX Spoofing Parameters
Enabled Enabled COD
To access the Factory Default menu
Factory Default Options
Factory Default Options
Setup Menu Factory Default Options
E1, T1 and Voice Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting
E1/T1 and Voice Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting
IP connection to LAN is Down
Router Connections Troubleshooting
Router Connections Troubleshooting
IP Connection to WAN Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Table A-1. Interface Signal List Female Connectors
Interface Signal List Female Connectors
DTE DTR
RS-530 21 / 15-pin
RS-530 RS-449/V.36 37-pin
E1 over Shdsl Line Connector
E1/T1 Connectors
Pin Designation Direction Function
RJ-45 DB-9
Control Cable Connector
Control cable connection pinout is provided in Table A-3
Table A-3. Control Cable RJ-45 to DB-9 Connection DCE
Fiber Optic Interface
Isdn Connector
Isdn connector pinout is provided in Table A-4
Table A-5. Fiber Optic Interface Specifications
Table A-7
E&M Connector
FXO/FXS Connector
Table A-6 RJ-45 E&M Connector Wiring
Preface
Accessing Boot Manager
Access via Software Download Menu
To access Boot manager via Software Download menu
Rescue
Boot Manager Menu
Immediately after the change
Load New Software
Partitions Status
Step
Duplicate Active Partition
Run Backup Partition
Reactivate Backup Partition
Erase Configuration
Immediately after performing the change
Set Baud Rate
Appendix B Boot Manager Boot Manager Menu
This section describes the Snmp environment
Snmp Environment
Snmp Principles
Snmp Operations
MIB Structure
Management Information Base
MIBs Supported by the FCD-IPM Snmp Agent
Management Domains Under Snmp
Snmp Communities
Authentication
Indexing Convention
Snmp Configuration
Community Configuration
Trap Configuration
Supported Traps
Snmp Traps
Appendix D Glossary
Appendix D Glossary
Appendix D Glossary
Appendix D Glossary
DC Power Supply Connection Terminal Block Connector
TB Plug with Captive Screws optional
DC Power Supply Wire Voltage Polarity
Excellent Good Fair Poor Very Poor
Manual Name FCD-IPM Publication Number 702-200-08/03
Manual as a whole What did you like about the manual?
Page
Style spelling, grammar, references, etc
Difficulty in finding needed information
Missing information
Illogical flow of information
Page
Page
Headquarters
International Headquarters