FY8-13EX-000
Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Introduction
Copyright 1997 Canon INC
System Configuration
Iii
General Description Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Contents
Exposure System
Image Formation System
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
Vii
Fixing System
Viii
Installation
Maintenance and Servicing
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms
Troubleshooting
II. Standards and ADJUSTMENTS..10-5
Arrangement and Functions
Appendix
Xii
Chapter General Description
Multiple front loading and multifeeder for space saving
Features
Practical basic features
Office amenities and ecology
Type
II. Specifications
Copier
System
Features
Others
201 Standard Reproduction Ratios
Cassette Feeding Module-B2/Cassette Feeding Module-A2
202 Copying Speed
III. Names of Parts
Exterior View
Cross Section
Body
Cassette Feeding Module-A2
IV. Operation
Control Panel
Operation Mode
Making Two-Sided/Overlay Copies manual
User Mode
Outline
Operation
Common Operations Keys to Use in User Mode
Changing the Auto Power-Off Time
Changing the Auto Clear Time
Zoom Fine-Adjustment
Reference
Turning On and Off the Auto Cassette Change Mechanism
Cleaning the Feeder with ADF installed-option
Selecting the Density Adjustment Method for Standard Mode
Initializing User Mode
Quick Guide to User Mode
VI. Routine Maintenance by the User
Handling the Toner Bottle
VII. Image Formation
Outline
General Description
General Description Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Chapter Basic Operation
Basic Construction
Functional Construction
Outline of the Electrical Circuitry
CPU
Basic Sequence of Operations 2 copies continuous, AE
Stby Intr Scfw Scrv Lstr AER
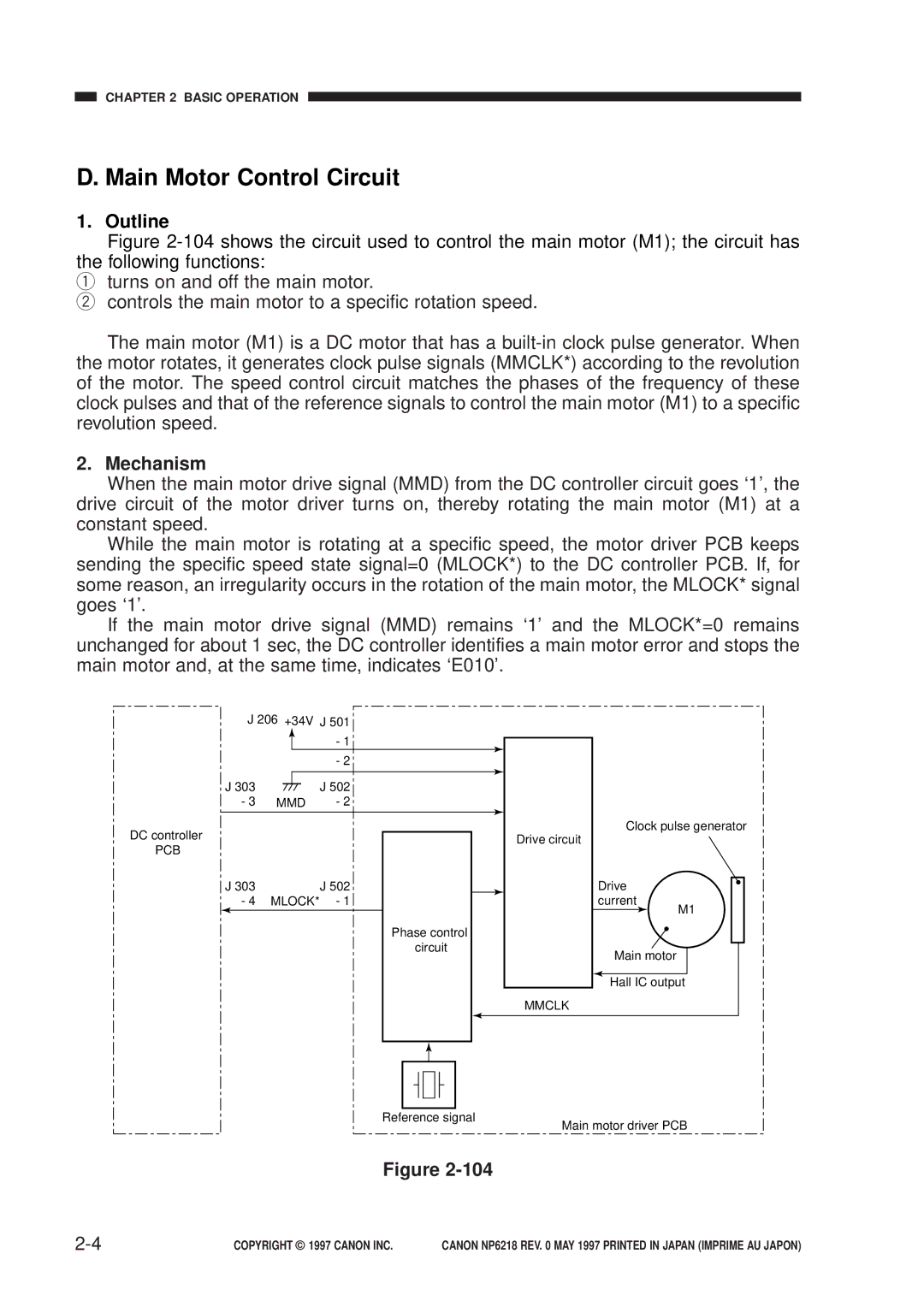
Main Motor Control Circuit
Mechanism
Inputs to the DC Controller PCB
Inputs to the DC Controller PCB 1/3
Inputs to the DC Controller PCB 2/3
CSZ3 CSZ4
Inputs to the DC Controller PCB 3/3
Outputs from the DC Controller PCB
Outputs from the DC Controller PCB 1/3
Outputs from the DC Controller PCB 2/3
Mfpucld
Outputs from the DC Controller PCB 3/3
Hefd
Inputs to and Outputs from the 1-Cassette Unit Driver PCB
CS2
Inputs to and Outputs from the 2-Cassette Unit Driver PCB
C3VPD
C2PUCLD
Basic Operation Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Chapter Exposure System
II. Lens Drive System
Varying the Reproduction Ratio
Chsld
Lens Motor Drive Circuit
Keeping the Lens Motor Stationary
Driving the Lens Motor
Basic Sequence of Operations lens drive system non-Direct
Stby Intr Scfw Scrv Lstr AER
III. Scanning Drive System
Driving the Scanner
Relationship between the Scanner Sensor and Signals
Basic Sequence of Operations scanner
Driving the Scanner Motor Outline
Exposure System
IV. Disassembly and Assembly
Scanner Drive Assembly
Detaching the Scanner Drive Motor
Detaching the Scanner Cable
Exposure System
Assembling the Mirror Position Tool
Routing the Scanner Cable
Set screws Loosen the set Screw to free Totation Pulley
Hook Wirespring Cable
Frontrear
Cleaning the Scanner No Mirror
Lens Drive Assembly
Detaching the Lens Drive Motor
Exposure System
421 Lens Drive Assembly
Routing the Lens Cable
Adjusting the Position of the Change Solenoid
Exposure System Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Chapter Image Formation System
Composite Power Supply PCB DC controller PCB
Processes
T101
Basic Sequence of Operations image formation system
On on
Controlling the Scanning Lamp
Flprht
Turning On and Off the Scanning Lamp
Pre-Heating Control scanning lamp
OFF
Controlling the Intensity of the Scanning Lamp FL1
Controlling the Fluorescent Lamp Heater
Fluorescent Lamp Automatic
Fluorescent Lamp Protection Mechanism
Controlling the Primary Charging Roller Bias
Mpwm
Turning On and Off the Primary Charging Roller Bias
Image Formation System
Transfer Bias
Cleaning Bias
Controlling the Transfer Roller Bias
Reference Bias Atvc
Tfwon Tfwpwm Tfws Trevon
Controlling the Transfer Bias to a Constant Voltage
Current Limiter Circuit cleaning bias
Turning On and Off the Transfer Roller Bias
Current Limiter Circuit transfer bias
Controlling the Static Eliminator Bias
Switching the Static Eliminator Bias Voltage Level
Ensuring Proper Separation of Thin Paper
Controlling Blank Exposure
Bssld
Blanking Whiting of Non-Image Areas for Reduction
Controlling the Primary Corona Roller Cleaning Mechanism
Primary Charging Roller Cleaning Operation
Releasing the Transfer Roller
II. Developing Assembly and Cleaning Assembly
Controlling the Toner Level Detection
Stby
Controlling the Development Bias
Mpwm
Turning On and Off the AC Component of the Development Bias
Automatic Control of Copy Density
Control Method
207 Area Read by the AE Sensor Reference
AE Adjustment
III. Disassembly and Assembly
Illumination Assembly
Detaching the Scanning Lamp/Fluorescent Lamp Heater
Image Formation System
~5mm 60mm
306 front view
Detaching the Blank Exposure Assembly
Detaching the Blank Exposure Lamp
Detaching the Blank Shutter Solenoid
Positioning the Blank Shutter Solenoid
314a
Routing the Blanking Cable
Positioning the Left/Right Margin
Drum Unit
Detaching the Drum Unit
Cleaning
Primary Corona Assembly
Detaching the Primary Corona Assembly
Cleaning the Cleaning Pad and the Primary Corona Roller
Positioning the Solenoid for the Primary Charging Roller
Transfer Charging Assembly
Detaching the Transfer Roller
Attaching the Drum Heater
Image Formation System
Image Formation System
Removing the Developing Assembly
Removing the Blade Assembly
Developing System
Removing the Developing Cylinder Side Seal
Image Formation System
Image Formation System
Installing the Side Seal and the Blade Assembly
Image Formation System
Chapter PICK-UP/FEEDING System
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
PS4
II. PICK-UP Operation Copier
Sequence of Operations pick-up/feeding assembly A4, 2 copies
III. PICK-UP from the Cassette Feeding MODULE-A2
Pick-Up Operation
Sequence of Operations cassette 2 A4, 2 copies
Intr Scfw Scrv Scfw Scrv Lstr
IV. Multifeeder
PS5
Identifying the Size of Paper on the Multifeeder
Sequence of Operations multifeeder A4, 2 copies
Intr Scfw Scrv Scfw Lstr
Identifying the Cassette Size
Guide plate horizontal Paper size lever Guide plate vertical
Pre-Registration Delay Jam
VI. Identifying Jams
Pre-Registration Timing Jam
Pre-Registration Stationary Jam
Separation Delay Jam
Separation Stationary Jam
Delivery Delay Jam
Delivery Stationary Jam
VII. Disassembly and Assembly
Pick-Up Assembly
Detaching the Pick-Up Roller Unit
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
Detaching the Pick-Up Roller
Points to Note When Attaching the Pick-Up Roller
Detaching the Pick-Up Clutch
Detaching the Separation Pad
Adjusting the Left/Right Registration
Pick-Up from the Cassette
Multifeeder Assembly
Detaching the Multifeeder Assembly
Detaching the Multifeeder Pick-Up Roller Unit
Detaching the Multifeeder Pick-Up Roller
Front of copier
Detaching the Multifeeder Drive Unit
Detaching the Multifeeder Clutch
Positioning the Multifeeder Assembly paper guide plate cam
Adjusting the Left/Right Registration
Registration Roller Assembly
Detaching the Registration Clutch
Detaching the Upper Registration Roller
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
Detaching the Lower Registration Roller
Feeding Assembly
Detaching the Feeding Belt
PICK-UP/FEEDING System
Cassette Feeding Module
Detaching the Copier from the Cassette Feeding Module
Detaching/Attaching the Pick-Up Roller
Chapter Fixing System
Basic Operations
Pwsw
Controlling the Fixing Heater Temperature
Reference
Controlling the Supply Power for the Fixing Heater
Thermistor TH1, TH2
Detecting Overheating at the End of the Fixing Heater
Protection Mechanism
Thermal Fuse FU1
Correcting Displacement of the Fixing Film
OFF
Fixing System
Controlling the Fixing Film Motor
II. Disassembly and Assembly
Fixing Assembly
Construction1
Detaching the Upper Fixing Unit
Fixing System
Fixing System
Fixing System
Fixing System
Fixing System
Fixing System
Fixing System
Points to Note When Attaching the Fixing Film
Points to Note When Attaching the Heater Connector
Points to Note When Replacing the Fixing Upper Unit
Adjusting the Fixing Film Drive Roller Pressure
Fixing System
Detaching the Lower Fixing Unit
Fixing System
Adjusting the Lower Fixing Roller Nip
Measuring the Nip
Delivery Assembly
Fixing System Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Chapter
Power Supply
Power Supply Circuit Assembly
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Low-Voltage Output Data Error
Detecting Errors in the Power Supply PCB
Error in the High-Voltage Output Data
Overcurrent in the Low-voltage Power Supply
Protection Mechanisms for the Power Supply Circuit
External Covers
Cover
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms
Detaching the Control Panel
Fans
Detaching the Exhaust Fan
Main Motor/Main Drive Assembly
Detaching the Main Drive Assembly
Detaching the Main Motor Unit
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms
Routing the Drive Belt
Cassette unit
Detaching the Pick-Up Drive Unit
Detaching the Cassette Motor
Detaching the Cassette Driver PCB
Points to Note When Replacing the DC Controller PCB
DC Controller PCB
Detaching the DC Controller PCB
Composite Power Supply PCB
Detaching the Composite Power Supply PCB
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms
Points to Note When Handling the Composite Power Supply PCB
AE Sensor PCB
Points to Note When Replacing the AE Sensor
Points to Note When Replacing the Intensity Sensor
Intensity Sensor PCB
EXTERNALS/AUXILIARY Mechanisms Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Chapter Installation
Selecting the Site
II. Unpacking and Installing the Copier
Unpacking and Removing Fixings
Installation
Installation
Turning On the Copier
Installation
Installation
Checking the Images and Operations
Attaching the Drum Unit
Changing the Cassette Size
A5 R A4
Set the paper size plates selected in step
III. Relocating the Copier
Direct position refers to
Go through the following when replacing the drum unit
IV. Replacing the Drum Unit
Installation
Installation
Installing the Control Card IV N
Installation
VI. Cassette Heater KIT 5 Installation PROCE- Dure
Unpacking
Installation to a Cassette Feeding Module-A2/B2
Screws
Tie-wrap Connector Cord clamp
Copiers connector Molded member Copiers base plate
Relay harness
Installation
VII. Installing the Remote Diagnostic Device
Installation to the Copier
Installation
Installation
SW2 SW3
LED1 LED2 LED3 BAT1
AII
Bits on SW2 Setting
SW2-3
Shift bit 6 of the DIP switch 2 !9on the RDD’s PCB to OFF
Installation
Installation
Installation
Chapter Maintenance and Servicing
Periodically Replaced Parts
Periodically Replaced Parts
II. Durables
Pick-up roller FB2-2251-000 100,000
III. Periodical Servicing
IV. Servicing Chart
Maintenance and Servicing
Chapter Troubleshooting
Guide to Troubleshooting Tables
10-1
10-2
Maintenance and Inspection
Image Adjustment Basic Procedure
10-3
Periodical Servicing
10-4
II. Standards and Adjustments
Image Adjustment
10-5
10-6
10-7
10-8
Adjusting the Left/Right Margin No left/right margin
10-9
Adjusting the Scanning Lamp Intensity
10-10
10-11
210 DC Controller PCB
10-12
10-13
10-14
Exposure System
Routing the Scanner Drive Cable
10-15
10-16
Adjusting the Scanner Cable Tension
Assembling the Mirror Positioning Tool
10-17
10-18
220 front view
10-19
Positioning the Change Solenoid
10-20
Image Formation System
10-21
Routing the Blank Shutter Cable
10-22
After Replacing the Drum Unit
10-23
10-24
Orientation of the Multifeeder Pick-Up Roller
Pick-Up/Feeding System
Orientation of the Pick-Up Roller
10-25
Positioning the Paper Guide Plate Cam multifeeder
10-26
Fixing System
10-27
236 rear view
10-28
Points to Note after Replacing the Fixing Upper Unit
10-29
Adjusting the Nip
10-30
Storing the Fixing Heater Resistance
10-31
Setting the Fixing Heater Temperature Control Value
240 Heater Stay Side Plate rear 10-32
Example
10-33
10-34
Clearing the Back-Up RAM
Electrical
After Replacing the PCB
10-35
Checking the Photointerrupters
10-36
Copier
10-37
10-38
PS9
Cassette Feeding Unit
10-39
10-40
10-41
10-42
Adjusting the Multifeeder Paper Width Sensor
10-43
Setting the Paper Size for the Universal Cassette
10-44
III. Troubleshooting Image Faults
Initial Checks
10-46
10-47
Samples of Image Faults
10-48
Troubleshooting Faulty Images
Copy is too light half-tone only
10-49
10-50
10-51
10-52
Copy is foggy overall
10-53
Copy has black lines vertical, fine
10-54
Copy has white spot vertical Copy has white lines vertical
10-55
Copy has white spots horizontal
10-56
Back of the copy is soiled
10-57
Copy has a fixing fault
15, 16, 17 The leading edge of the copy is displaced
10-58
Copy has a blurred image
10-59
Copy is foggy horizontal
10-60
Copy has poor sharpness
10-61
Copy is blank
Copy is solid black
10-62
E000
IV. Troubleshooting Malfunctions
Troubleshooting Malfunctions
10-63
E001
E002, E003
10-64
E004
E007
10-65
E010
E030
10-66
E064
E202 keys on control panel invalidated
10-67
12. E240
10. E210
11. E220
10-68
15. E803
13. E261
14. E710, E711, E712, E717
10-69
AC power supply is absent
10-70
DC power supply is absent
10-71
Blank shutter fails to move
Photosensitive drum fails to rotate
10-72
Pick-up operation fails from cassette
Pick-up operation from the multifeeder fails
10-73
Scanner fails to move forward/in reverse
Registration roller fails to rotate
10-74
Scanning lamp fails to turn on
Lens fails to move
10-75
Pre-exposure lamp fails to turn on
Add paper indicator fails to turn off
Fixing heater fails to operate
10-76
Jam message fails to turn off
10-77
Troubleshooting Feeding Problems
Jams copy paper
10-78
Pick-Up Assembly
10-79
Separation/Feeding Assembly
Fixing/Delivery Assembly
Wrinkling
Feeding Faults
Double feeding
10-81
VI ARRANGEMENT/FUNCTIONS of the Electrical Parts
Sensors
10-82
10-83
Clutches, Solenoids, and Switches
10-84
10-85
Motors, Heaters, and Lamps
10-86
10-87
PCBs
10-88
10-89
Cassette Feeding Module A2
10-90
Photointerrupter
10-91
Variable Resistors VR and Check Pins by PCB
DC controller PCB
10-92
Composite power supply PCB
10-93
Activating Service Mode
VII. Service Mode
Using Service Mode
10-94
Using Operation/Inspection Mode
Selecting a Service Mode
Using Adjustment Mode 3 and Specification Mode
Clearing Stored Error Code
Recording on the Service Mode Label
10-96
Control Display Mode
10-97
10-98
O Mode
10-99
No /202/203/204 Port C Digital Display
10-100
Port H Display
10-101
Adjustment Mode
10-102
10-103
10-104
Operation/Inspection Mode
10-105
10-106
Specification Settings Mode
10-107
Counter Mode
10-108
VIII. Self Diagnosis
10-109
E003
10-110
E210
10-111
10-112
E400
10-113
E500
10-114
10-115
10-116
Appendix
General Timing Chart
A4, 2 copies, Direct, from copier cassette
Signals and Abbreviations
Signals and Abbreviations
General Circuit Diagram
Copyright 1997 Canon INC
Special Tools
SOLVENTS/OILS
MEK
Canon INC
This publication is printed on 70% reprocessed paper