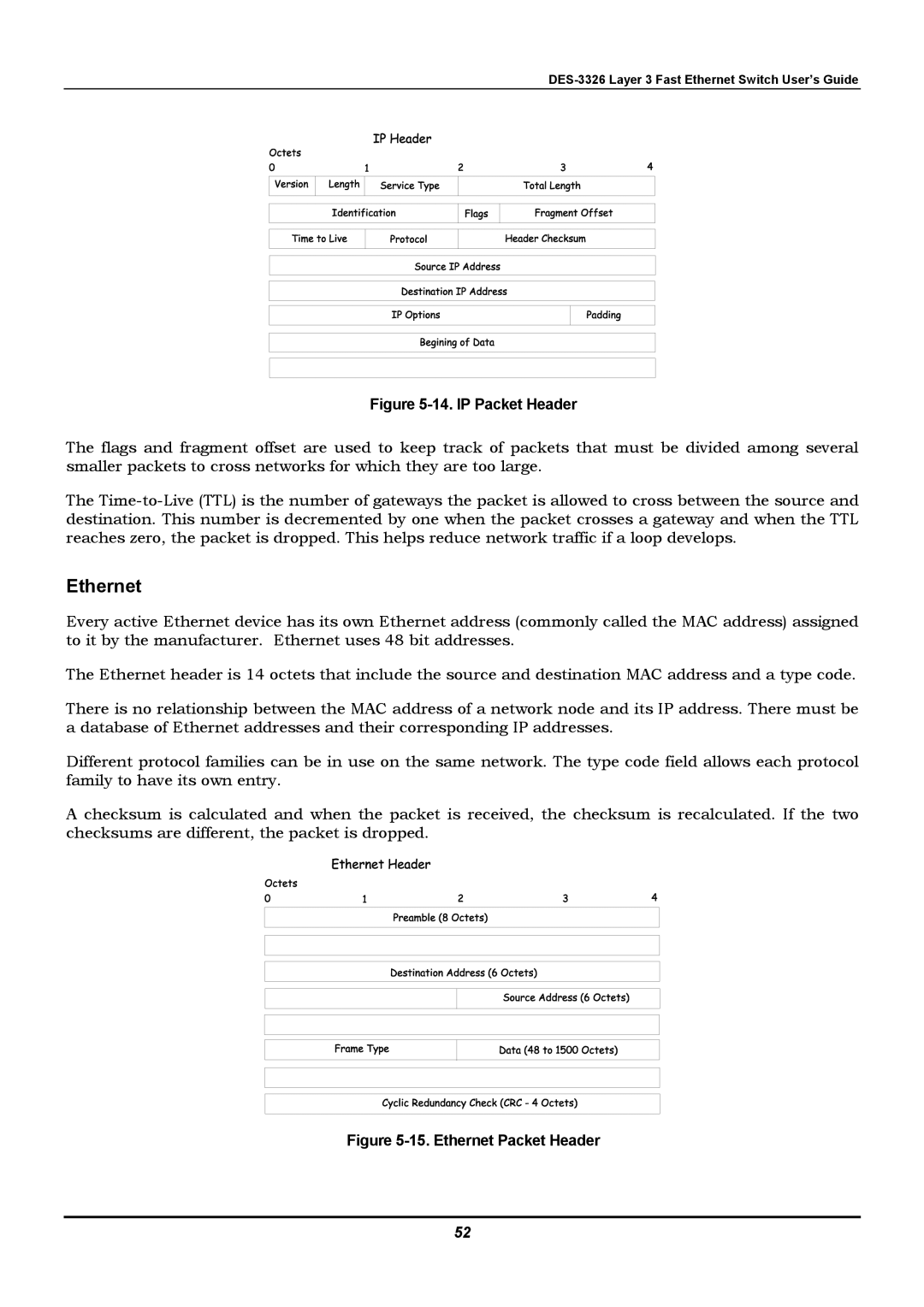
Figure 5-14. IP Packet Header
The flags and fragment offset are used to keep track of packets that must be divided among several smaller packets to cross networks for which they are too large.
The
Ethernet
Every active Ethernet device has its own Ethernet address (commonly called the MAC address) assigned to it by the manufacturer. Ethernet uses 48 bit addresses.
The Ethernet header is 14 octets that include the source and destination MAC address and a type code.
There is no relationship between the MAC address of a network node and its IP address. There must be a database of Ethernet addresses and their corresponding IP addresses.
Different protocol families can be in use on the same network. The type code field allows each protocol family to have its own entry.
A checksum is calculated and when the packet is received, the checksum is recalculated. If the two checksums are different, the packet is dropped.
Figure 5-15. Ethernet Packet Header
52