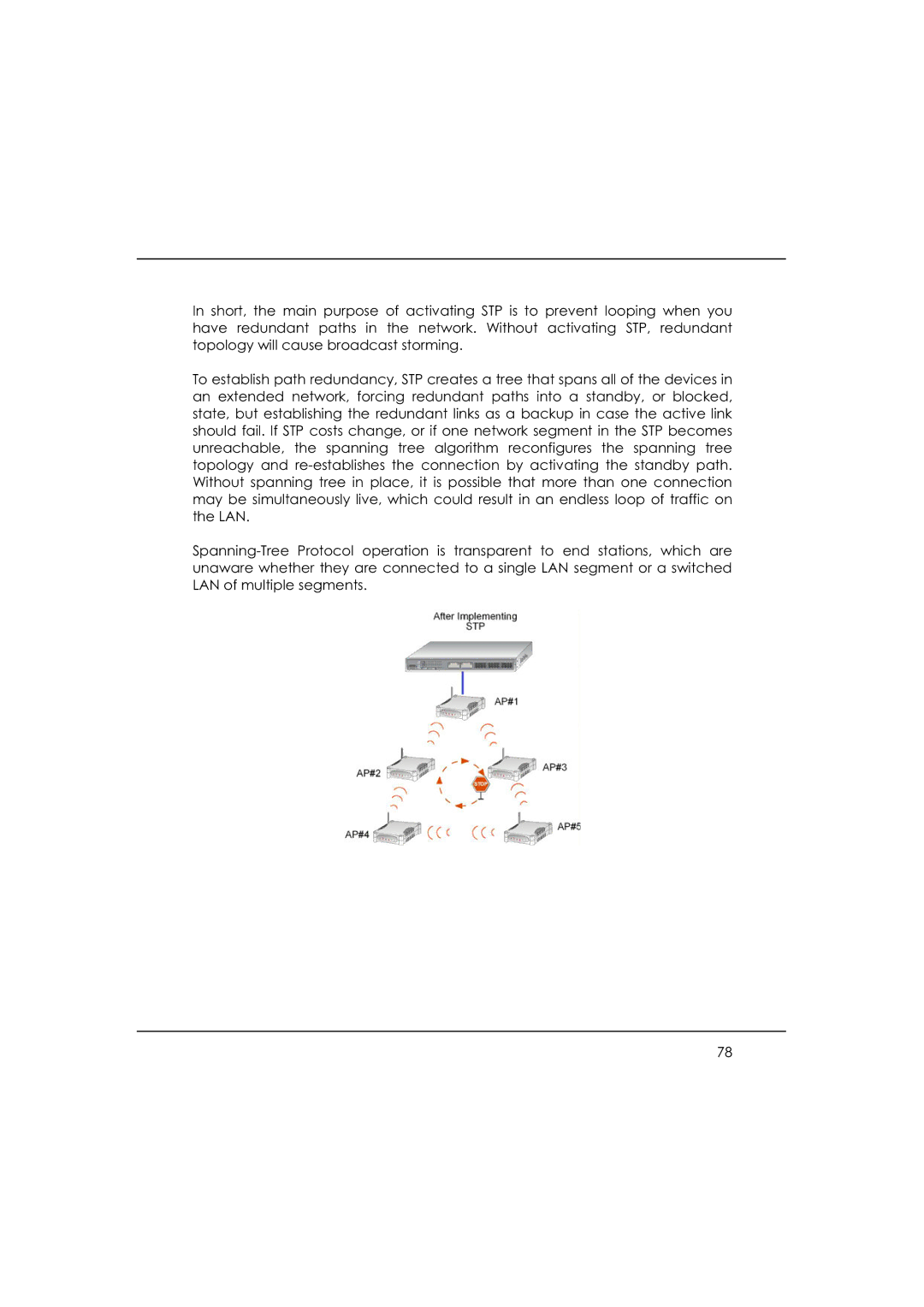
In short, the main purpose of activating STP is to prevent looping when you have redundant paths in the network. Without activating STP, redundant topology will cause broadcast storming.
To establish path redundancy, STP creates a tree that spans all of the devices in an extended network, forcing redundant paths into a standby, or blocked, state, but establishing the redundant links as a backup in case the active link should fail. If STP costs change, or if one network segment in the STP becomes unreachable, the spanning tree algorithm reconfigures the spanning tree topology and
78