GS716Tv2 and GS724Tv3 Software Administration Manual
The following table describes the information displayed in the MAC Binding Table.
Field | Description |
Interface | Displays the interface to which the MAC ACL is bound. |
|
|
Direction | Specifies the packet filtering direction for ACL. The only valid direction |
| is Inbound, which means the MAC ACL rules are applied to traffic |
| entering the port. |
|
|
ACL Type | Displays the type of ACL assigned to selected interface and direction. |
|
|
ACL ID | Displays the ACL Name identifying the ACL assigned to selected |
| interface and direction. |
|
|
Sequence No | Displays the Sequence Number signifying the order of specified ACL |
| relative to other ACLs assigned to selected interface and direction. |
|
|
To delete a MAC
IP ACL
IP ACLs allow network managers to define classification actions and rules for specific ingress ports. Packets can be filtered on ingress (inbound) ports only. If the filter rules match, then some actions can be taken, including dropping the packet or disabling the port. For example, a network administrator defines an ACL rule that says port number 20 can receive TCP packets. However, if a UDP packet is received the packet is dropped.
ACLs are composed of access control entries (ACE), or rules, that consist of the filters that determine traffic classifications.
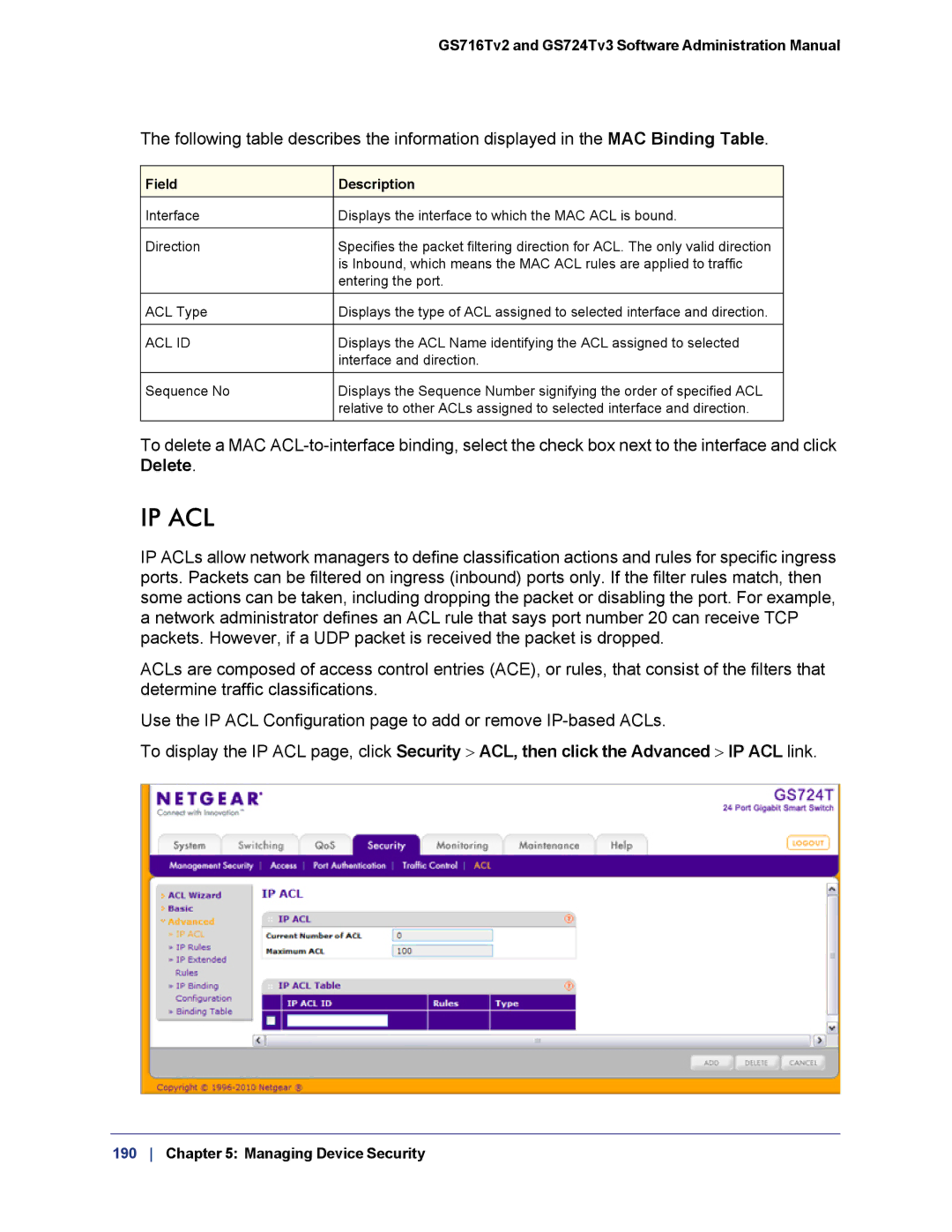
Use the IP ACL Configuration page to add or remove
To display the IP ACL page, click Security > ACL, then click the Advanced > IP ACL link.
190 Chapter 5: Managing Device Security