Understanding Tools and Options
Obtaining the Kernel and Configuration Files
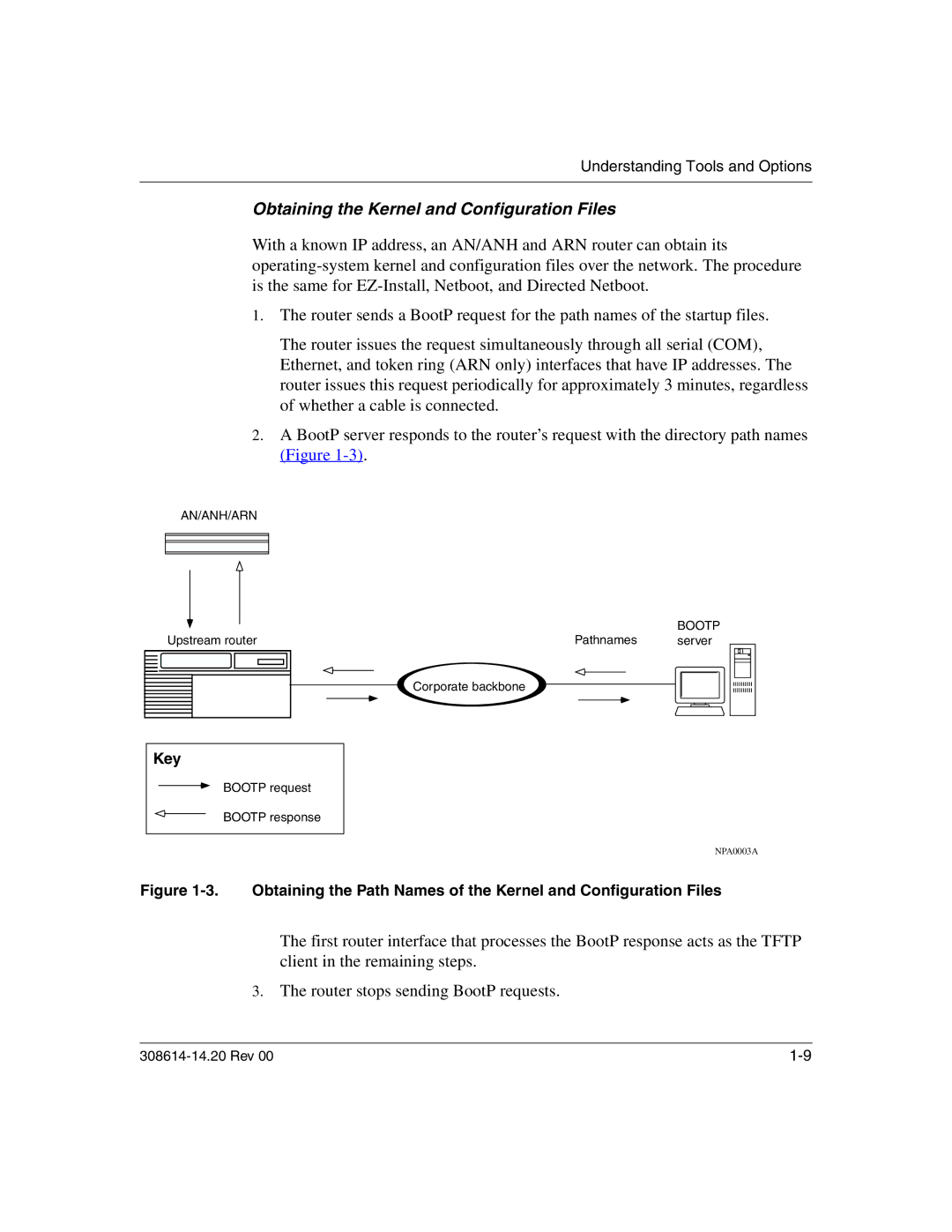
With a known IP address, an AN/ANH and ARN router can obtain its
1.The router sends a BootP request for the path names of the startup files.
The router issues the request simultaneously through all serial (COM), Ethernet, and token ring (ARN only) interfaces that have IP addresses. The router issues this request periodically for approximately 3 minutes, regardless of whether a cable is connected.
2.A BootP server responds to the router’s request with the directory path names (Figure
AN/ANH/ARN
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pathnames | BOOTP |
Upstream router |
|
| server | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Corporate backbone
Key
BOOTP request
BOOTP response
NPA0003A
Figure 1-3. Obtaining the Path Names of the Kernel and Configuration Files
The first router interface that processes the BootP response acts as the TFTP client in the remaining steps.
3.The router stops sending BootP requests.