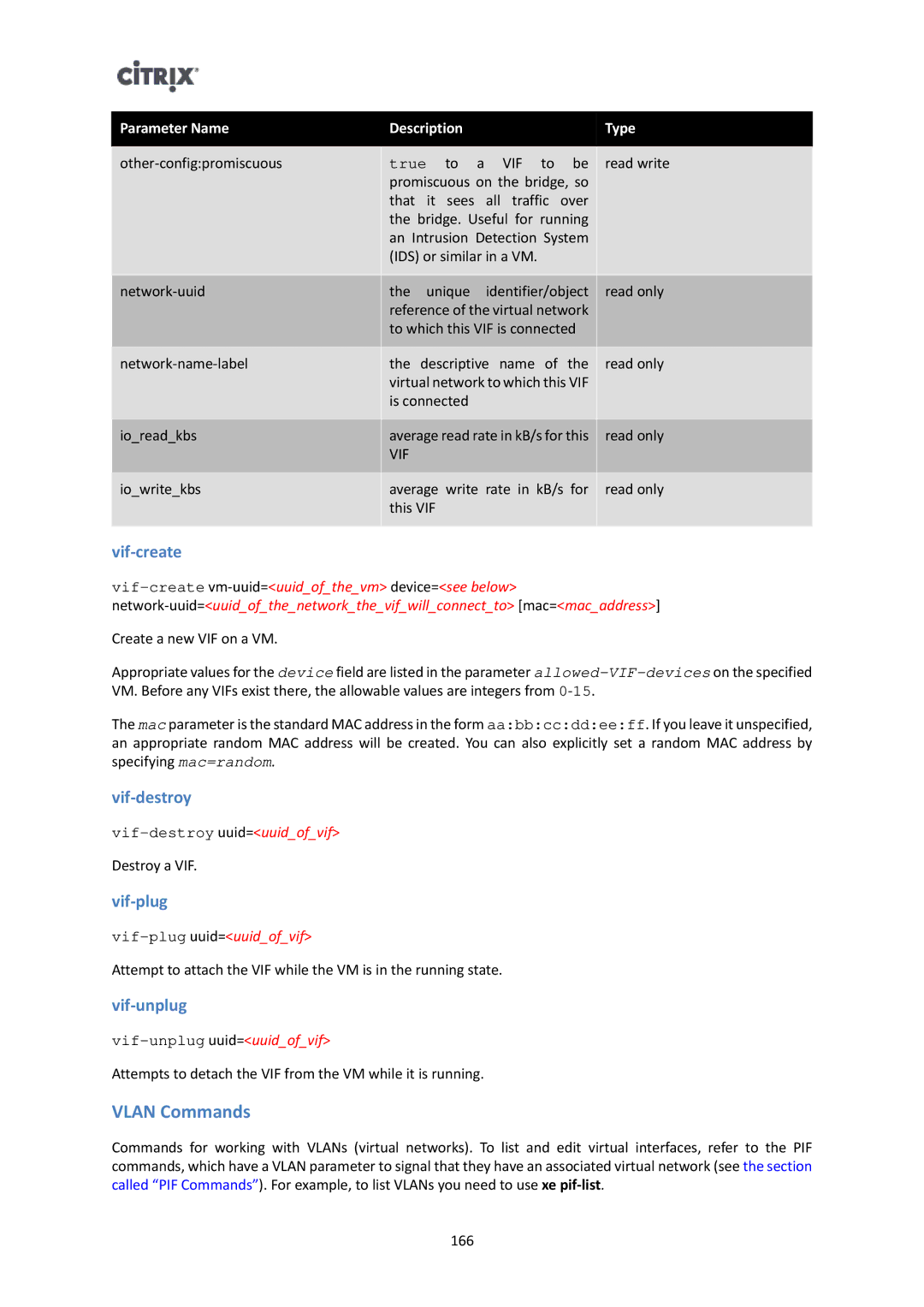
Parameter Name | Description |
| Type | |
|
|
| ||
true to a VIF to be | read write | |||
| promiscuous on the bridge, so |
| ||
| that | it sees | all traffic over |
|
| the bridge. Useful for running |
| ||
| an Intrusion Detection System |
| ||
| (IDS) or similar in a VM. |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
the | unique | identifier/object | read only | |
| reference of the virtual network |
| ||
| to which this VIF is connected |
| ||
|
|
| ||
the descriptive name of the | read only | |||
| virtual network to which this VIF |
| ||
| is connected |
|
| |
|
|
| ||
io_read_kbs | average read rate in kB/s for this | read only | ||
| VIF |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
io_write_kbs | average write rate in kB/s for | read only | ||
| this VIF |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
vif-create
Create a new VIF on a VM.
Appropriate values for the device field are listed in the parameter
The mac parameter is the standard MAC address in the form aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff. If you leave it unspecified, an appropriate random MAC address will be created. You can also explicitly set a random MAC address by specifying mac=random.
vif-destroy
Destroy a VIF.
vif-plug
Attempt to attach the VIF while the VM is in the running state.
vif-unplug
Attempts to detach the VIF from the VM while it is running.
VLAN Commands
Commands for working with VLANs (virtual networks). To list and edit virtual interfaces, refer to the PIF commands, which have a VLAN parameter to signal that they have an associated virtual network (see the section called “PIF Commands”). For example, to list VLANs you need to use xe
166