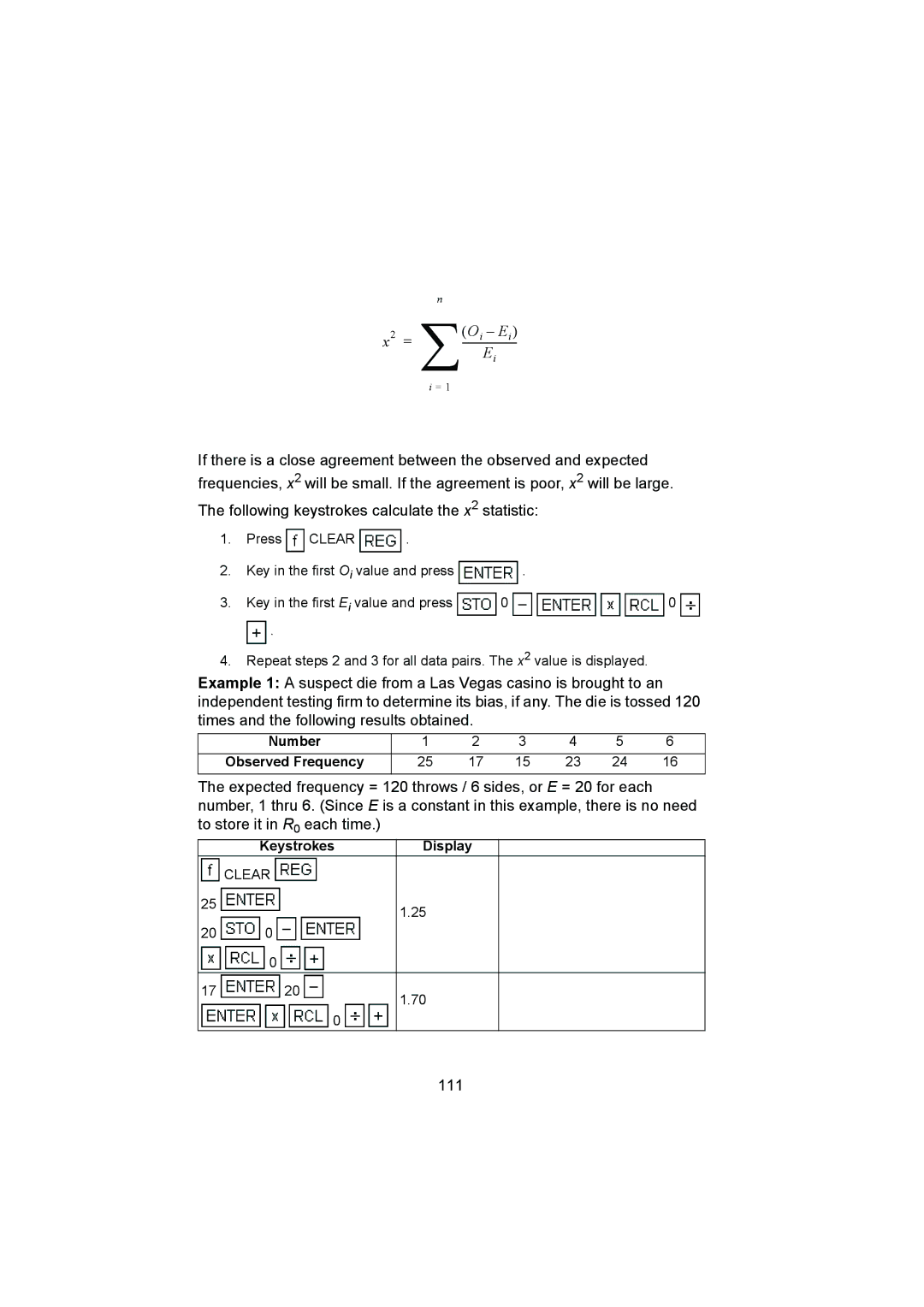
n
2 ∑(Oi – Ei )
x =
Ei
i = 1
If there is a close agreement between the observed and expected frequencies, x2 will be small. If the agreement is poor, x2 will be large.
The following keystrokes calculate the x2 statistic:
1.Press ![]() CLEAR
CLEAR ![]() .
.
2.Key in the first Oi value and press ![]() .
.
3.Key in the first Ei value and press ![]() 0
0 ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 0
0 ![]()
![]() .
.
4.Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all data pairs. The x2 value is displayed.
Example 1: A suspect die from a Las Vegas casino is brought to an independent testing firm to determine its bias, if any. The die is tossed 120 times and the following results obtained.
Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Observed Frequency | 25 | 17 | 15 | 23 | 24 | 16 |
The expected frequency = 120 throws / 6 sides, or E = 20 for each number, 1 thru 6. (Since E is a constant in this example, there is no need to store it in R0 each time.)
KeystrokesDisplay
| CLEAR |
|
25 |
| 1.25 |
|
| |
20 | 0 |
|
| 0 |
|
17 | 20 | 1.70 |
|
| |
|
| 0 |