HP Z820 Workstation slot identification and description
Maximum power used by all slots must not exceed total system power and is subject to configuration limitations.
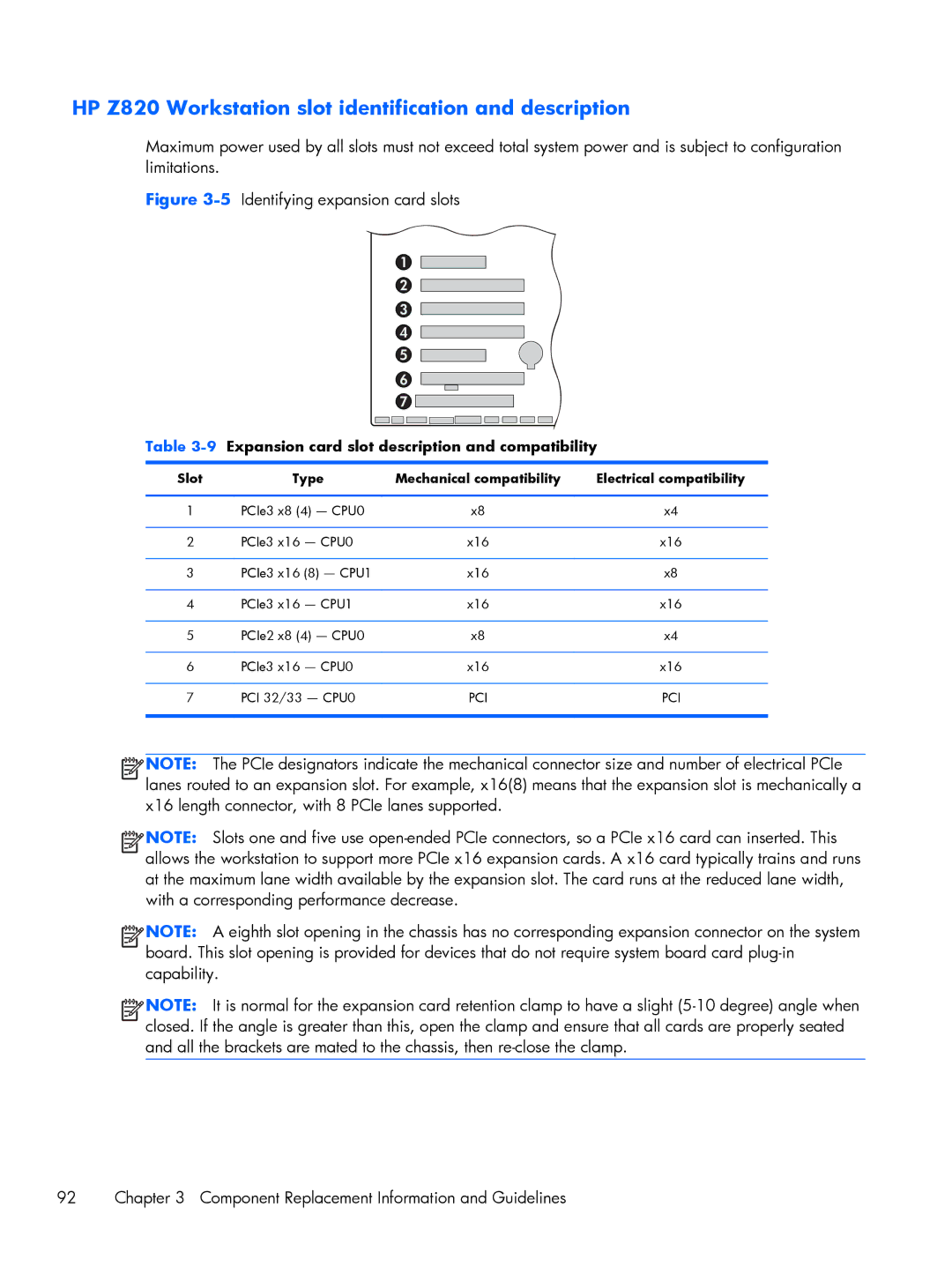
Figure 3-5 Identifying expansion card slots
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 ![]()
![]()
Table | Expansion card slot description and compatibility | |||
|
|
|
| |
Slot | Type | Mechanical compatibility | Electrical compatibility | |
|
|
|
| |
1 | PCIe3 x8 (4) — CPU0 | x8 | x4 | |
|
|
|
|
|
2 | PCIe3 x16 | — CPU0 | x16 | x16 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 | PCIe3 x16 | (8) — CPU1 | x16 | x8 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 | PCIe3 x16 | — CPU1 | x16 | x16 |
|
|
|
| |
5 | PCIe2 x8 (4) — CPU0 | x8 | x4 | |
|
|
|
|
|
6 | PCIe3 x16 | — CPU0 | x16 | x16 |
|
|
|
| |
7 | PCI 32/33 — CPU0 | PCI | PCI | |
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() NOTE: The PCIe designators indicate the mechanical connector size and number of electrical PCIe lanes routed to an expansion slot. For example, x16(8) means that the expansion slot is mechanically a x16 length connector, with 8 PCIe lanes supported.
NOTE: The PCIe designators indicate the mechanical connector size and number of electrical PCIe lanes routed to an expansion slot. For example, x16(8) means that the expansion slot is mechanically a x16 length connector, with 8 PCIe lanes supported.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() NOTE: Slots one and five use
NOTE: Slots one and five use
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() NOTE: A eighth slot opening in the chassis has no corresponding expansion connector on the system board. This slot opening is provided for devices that do not require system board card
NOTE: A eighth slot opening in the chassis has no corresponding expansion connector on the system board. This slot opening is provided for devices that do not require system board card
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() NOTE: It is normal for the expansion card retention clamp to have a slight
NOTE: It is normal for the expansion card retention clamp to have a slight
92 | Chapter 3 Component Replacement Information and Guidelines |