MERLIN LEGEND Communications System Release 6.1 | Issue 1 | ||
Network Reference | August 1998 | ||
1 Introduction |
|
| |
| Tandem Trunking and Tandem Switching | Page | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
ML A
PRI
ML B
PRI
ML C
Tie
ML D
New York, NY | Chicago, IL | Los Angeles, CA |
| Santa Monica, CA |
Ext. |
| Ext. | Ext. | Ext. |
4321 |
| 5455 | 3699 | 6233 |
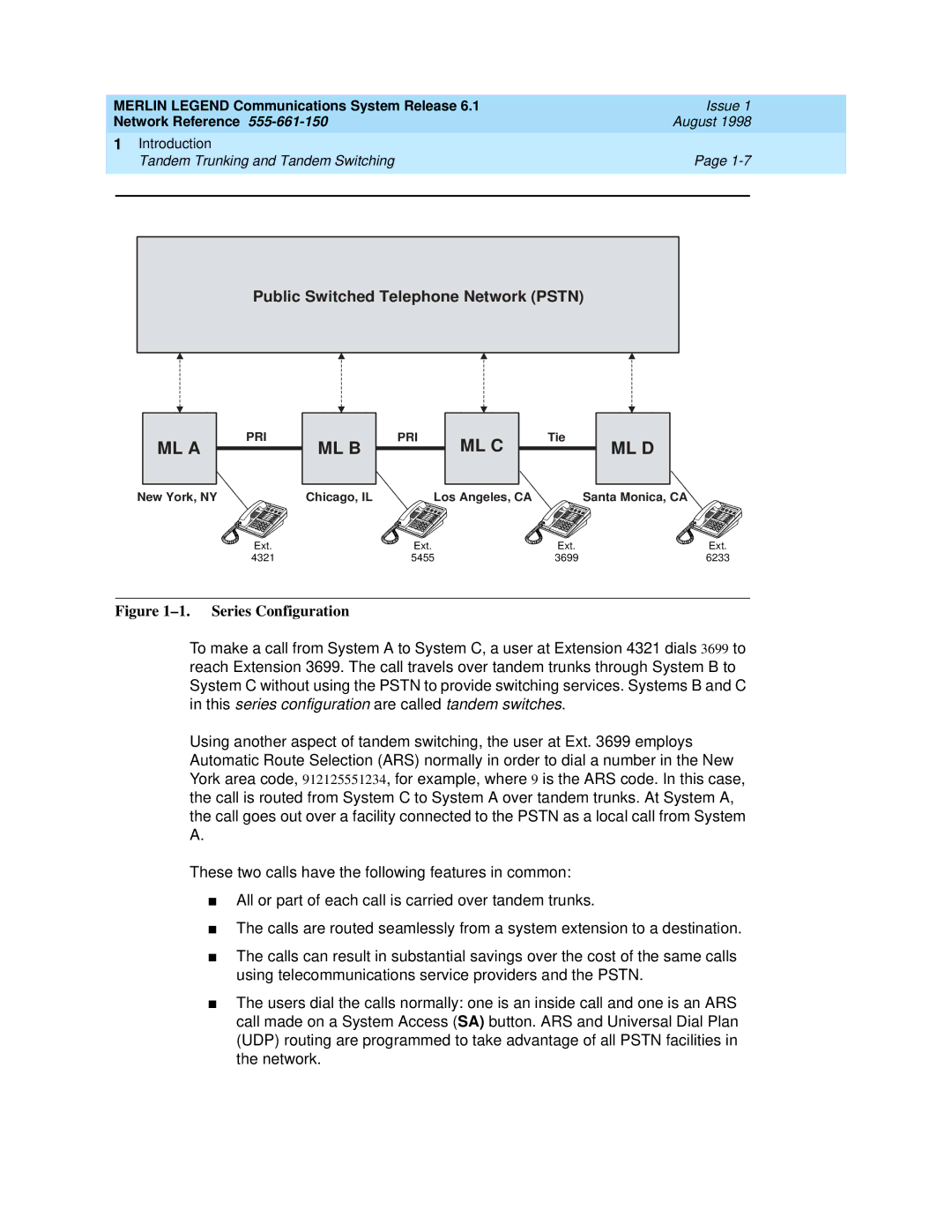
Figure 1–1. Series Configuration
To make a call from System A to System C, a user at Extension 4321 dials 3699 to reach Extension 3699. The call travels over tandem trunks through System B to System C without using the PSTN to provide switching services. Systems B and C in this series configuration are called tandem switches.
Using another aspect of tandem switching, the user at Ext. 3699 employs Automatic Route Selection (ARS) normally in order to dial a number in the New York area code, 912125551234, for example, where 9 is the ARS code. In this case, the call is routed from System C to System A over tandem trunks. At System A, the call goes out over a facility connected to the PSTN as a local call from System A.
These two calls have the following features in common:
■All or part of each call is carried over tandem trunks.
■The calls are routed seamlessly from a system extension to a destination.
■The calls can result in substantial savings over the cost of the same calls using telecommunications service providers and the PSTN.
■The users dial the calls normally: one is an inside call and one is an ARS call made on a System Access (SA) button. ARS and Universal Dial Plan (UDP) routing are programmed to take advantage of all PSTN facilities in the network.