Apple II Original ROM Information
Data
Qjjj
0005A0 FDA9A920 EDFDA98D 4CEDFDA9 8D4CEDFD
Page
Page
Page
JI@
Page
001AE0 E8EEE7E8 Efefeeef Eeefeeee Efeeeeee
001AA0 F3FFE8E1 E8E8EFEB FFFFE0FF Ffefeeef
001AC0 FFFFE1E1 EFEEE7E8 EEE7F3FB FBEEE1EF
001DB0 9CDD9CDE DD9EC3DD Cfcacdcb 00479AAD
001FB0 Ffffffff FFFF2071 E14CBFEF 2003EEA9
Page
DDBAF9F0 0DBDBAF9
FA60FFFF
02E61FBD JJJ
60FFFFFF .JJ
AEAEA8AD
Page
Page
Return
Page
System Monitor Copyright
LOC0
LOC1
Basl
Mask
INY NO, INC Index X-COORD
LDY PCH
PRMN1 LDA
FMT1 DFB
Format Above
EOR
STA A3H FAE2 A2 FB
Tabv STA Vtabs to ROW in A-REG
STA Bash
BCC Clreol Clear to END of Line
NXTA4 INC A4L Incr 2-BYTE A4
STA BASL,Y Replace Flashing Screen
Fdad A5 3C
LT2 LDA A2L,X Copy A2 2 Bytes to
Ioprt LDA A2L SET RAM IN/OUT Vectors
BCC RD3 Loop Until Done
STA A3H,X
DFB LIST-1 FFF3 CC
Save
BRTBL,X
LSR Prepare Carry for BC, BNC
Stat LDA R0L
JSR STAT2 Push LOW PC Byte VIA R12
LDA IN,Y
CMP
BNE Nomove
JSR
Mloop
DCR
BNZ Mloop
RTN
INR
BNC
BNZ
BM1
Example
Load Indirect
Store Indirect
Load DOUBLE-BYTE Indirect
Store POP Indirect
Store DOUBLE-BYTE Indirect
POP Indirect
POP DOUBLE-BYTE Indirect
ACC
Subtract
Compare
BF A0 SET $A0BF
LOOP1 SUB
BNC LOOP1
Return to 6502 Mode
Decrement
LOOP2
BNZ LOOP2
Branch if no Carry
Branch if Carry SET
Branch if Plus
LOOP3 SUB
Branch if Minus ONE
Branch if not Minus ONE
Break
Return from Sweet 16 Subroutine
STA IND JMP
LDA #ADRH
STA IND+1 LDA OPTBL,X
Page
Page
Sweet 16 Introduction
Page
Source
DSP
Print Dbload Sweet REM Ctrl D
Input Enter String a $ , a $
NVA
Poke 776 , a REM Poke Destination
Print Print Goto
Call -605 Return REM XAM8 in Monitor
Sweet
MINI-ASSEMBLER
Baum
Mneml
Mnemr
SBC PCL Form ADDR-PC-2
JSR Cout Position
FORM7 STX A1H Save Index
ORG
CLC
STA
BNE
Norm LDA EXP1 ZERO?
Shift Dividend Left
Floating Point Package
Floating Point Representation LOW
Stored
High LOW EXP Mantissa
Floating Point Representation Examples
Number Exponent Mantissa
Floating Point Subroutine Descriptions
Page
Page
Page
Page
STY Init MANT1 LDY
STY
Calling Sequence
HIGH-ORDER
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Fsub
Seeeeeee
Mmmmmmmm
ORG SET Base page Adresses
STA X2,X
Common LOG of MANT/EXP1 Result in MANT/EXP1
Ovflw BRK Overflow
1EBB STA X2,X Load EXP/MANT2 with Z 1EBD DEX 1EBE BPL LF3
YES,RETURN with MANT1 Normalized
Right Shift MANT1 or Swap with MANT2 on Carry
CMP
Addend
Normx BCC Norm If EXEN, Normalize PRODUCT, Else Complement
LDA STA
Errata for Rankins Floating Point Routines
LDX Load X for High Byte of Exponent
LOG
Fadd
Fsub
Fmul
Page
Mantissa
MOD 9/76 Load X for Later
M2MHL
Contin
1EAD LFA LDA Z,X
L2E DCM
Normx
RTLOG1
Mdend
Object Code Dump
Page
Tapdel
Hsbdry
Toutfl
Lstcom
Outvec
Urcvec
=UBRKVC
=UIRQVC
TAX
ADC
ORA
Stocom STA
BPL HASHUS+2
Restore Except A,F
BEQ
STX
CPX
JMP
Exwrap RTS
Chksad PHP
Outxah PHA
TXA
Nibasc and #$0F Nibble in a to Ascii in a
BCS INST1
RTI
Ldbyte JSR Inbyte
Verify MEM
E1PARM JMP
STD2
MORED2 LDY
JSR Brtt INC Ercnt UP to FF
MEM3EX CLC
SBC P3L
BNE Exitgk
Ksconf LDA
Txtmov LDA
BNE INRT2
Outone
Dftxfr LDX
Newdev LDA
LDA Toutfl
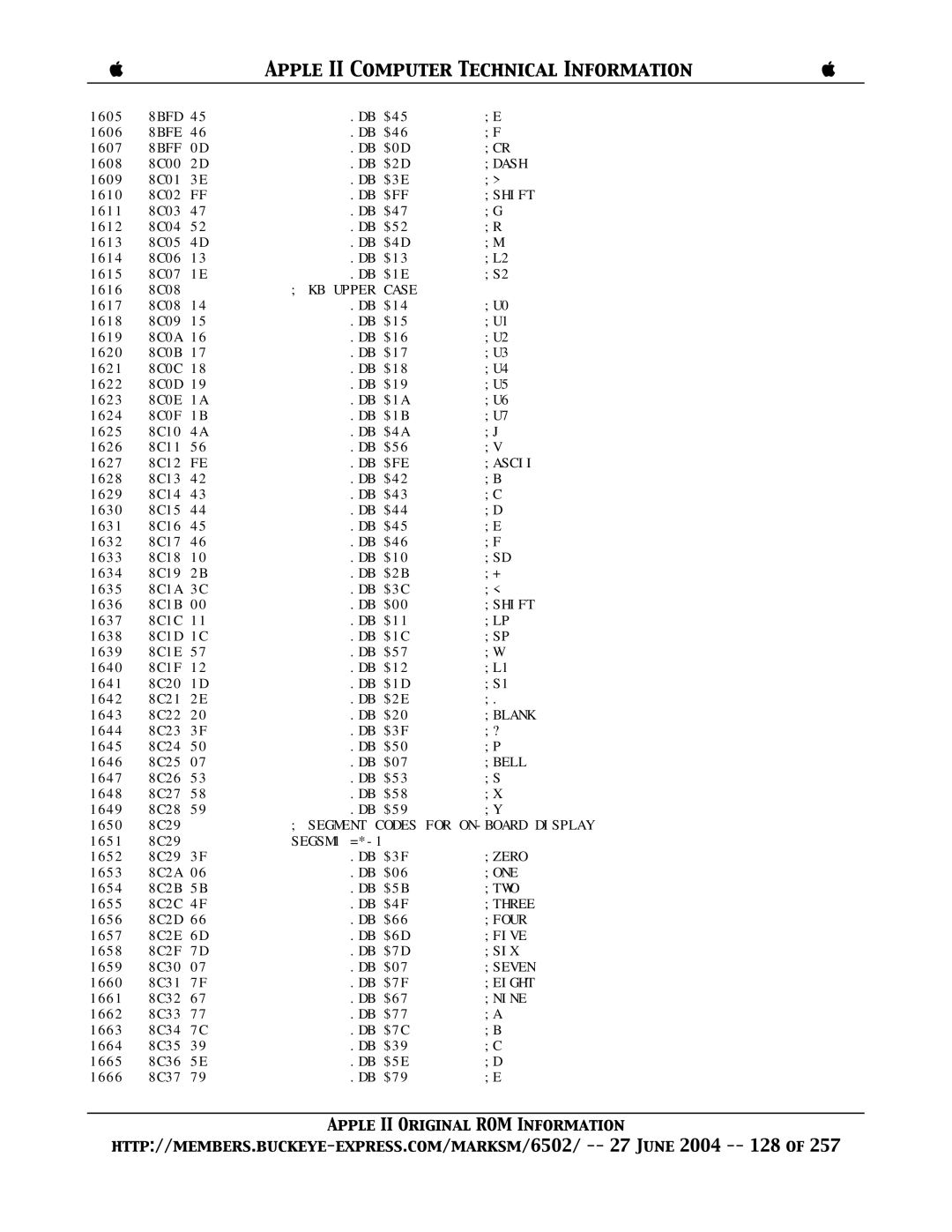
8BFF 0D
Msfirst
LOADT2
Bufadh
Ddrdig
STA Mode
BNE Lcerr Last Char not
Kgettr LDA
H8DFF
BCC PACKT3
Dumpt
DUMPT1 TXA
DMPT1A LDA
DUMPT4 LDY
Outbth LDX
Register Name Patch
Outcht STX
HS Tape Boundary
Rockwell International
Udrah
Uddra
Nowln
Oldlen
Length
Movad
TMASK1 =MOVAD
Curpos
Checksum
Tabuff
TABUF2
Write Edge Detect Control not Used Because KB
CRB
EQS
DB TO,EQS
CFD2A0A0A0A0
SEI Disable Interrupt
RS6 JSR Crlow Clear Display
E1AC Have Valid Command
Nxtadd TYA
Space Comm
For
LOAD1A LDA
LOADK5 LDX
JMP LOADK5 Next
E46A EE INC Bkflg SET FLG
Outcks LDA
OUTCK1 PHA
Dumpta LDX
DUMPT1 LDA
E5EA
TOGTA1 LDA
TOGTA2 LDA
BCC JD3
MSG
Whereo LDY
ANY Other
CPY
STA Outflg
Output PHA
Outall PHA
ROL Priflg Restore FLG
Wrax JSR Numa
EAA3 CA DEX
Memerr JSR
STA STIY+2
Dehalf LDA
EC5E 4A LSR Only ROW
Onekey LDA
Debkey LDX
ED3B GET a Char from Tape Subroutine
Edba
LSR Cpiy Make Room for MSB
Outtty PHA
OUTDD1 PHA
OUTD1A CPX
OUTD2A TXA
LDA First Chip Select
Prndot LDA
LDA #PRTIME/256 Start T2 for 1.7 Msec
BIT Imask See if DOT is SET
NEW Print ROW
Newcol LDA
Ckbuff LDA
Bkcksm LDA
OUTTA1 PHA
OUTTA2 LDX
F2E1 3E7E7F3E7F7FCOL0
Zero Leftmost Column
DB BGYU76HN
Rtmode
Getfmt TAX
MNNDX1 LSR
MNNDX2 LSR
PRADR4 DEX
PRADR2 LDA
PLA
BPL PCADJ4
AIM Text Editor
LDA END+1 CMP with END
AF E7 JMP KEP
RUB
COMMAND-FIND String
JMP CHN1
See if WE RAN Past END of Buffer Limit
BEQ REP2
SBC Oldlen
GOGO1 RTS
Startm JSR
ROM Table
FB46 8A9AAABACADA
Rdaddr LDY
Tryjmp LDA
IMMED1 LDX
Convrt LDA
OPCMP1 LDA
Brnchc JMP
Compbr LDX
FORMD2 LDX
Brcomp LDA
Backwd LDA
Forwrd LDA
MATCH1 JMP
Curead TXA
PATCH4 LDX CURPO2 Dont do Anything if 8D
PATC15 JSR Crlf Decode Command
Addblk
ADDS1A
Bkcksm
Brcomp
CRA
Goerr
Namo E8CF NAMO1
RD2 EA5D RD1
AIM 65 Microcomputer Monitor Program Listing
E6AC
Introduction
Table of Contents
AIM 65 Microcomputer Basic Language Reference Manual
Installing Basic in the AIM ROM Installation Procedure
Entering Basic
Memory SIZE?
WIDTH?
Exiting Basic
Reentering Basic
Basic Cursor
Printer Control
CHR$
Getting Started with Basic Basic Command SET
ASC
Direct and Indirect Commands Direct Commands
Indirect Commands
Operating on Programs and Lines
Listing a Program
Deleting a Line
Replacing a Line
Deleting a Program
List Printing Data
Number Output Format
Print ONE Half Equals 1/2
Number Format
Variable Names
Variables Assigning Variables with AN Input Statement
Input R
Reserved Words
PSTG$
Print A, A*2 LET Z=7 Print Z, Z-A
Program Using Relations
Remarks
Relational Tests
Input B
Looping
Square Root Program
AN Improved Square Root Program
Print Nsqrn
Another Square Root Program
Print Nsqrn Next N
COUNT-BACKWARD Program
Some Other Looping Operations
Print What is the Number
Print I,J Next Next J
Matrix Operations
Sort Program
Print BAD GUESS, TRY Again Restore
Input N
Print Must be Integer
Stopping a Program
Strings
$=ROCKWELL R6500 Print A$ Rockwell R6500
LEN Function
Print LENA$,LENMICROCOMPUTER
RIGHT$ Function
MID$ Function
Print B$ Basic for Rockwell R6500
Print C$ Basic FOR-ROCKWELL-R6500 VAL and Strs Functions
CHR$ Function
Data AIM 65,DOG
Additional String Considerations
Name Example PURPOSE/USE DIM
Input Input X$
Print Print X$
Operators Symbol Sample Statement
ESC
Cntl Print
Print X/1.3
Relational Operators
Symbol Sample Statement PURPOSE/USE
Negation
Not If not Q3 then
Operator Argument Result Not
Commands
Print Intruder Alert
Alert
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example Clear
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION FRE
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION List
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Load
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION NEW
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example RUN
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example Save
Program Statements
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example DEF
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION For
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION DIM
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION END
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Gosub
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Goto
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION IF...GOTO
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION IF...THEN
If X0 then Print ERROR, X Negative Goto Example
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION LET
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Next
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION ON...GOSUB
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Restore
Symbol SYNTAX/FUNCTION Wait
Example Restore Return
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Return
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Input
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION POS
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Print
Print Value ISA
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Read
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION SPC
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION TAB
String Functions Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION ASC
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION LEFT$
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION LEN
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION MID$
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION RIGHT$
Arithmetic Functions Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION ABS
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION ATN
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION COS
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION EXP
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example SGN
Print Sgnx
Statement SYNTAX/FUNCTION Example SIN
Print Sinx
Inverse Hyperbolic Secant
Error Messages
?XX Error
PRINTX,Y,Z
TAB, SPC
Space Hints
Storage Allocation Information
Speed Hints
This is Probably the Most Important Speed Hint
Converting Basic Programs not Written for AIM 65 Basic
OLD AIM
OLD
Assembly Language Subroutines
Ascii Character Codes Decimal
NUL
SOH
Address Content
$AE
Inputnumbern
Printx
Storing AIM 65 Basic Programs on Cassette
Recording on Cassette Using the Basic Save Command
RUN NUMBER?
Cassette Operations Using the AIM 65 Editor
OUT=T F=
OUT=T F=FNAME T=
IN=
ATN Implementation
Entered by Alter Memory M
OF9C
0FAC
WIDTH? Bytes Free AIM 65 Basic
Saving ATN Object Code on Cassette