Chapter 3: Configuration
3.12 GARP
The Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) provides a generic framework in which devices in a bridged LAN, e.g. end stations and switches, can register and
3.12.1 Configuration
This page describes how to configure the basic GARP Configuration settings for all switch ports. The settings relate to the currently selected unit, as shown in the page header.
Web Interface
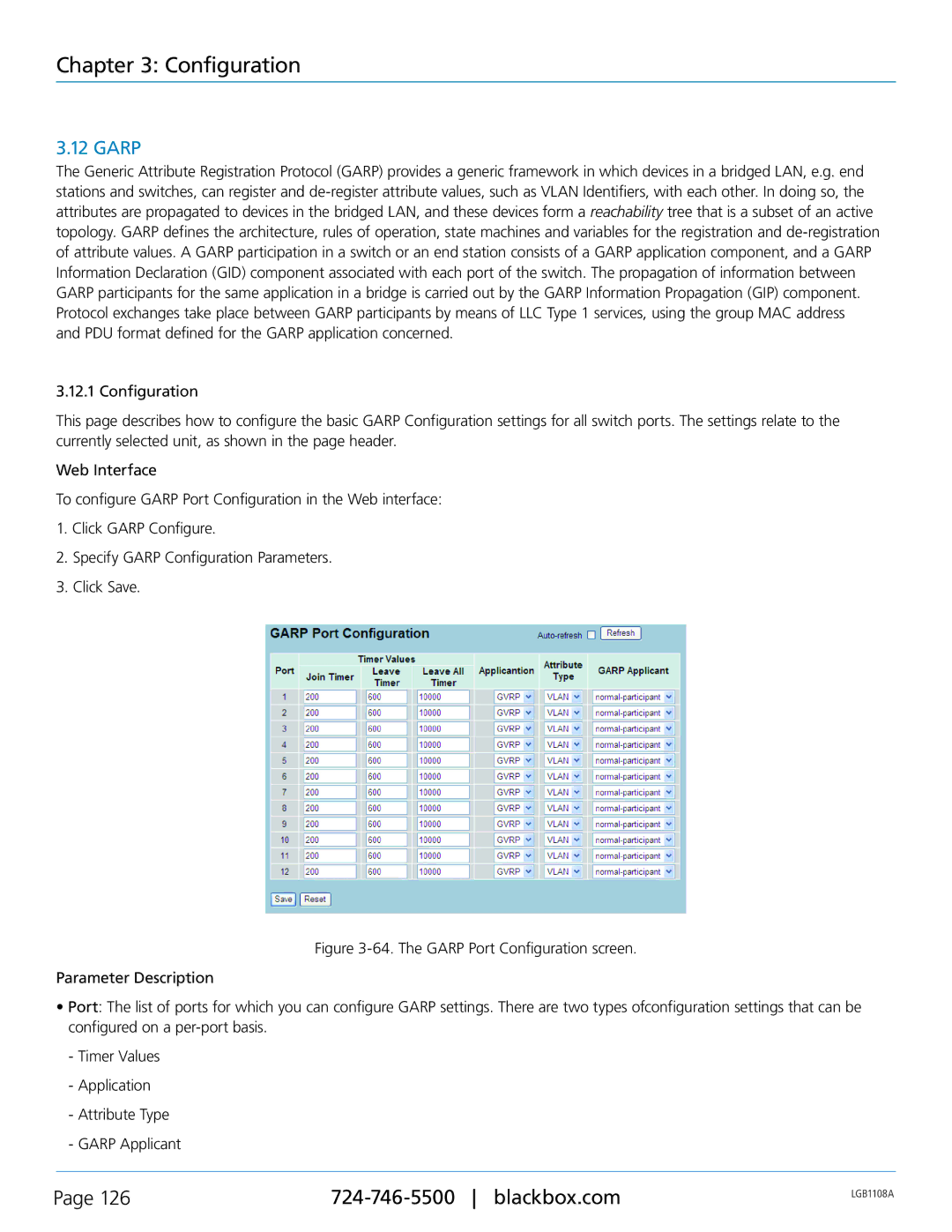
To configure GARP Port Configuration in the Web interface:
1.Click GARP Configure.
2.Specify GARP Configuration Parameters.
3.Click Save.
Figure 3-64. The GARP Port Configuration screen.
Parameter Description
•Port: The list of ports for which you can configure GARP settings. There are two types ofconfiguration settings that can be configured on a per-port basis.
-Timer Values
-Application
-Attribute Type
-GARP Applicant
Page 126 | LGB1108A | |
|
|