Administration Guide
Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved 78-20776-03
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement For ISA550W and ISA570W
Important Note
Canada Radiation Exposure Statement For ISA550W and ISA570W
Industry Canada statement
Déclaration dexposition aux radiations
UL/CB
Getting Started
Configuration Wizards
Using Remote Access VPN Wizard for SSL Remote Access
Status
Networking 115
Understanding Dscp Values 171
Vlan Setup 180 Wireless Setup 181 User Authentication
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only 206
Firewall 251
Vlan Setup 222 Wireless Setup 223 User Authentication
Security Services 291
VPN 333
General Application Control Settings 314
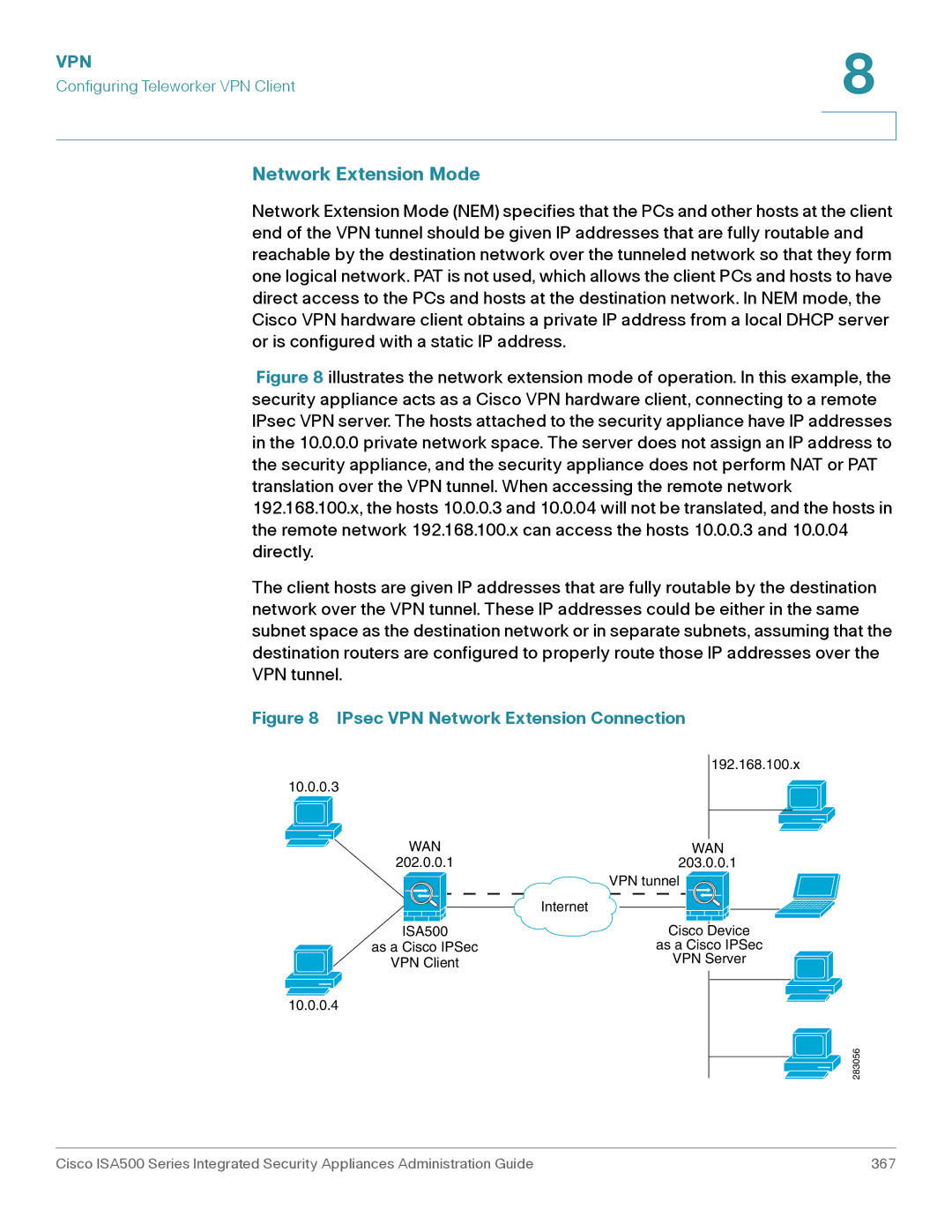
Client Mode 366 Network Extension Mode 367
Device Management 403
User Management 388
Contents
Appendix D Where to Go From Here 479
Appendix a Troubleshooting 453
Getting Started
ISA550W
Model Description Configuration
Introduction
Getting Started
Front Panel
Product Overview
Front Panel, Back Panel,
USB
POWER/SYS
Light Description
VPN
ISA550 and ISA550W Back Panel
Back Panel
Speed
LINK/ACT
ANT01/ANT02
Feature Description
Power
Getting Started with the Configuration Utility
Reset Button
Power Switch
Logging in to the Configuration Utility
Number Component Description
Navigating Through the Configuration Utility
Configuration Utility Icons
Using the Help System
Icon Description Action
Getting Started
Default Settings of Key Features
Factory Default Settings
Restoring the Factory Default Settings
Changing the Default Administrator Password
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
Parameter Default Value
Click Continue
Upgrading your Firmware After your First Login
Backing Up Your Configuration
Configuration Wizards
Configuration Wizards
Using the Setup Wizard for the Initial Configuration
Starting the Setup Wizard
Enabling Firmware Upgrade
Enabling Bonjour and CDP Discovery Protocols
Validating Security License
Configuring Remote Administration
Configuring Physical Ports
Configuring the Secondary WAN
Configuring the Primary WAN
Configuring WAN Redundancy
Configuring Default LAN Settings
Configuring DMZ
Configuring DMZ Services
Configuration Wizards
WAN
Configuring Wireless Radio Settings
WAN IP
Configuring Intranet Wlan Access
Security Services
Configure Security Services
Viewing Configuration Summary
Click Configuration Wizards Dual WAN Wizard
Configuring a Configurable Port as a Secondary WAN Port
Starting the Dual WAN Wizard
Configuring the Primary WAN
Configuring Network Failure Detection
Using the Remote Access VPN Wizard for IPsec Remote
Using the Remote Access VPN Wizard
Configuring IPsec Remote Access Group Policy
Starting the Remote Access VPN Wizard
Click Configuration Wizards Remote Access VPN Wizard
Configuring Operation Mode
Configuring WAN Settings
Configuring DNS and Wins Settings
Configuring Access Control Settings
Configuring Split Tunneling
Configuring Backup Servers
Viewing Group Policy Summary
Viewing IPsec Remote Access Summary
Configuring IPsec Remote Access User Groups
Configuring SSL VPN Gateway
Using Remote Access VPN Wizard for SSL Remote Access
Client Netmask Client Address Pool
Configuring SSL VPN Group Policy
Configuration Wizards
Configuration Wizards
Configuring SSL VPN User Groups
Viewing SSL VPN Summary
Using the Site-to-Site VPN Wizard to Configure Site-to-Site
Click Configuration Wizards Site-to-Site VPN Wizard
Configuring VPN Peer Settings
Starting the Site-to-Site VPN Wizard
Configuring IKE Policies
Configuring Transform Policies
Configuring Local and Remote Networks
Starting the DMZ Wizard
Using the DMZ Wizard to Configure DMZ Settings
Configuring Ddns Profiles
Click Configuration Wizards DMZ Wizard
Configuring DMZ Network
Configuration Wizards
Configuring DMZ Services
WAN
Starting the Wireless Wizard
Using the Wireless Wizard for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Click Configuration Wizards Wireless Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connectivity Types
Configuring the Ssid for Intranet Wlan Access
Specify Wireless Connectivity Settings for All Enabled SSIDs
Configuring Wireless Security,
Configuring the Ssid for Guest Wlan Access
Configuration Wizards
Configuration Wizards
Configuration Wizards
System Information
Device Status Dashboard
Status Dashboard
Field Description
Syslog Summary
Status
Resource Utilization
Licenses
Physical Ports
Remote Access VPN
Routing Mode
Site-to-Site VPN
Field
Ethernet
Network Status
Status Summary
Status Summary
Vlan Pvid
DMZ
Vlan
Traffic Statistics
Traffic Statistics
Usage Reports
Status
WAN Bandwidth Reports
Dhcp Bindings
ARP Table
Dhcp Bindings
ARP Table
STP Status Global Status
STP Status
Interface Status Table
Status
CDP Neighbor
Wireless Status
Wireless Status for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless Status, Client Status,
Client Status
NAT Status
NAT Status
VPN Status IPsec VPN Status
VPN Status
IPsec VPN Status
IPsec VPN Status, SSL VPN Status,
Statistics
Teleworker VPN Client
SSL VPN Status
VPN Status SSL VPN Status
SSL VPN Statistics
Active User Sessions
Active User Sessions
Web Security Report
Security Services Reports
Anti-Virus Report
Email Security Report
Network Reputation Report
IPS Report
Application Control Report
System Status Processes
System Status
Processes
Processes, Resource Utilization,
Memory Utilization
Resource Utilization
System Status Resource Utilization
CPU Utilization
Status
Networking
Networking
Configuring IPv4 or IPv6 Routing
Viewing Network Status
Managing Ports
Viewing Status of Physical Interfaces
Configuring Physical Ports
Configuring Port Mirroring
Configuring Port-Based 802.1x Access Control
Networking
Configuring WAN Settings for Your Internet Connection
Configuring the WAN
Release or renew a Dhcp WAN connection,
Configure the primary WAN
Networking
Dhcp Client
Configure a secondary WAN
Network Addressing Mode
Network Addressing Configuration Mode
Static IP
ISP
PPPoE
Pptp
L2TP
Dual WAN Settings
Networking
Configuring Link Failover Detection
Networking
Ddns Services Table
Configuring Dynamic DNS
Adding or modifying a Ddns service
Measuring and Limiting Traffic with the Traffic Meter
Networking
Configuring a Vlan
Networking
Networking
Networking
About DMZ networks
Configuring DMZ
Example DMZ with One Public IP Address for WAN and DMZ
Example DMZ with Two Public IP Addresses
Configuring a DMZ
Networking
Networking
Security Levels for Zones
Configuring Zones
Predefined Zones
Configuring Zones
Services
Configuring Routing
Configuring Dhcp Reserved IPs
Viewing the Routing Table
Configuring Routing Mode
Configuring Static Routing
Configuring Dynamic Routing RIP
Configuring Policy-Based Routing
Networking
General QoS Settings
Configuring Quality of Service
Click Networking QoS General Settings
Managing WAN Bandwidth for Upstream Traffic
Configuring WAN QoS
Click Networking QoS WAN QoS Bandwidth
Configuring WAN Queue Settings
Click Networking QoS WAN QoS Queue Settings
Configuring Traffic Selectors
Networking
Configuring WAN QoS Class Rules
Configuring WAN QoS Policy Profiles
Click Networking QoS WAN QoS QoS Policy Profile
Mapping WAN QoS Policy Profiles to WAN Interfaces
WAN QoS Configuration Example
WAN1IP
WAN1
Policy Name
Configure WAN QoS for Voice Traffic from LAN to WAN
Class Name
Source Address
QoS Class Rule
Configuring WAN QoS for Voice Traffic from WAN to LAN
QoS Class Rules
Configuring LAN QoS
Click Networking QoS LAN QoS Classification Methods
Configuring LAN Queue Settings
Configuring LAN QoS Classification Methods
Click Networking QoS LAN QoS Queue Settings
Click Networking QoS LAN QoS Mapping CoS to Queue
Mapping CoS to LAN Queue
Mapping Dscp to LAN Queue
LAN Queue CoS Value
802.1p Priority 802.11e Priority
Configuring Wireless QoS
Configuring Default CoS
Default Wireless QoS Settings
802.11e Priority 802.1p Priority
Configuring Wireless QoS Classification Methods
Click Networking QoS Wireless QoS Classification Methods
Ieee 802.11e to 802.1p Mapping
Dscp Value Decimal Value Meaning
Mapping CoS to Wireless Queue
Mapping Dscp to Wireless Queue
Understanding Dscp Values
Click Networking Igmp
Configuring Igmp
011
100
Click Networking Vrrp
Configuring Vrrp
Networking
Click Networking Address Management
Configuring Addresses
Configuring Addresses, Configuring Address Groups,
Address Management
Configuring Address Groups
Click Networking Service Management
Service Management
Configuring Services
Configuring Services, Configuring Service Groups,
Configuring Service Groups
Requirements
Configuring Captive Portal
Before You Begin
Vlan Setup
Wireless Setup
Configuring a Captive Portal
User Authentication
Networking
Networking
Networking
Troubleshooting
Using External Web-Hosted CGI Scripts
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
CGI Source Code Example No Authentication and Accept Button
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
Networking
If result == 2 result == 5 //document.form1.UserName.focus
Networking
Networking
Cisco Small Business
Related Information
Support
Documentation
Cisco Small Business Home
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless Wireless Status Wireless Status
Viewing Wireless Status
Viewing Wireless Statistics
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Viewing Wireless Client Status
Configuring the Basic Settings
Click Wireless Basic Settings
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Configuring Ssid Profiles
Security Mode Description
Configuring Wireless Security
Open
WPA
WEP
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise mixed Supports
WPA2
WPA + WPA2
WPA/WPA2-Personal mixed Supports
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Controlling Wireless Access Based on MAC Addresses
Mapping the Ssid to Vlan
Configuring Ssid Schedule
Click Wireless Wi-Fi Protected Setup
Configuring Wi-Fi Protected Setup
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Configuring Captive Portal
Requirements
Configuring a Captive Portal
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Troubleshooting
Using External Web-Hosted CGI Scripts
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
CGI Source Code Example No Authentication and Accept Button
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
If result == 2 result == 5 //document.form1.UserName.focus
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Related Information
Click Wireless Rogue AP Detection
Configuring Wireless Rogue AP Detection
Click Wireless Advanced Settings
Advanced Radio Settings
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Wireless for ISA550W and ISA570W only
Firewall
Firewall
About Security Zones
Security Levels and Predefined Zones Description
Click Firewall Access Control Default Policies
Default Firewall Settings
Priorities of Firewall Rules
Preliminary Tasks for Configuring Firewall Rules
Click Firewall Access Control ACL Rules
General Firewall Settings
Configuration Examples,
Configuring a Firewall Rule
Firewall
MAC Address Filtering to Permit or Block Traffic,
Configuring a Firewall Rule to Allow Multicast Traffic
Configuring Firewall Logging Settings
Configuring NAT Rules to Securely Access a Remote Network
Firewall NAT NAT Status
Viewing NAT Translation Status
Inbound Traffic
Priorities of NAT Rules
Outbound Traffic
Click Firewall NAT Dynamic PAT
Configuring Dynamic PAT Rules
Click Firewall NAT Static NAT
Configuring Static NAT Rules
Click Firewall NAT Port Forwarding
Configuring Port Forwarding Rules
Firewall
Click Firewall NAT Port Triggering
Configuring Port Triggering Rules
Click Firewall NAT Advanced NAT
Configuring Advanced NAT Rules
Configuring IP Alias for Advanced NAT rules
Http
As Any
From Any
Configuring an Advanced NAT Rule to Support NAT Hairpinning
WAN WAN1 WAN IP WAN1IP
Default
Defaultnetwork
FTP-CONTROL
Allowing Inbound Traffic Using the WAN IP Address
Firewall and NAT Rule Configuration Examples
Translated IP InternalFTP
Enable Port Forwarding
ANY
WAN WAN1 WAN IP
Allowing Inbound Traffic Using a Public IP Address
RDP
Translated IP RDPServer
Address Original Destination PublicIP Original Services
Zone
Name
Netmask
Port
CU-SEEME
Enable Port Forwarding Create Firewall Rule Off
Translated IP InternalIP
Blocking Outbound Traffic to an Offsite Mail Server
Blocking Outbound Traffic by Schedule and IP Address Range
Schedule
Configuring Content Filtering Policy Profiles
Configuring Content Filtering to Control Internet Access
Click Firewall Content Filtering Content Filtering Policies
Configuring Website Access Control List
Click Firewall Content Filtering Policy to Zone Mapping
Mapping Content Filtering Policy Profiles to Zones
Click Firewall Content Filtering Advanced Settings
Configuring Advanced Content Filtering Settings
Click Firewall MAC Filtering MAC Address Filtering
Configuring MAC Address Filtering to Permit or Block Traffic
Click Firewall MAC Filtering IP MAC Binding Rules
Configuring IP-MAC Binding to Prevent Spoofing
Click Firewall Attack Protection
Configuring Attack Protection
Click Firewall Session Limits
Configuring Session Limits
Click Firewall Application Level Gateway
Configuring Application Level Gateway
Firewall
Security Services
IPS
About Security Services
Priority of Security Services
Activating Security Services
Click Security Services Dashboard
Security Services Dashboard
Viewing Security Services Reports
Viewing IPS Report, Viewing Application Control Report,
Viewing Web Security Report
Viewing Anti-Virus Report
Viewing Email Security Report
Total Last 7 Days
Viewing Network Reputation Report
System Date
Total Since Activated
Total Today
Viewing IPS Report
Graph
Viewing Application Control Report
Configuring Anti-Virus
Click Security Services Anti-Virus General Settings
General Anti-Virus Settings
FTP
Protocol Action
Notify + Drop Connection Drop the connection
Http Notification,
Notification,
Netbios
Cifs
Click Security Services Anti-Virus Advanced Settings
Configuring Advanced Anti-Virus Settings
Click Security Services Anti-Virus Email Notification
Configuring Http Notification
Configuring Email Notification
Click Security Services Anti-Virus Http Notification
Updating Anti-Virus Signatures
Updating Application Signature Database,
Configuring Application Control
General Application Control Policy Settings
Configuring Application Control Policies
Important Tips
Adding an Application Control Policy
Security Services
Permitting or Blocking Traffic for an Application
General Application Control Settings
Mapping Application Control Policies to Zones
Enabling Application Control Service
Configuring Application Control Policy Mapping Rules
Updating Application Signature Database
Click Update Database
Advanced Application Control Settings
Click Security Services Spam Filter
Configuring Spam Filter
Security Services
Configuring Intrusion Prevention
Security Services
Configuring Signature Actions
Updating IPS Signature Database
Configuring Web Reputation Filtering
Click Security Services Web Reputation Filtering
Configuring Web URL Filtering
Click Security Services Web URL Filtering Policy Profile
Configuring Web URL Filtering Policy Profiles
Configuring Website Access Control List
Click Security Services Web URL Filtering Advanced Settings
Configuring Advanced Web URL Filtering Settings
Mapping Web URL Filtering Policy Profiles to Zones
Security Services
Network Reputation
VPN
About VPNs
VPN VPN Status IPsec VPN Status
Viewing VPN Status
Viewing IPsec VPN Status
Viewing IPsec VPN Status, Viewing SSL VPN Status,
Field Description
VPN VPN Status SSL VPN Status
Viewing SSL VPN Status
SSL VPN Statistics
VPN
Site-to-Site VPN
Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN
General Site-to-Site VPN Settings
Configuration Tasks to Establish a Site-to-Site VPN Tunnel
Click VPN Site-to-Site IPsec Policies
VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
VPN
VPN
VPN
283058
VPN
Click VPN Site-to-Site IKE Policies
VPN
Click VPN Site-to-Site Transform Policies
Configuring Transform Sets
IKE Policy
Remote Teleworker Configuration Examples
Field Setting
Remote Network
Transform
Name Enable From
Address Translated
Destination Address Translated Services
Configuring IPsec Remote Access
Then choose Cisco VPN Client
Cisco VPN Client Compatibility
Configuring IPsec Remote Access Group Policies
Enabling IPsec Remote Access
Click VPN IPsec Remote Access
VPN
VPN
WAN Interface
Allowing IPsec Remote VPN Clients to Access the Internet
IKE Authentication
Group Name
LAN
Mode Client Pool Range for Client Start IP
Client Internet Disable Access WAN Failover
Name VPNClienttoWAN1 Enable From Any
WAN2
Name VPNClienttoWAN2 Enable From Any
WAN2IP
Translated Any Destination Address Translated Services
Configuring Teleworker VPN Client
Transform Set
Required IPsec VPN Servers
Modes of Operation
Benefits of the Teleworker VPN Client Feature
Client Mode,
Network Extension Mode,
Client Mode
IPsec VPN Network Extension Connection
Network Extension Mode
Click VPN Teleworker VPN Client
General Teleworker VPN Client Settings
Configuring Teleworker VPN Client Group Policies
VPN
VPN
Configuring SSL VPN
Elements of the SSL VPN
SSL Remote User Access
Configuration Tasks to Establish a SSL VPN Tunnel
Installing Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client
Click VPN SSL Remote User Access SSL VPN Configuration
Importing Certificates for User Authentication
Configuring SSL VPN Users
Configuring SSL VPN Gateway
Client Netmask Client Address Pool
VPN
Click VPN SSL Remote User Access SSL VPN Group Policies
Configuring SSL VPN Group Policies
VPN
VPN
Allowing SSL VPN Clients to Access the Internet
Accessing SSL VPN Portal
Sslvpnaddresspool
Enable From Any
Name SSLVPNtoWAN1 Enable From Any
Address Original Destination Any Original Services
Name SSLVPNtoWAN2 Enable From Any
Click VPN L2TP Server
Configuring L2TP Server
Service
Click VPN VPN Passthrough
Configuring VPN Passthrough
Users Active User Sessions
Viewing Active User Sessions
User Management
Configuring Users and User Groups
Default User and User Group
Available Services for User Groups
Configuring Local Users
Preempt Administrators
Click Users Users and Groups
Configuring Local User Groups
User Management
Configuring User Authentication Settings
Using Radius Server for User Authentication
Using Local Database for User Authentication
Click Users User Authentication
Local Database Settings Radius Server Settings
Local Radius Server Settings Database
Click Users User Authentication
Using Ldap for User Authentication
User Management
Using Local Database and Ldap for Authentication
Click Users Radius Servers
Configuring Radius Servers
User Management
Device Management
Viewing Process Status
Viewing System Status
Viewing Resource Utilization
Administration
Configuring Administrator Settings
Example https//209.165.201.18080
Configuring Email Alert Settings
Click Device Management Administration Email Alert
Your Firmware from Cisco.com,
Event Description
CPU Overload Alert
New Firmware Alert
Security License,
Settings page. See Configuring Log Settings,
Log Facilities,
Up/Down Alert
Check Site-to-Site VPN Up/Down Alert in the Enable column
WAN Up/Down Alert
Anti-Virus Alert
Traffic Meter Alert
IPS Alert
Settings. See Configuring Application Control,
Click Device Management Administration Snmp
Configuring Snmp
Click Device Management Backup/Restore
Backing Up and Restoring a Configuration
Device Management
Managing Certificates for Authentication
Click Device Management Certificate Management
Viewing Certificate Status and Details
Certificate Type Details
Exporting Certificates to Your Local PC
Importing Certificates from Your Local PC
Exporting Certificates to a USB Device
Generating New Certificate Signing Requests
Importing Certificates from a USB Device
Importing Signed Certificate for CSR from Your Local PC
Configuring Cisco Services and Support Settings
Configuring Cisco OnPlus
Sending Contents for System Diagnosis
Configuring Remote Support Settings
Click Device Management Date and Time
Configuring System Time
Ping, Traceroute, DNS Lookup, Packet Capture,
Configuring Device Properties
Diagnostic Utilities
Click Device Management Device Properties
Traceroute
Click Device Management Diagnostic Utilities Ping
Click Device Management Diagnostic Utilities Traceroute
Ping
UPnP Discovery, Bonjour Discovery, CDP Discovery,
Device Discovery Protocols
DNS Lookup
Packet Capture
Lldp Discovery,
UPnP Discovery
Click Device Management Discovery Protocols UPnP
Click Device Management Discovery Protocols CDP
Bonjour Discovery
CDP Discovery
Click Device Management Discovery Protocols Bonjour
Click Device Management Discovery Protocols Lldp
Lldp Discovery
View the firmware status. See Viewing Firmware Information,
Firmware Management
Click Device Management Firmware
Using the Secondary Firmware
Firmware Version area, click Switch Firmware
Viewing Firmware Information
Upgrading your Firmware from Cisco.com
Upgrading Firmware from a PC or a USB Device
Firmware Auto Fall Back Mechanism
Using Rescue Mode to Recover the System
Managing Security License
Click Device Management License Management
Checking Security License Status
Installing or Renewing Security License
Viewing Logs
Log Management
Click Device Management Logs View Logs
Click Query
Click Device Management Logs Log Settings
Configuring Log Settings
Notification level
Severity Level Description
Emergency level
Critical level
Device Management
Click Device Management Logs Logs Facilities
Configuring Log Facilities
Click Device Management Reboot/Reset
Rebooting and Resetting the Device
Reset Device area, click Reset to Factory Defaults
Rebooting the Security Appliance
Configuring Schedules
Click Device Management Schedules
Device Management
Device Management
Device Management
Recommended Actions
Internet Connection
Click Status Dashboard
Troubleshooting
Recommended Actions Click Networking WAN WAN Settings
Date and Time
Enable the Daylight Saving Time Adjustment feature
Date and Time
Pinging to Test LAN Connectivity
Testing the LAN Path from Your PC to Your Security Appliance
Testing the LAN Path from Your PC to a Remote Device
ISA570
Feature ISA550
Physical Specifications
Internal Power Supply
Remote Administration
Feature Setting
Device Management
Lldp
Factory Default Settings
Snmp
CDP
User Groups
User Management
Local Users
Network Addressing Modes
User Authentication Methods
Networking
IPv4 or IPv6 Routing
WAN Redundancy Operation Modes
Port-based Access Control
VLANs
Routing
Zones
Vrrp
LAN QOS
Wireless
IKE Policies
Wi-Fi Protected Setup WPS
Rogue AP Detection
Captive Portal
SSL VPN
IPsec Remote Access
Features Setting
Security Services
Firewall
IP MAC Binding
Content Filtering
NAT
MAC Address Filtering
Reports
Service Name Protocol Port Description Start End
Default Service Objects
FTP-DATA TCP
IKE UDP
Rtelnet TCP
Address Name Type IP, IP/Netmask, or IP Range
Default Address Objects
Cisco Small Business
Product Resources
Support
Product Documentation