User’s Handbook
HP Part No Microfiche Part No Edition
Restricted Rights
Certification Warranty
Assistance Safety Notes
General Safety Considerations
If this instrument is used in a manner not specified by
Before switching on this instrument, make sure that the line
Figure O-l. Typical Serial Number Label
Vii
Typeface Conventions
Regulatory Information
Manufacturer’s Declaration
Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer’s Address
Instrument MarkingsA
Xii
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Offices
US Field Operations
Contents
Contents-2 User’s Handbook
HP-IB
Contents-3
Contents-4 User’s
Contents-6
Delta Ma&e+
Contents-6 User’s
Freq Mult Freq Offset
Local
Contents-8 User’s
Marker
Contents-9
Recall
Contents-l User’s
User Defined Menu
ZeroFreq
AM,FM
Contents-13
Contents-14 User’s
Contents-15
Figures
Contents-16
ALC
Tables
What Is In This Chapter
Getting Started Introduction l-1
Equipment Used In Examples
How To Use This Chapter
Getting Started Introduction
Getting Started Basic
Introducing HP 8360 Series Synthesized Sweepers
Getting Started Basic l-3
Display Area
Figure l-2. Display
Entry Area
Getting Started Basic l-5
CW Operation
CW Operation Start/Stop Frequency Sweep
Start/Stop Frequency Sweep
CW Operation and Start/Stop Frequency Sweep
Center Frequency/Span Operation
Center Frequency and Span Operation
Getting Started Basic l-9
Power Level Sweep Time Operation
Power Level Operation
Power Level and Sweep Time Operation
Getting Started Basic l-l
Continuous, Single Manual Sweep Operation
Continuous, Single, and Manual Sweep Operation
Marker Operation
Marker Operation
Saving Recalling an Instrument State
Saving and Recalling an Instrument State
Getting Started Basic l-17
Power Sweep Power Slope Operation
Power Sweep Operation
Getting Started Basic l-19
Figure l-10. Power Sweep and Power Slope Operation
Table l-l. Keys Under Discussion in This Section
Advanced
Getting Started Advanced
Advanced Table l-l Keys Under Discussion in This Section
Externally Leveling the Synthesizer
12 shows the input power versus output voltage
Hint
10 mV Detector Input POWER, dBm
60 dBV
External Leveling Used With the Optional Step Attenuator
Leveling with Power Meters
Getting Started Advanced l-27
Leveling with MM-wave Source Modules
Awplifier
Working with Mixers/Reverse Power Effects
SwrNEsl2ER WlTN OPflON Do1
Ig-y-LO Ll%EL
= +lO dBm
5dBm Measures -8 dBm
Working with Spectrum Analyzers/Reverse Power Effects
Optimizing Synthesizer Performance
Creating and Applying User Flatness Correction Array
Creating a User Flatness Array Automatically, Example
Select Auto Fill Stop a@=, Auto Fill Incr aGHz
Getting Started Advanced l-35
Creating a User Flatness Array, Example
19. Creating a User Flatness Array
Activate List Mode
Example
Synthesizer
Band power sensors are not available from
Enable User Flatness Correction
Figure l-2 1. Scalar System Configuration
On the synthesizer, press Power Cm. Select
Getting Started Advanced l-45
Getting Started Advanced
Using Detector Calibration
Getting Started Advanced
Peaking
Tracking
ALC Bandwidth Selection
Using Step Sweep
Select Step Swp Menu
Creating and Using a Frequency List
Using the Security Features
Getting Started Advanced l-53
Changing the Preset Parameters
User Defined Preset Recalled
Programming
Getting Started Programming l-55
HP-IB General Information
Interconnecting Cables
Programming the Synthesizer
HP-IB Command Statements
Halt Reset
Abort
ABORT7
Remote
Remote
Resume
Local Lockout
Local
Clear
CLEAR7
Getting Started Programming l-59
Reset Control Send
Output
Convert Image Iobuffer Transfer
ENTER719USING
Enter
Convert Image Iobuffer On Timeout SET Timeout Transfer
Getting Started with
Query
Command Examples
Command Mnemonics
Angle Brackets
Response Examples
Program and Response Messages
Forgiving Listening and Precise Talking
Page
Figure l-25. a Simplified Command Tree
Paths Through the Command Tree
Semicolon
Figure l-26. Proper Use of the Colon and Semicolon
Aabbff Aabbgg
Reading the Command Table Getting Started Programming
Subsystem Command Tables
Auto
State Power Level
More About Commands
Program Message Examples
Parameter Types
MAX
Reading Instrument Errors
Repeat
Example Program
Print
Output OStimulus*IDN? Enter OStimulusId$ Print Id$
Getting Started Programming
Details Commands Responses
This Subsection
Program Message Syntax
Getting Started Programming l-79
Subsystem Command Syntax
Common Command Syntax
Response Message Syntax
Getting Started Programming l-81
Discrete
Scpi Data Types
Examples of numeric Parameters 100
Response Data Types
SO is this
Getting Started Programming l-85
Using the Example Programs
Programming Typical Measurements
Use of the Command Tables
Sample Synthesizer Commands
Command Parameters Parameter Type Allowed Values POWer
HP-IB Chec Example lrogram
Local Lockout Demonstration Example Program
Program Comments
Pause
Local Lockout Print
Setting Up a Typical Sweep, Example Program
Hint
Program Comments
Queries, Example Program
Saving and Recalling States, Example Program
Getting Started Programming l-93
Pause
Looping Synchronization Example Program
Using the *WAI Command, Example Program
Program Comments
Using the User Flatness Correction Commands Example Program
Clear Screen
END While
Subend
Fnend
Condition Register
Getting Started Programming l-101
Enable Register
Transition Filter
Event Register
An Example Sequence
Case a Case B Case C Case D Condition N-L TlT2T3T4T5
Overview
04 Getting Started Programming
Getting Started Programming l-1
Figure l-36. Inside the Idle State
Getting Started Programming l-107
Page
Init Configuration
Common Trigger Configurations
Getting Started Programming l-109
Trig Configuration
10 Getting Started Programming
Description Triggering in the HP Series Synthesizers
Getting Started Programming l-l11
Advanced Trigger Configurations
Trigger Keyword Definitions
BUS
12 Getting Started Programming
ODELay
IMMediate
SOURce
HP Basic
USA
Related Documents
14 Getting Started Programming
Operating and Programming Reference
Operating and Programming Reference
Address
Function Group Menu Map Description
Programming Codes See Also
Function Group System Menu Map
Scpi NONE, see the individual softkeys listed
Function Group ALC Menu Map
ALC System Overview
Page
Operating and Programming Reference User’s
Operating and Programming Reference A-7
Figure A-2. Typical External Leveling Hookup
Operating and Programming Reference A-9
ALC Bandwidth Select Auto
See Also ALC, ALC BW Menu
ALC Bandwidth Select Low
See Also ALC
Programming Codes Scpi
See Also RECALL,SAVE
Function Group Menu Map Description Programming Codes
AM BW Cal Once
Function Group User CAL Menu Map
AM Menu
Function Group MOD Menu Map
AM On/OffIO dBfV
MOD Modulation
AM On/Off Ext
Function Group Ilvloo Menu Map
AM On/Off In-t
Function Group Marker Menu Map
LALC, CONNECTORS, Iniod
AM Type 10 dB/V
Programming Codes
None
RQS
Arrow Keys
Arrow Keys
Scpi Status Register
Entry None
EiEi
User Defined None
TOO Many Correction PTS Requested
Menu Map 2,s
TOO Many List PTS Requested
Auto Fill #Fts
Auto Fill Start
Function Group POWER, User CAL Menu Map 5,9
Programming Codes Scpi CALibrationTRACk
Blank Disp
See Also SPAN,m,STOP
Frequency None
Service
See Also Fault Menu
See Also w
# of Times to Clear Memory
SHMZ18HZ Shkzohz
Function Group P O W E R Menu Map
BNC Connectors
Programming Codes Scpi NONE, see Fltness Menu
Operating and Programming Reference C-5
Connectors
Figure C-l. Auxiliary Interface Connector
Out
Table C-l. Pin Description of the Auxiliary Interface
Operating and Programming Reference C-9
MTA
Figure C-3. Interface Signals of the Source Module Connector
Operating and Programming Reference C-l
Sweep
Copy List
CorPair Disable
W E R
See Also Aalc
Coupling Factor
Frequency
CW/CF Coupled
$iEqICW
Dblr Amp Menu
Programming Codes Scpi None
Delay Menu
Deep AM
Function Group Modulation Menu Map
Ammode Deep
Delete Menu
Delete All
Menu Map 2,5
Menu Map ‘4
Delete Current
Delete Undef
Delta Marker
Delta Mkr Ref
Disp Status
Function Group System Menu Map k
Marker
Disp Status
Table D-l. Mnemonics used to Indicate Status
Function Group Power Menu Map
Daubler Amp Mode Auto
Table D-l Mnemonics used to Indicate Status
Doubler Amp Mode Off
See Also Dblr hnp Menu
Dwell Coupled
Function Group Frequency Menu Map
Enter Corr
Adrs
System
Enter Freq
Enter List Dwell
Programming Codes Scpi NONE, see Fitness Menu
Programming Codes SCPINONE, see Fltness Menu
Enter List Freq
Description Programming Codes See Also
Programming Codes Scpi NONE, see List Menu
See Also List Menu
Entry Keys
Enter List Offset
Ext Det Cal
Fault Menu
Function Group Service Menu Map
Operating and Programming Reference User’s
Fault Info
Programming Codes SCPISee Fault Menu
Pwron Fail
Calco Fail
Calyo Fail
TMR
Cnflct
Fail Search
Fltness lbnu
Fitness Menu
Frequency MHZ 10 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 0
Start stop # Pts Correction Undefined More Incr
Theory of operation
Operating and Programming Reference F-9
Fitness EIenu
FM Coupling 1OOkHz
FM Coupling DC
FM Menu
FM adaff
MOD, Connectors
FM On/Off AC
FM On/Off DC
Modulation
See Also MOD,CONNECTORS EN On/Off Ext
Function Group &j@ Menu Map
Freq Cal Menu
FM On/Off Int
Function Group IhnoD Menu Map
Freq Follow
Frequency Menu
Freq Mult
Operating ahd Programming Reference
Freq Offset
Freq Offset
FulliTsr Cal
Global Dwell
Global Offset
HP-IB Menu
HP-IB Address
Ciil
See Also CONNECTORS, HP-IB Getting Started Programming
Internal AM Depth
Unitam Dbpct
Internal AM Rate
Internal AM Waveform Noise
Internal AM Waveform Ramp
Internal AM Waveform Sine
Internal AM Waveform Square
Internal AM Waveform Triangle
Internal FM Deviation
Internal FM Rate
Noise
Ramp
Function Group
Menu Map Description
Internal FM Waveform Sine
Internal FM Waveform Square
Internal FM Waveform Triangle
Internal Menu
Internal Pulse Generator Period
Function Group Iniod Menu Map
Internal Pulse Generator Rate
Internal Pulse Generator Width
Function Group Imod Menu Map
Function Group IlvloD Menu Map
Internal Pulse Mode Gate
Internal Pulse Mode Auto
Function Group MOq Menu Map
Internal Pulse Mode Trigger
Invert Input
Leveling Mode ALCof f
Leveling Mode Normal
Leveling Mode Search
Leveling Point ExtDet
Leveling Point Intrnl
Leveling Point Module
ALC, Connectors
Leveling Point PwrMtr
List Menu
Programming Codes See Also
Global Duel1
Operating and Programming Reference L-7
List Mode Pt Trig Auto
List Mode Pt Trig Bus
List Mode Pt Trig Ext
Instrument State None
Manual Sweep
Ml--M2 Sweep
Function Group Sweep Menu Map
KimaL Suesp
Function Group Menu Select Menu Map
Amp1 Markers Center=Marker
Marker Ml
Marker M2
Marker M3
Marker M5
Marker M4
See Also
Measure Corr All
Markers All Off
Programming Codes Scpi MARKerAOFF
Measure Corr Current
Measure Corr Undef
Meter Adrs
Meter On/Off AM
Meter On/Off FM
Programming Codes Scpi MEASureFM?
ModOut On/Off AM
Modulation
ModOut On/Off FM
Figure M-l. ALC Block Diagram
Amplitude Modulation
User’s Handbook Amplitude Modulation
Operating and Programming Reference M-15
Figure M-2. Power Accuracy Over the AM Dynamic Range
User’s Handbook FM Modulation
FM Modulation
Operating and Programming Reference M-17
Figure M-3. FM Deviation and Rate Limits
Pulse Modulation
Pulse Modulation
Figure M-4. ALC Block Diagram
Operating and Programming Reference M-21
Figure M-8. Video Feedthrough
Module Menu
Module Select Front
Module Select Auto
Module Select None
Monitor Menu
Mudule Select Rear
More n/m
ALL Function Groups ALL Menu Maps
Mtr Meas Menu
Peak RF Always
Power None
Peak RF Once
PowerdBm INT
INT
See Also ALC, CONNECTORS, Det Gal Menu, Fltness ON/OFF
Power iZiG
Power Offset
Power Slope
Power Sweep
Scpi SYSTemPRESetEXECute
Preset Mode Factory
Preset Mode User
Printer Adrs
Menu Select None
Figure P-l. How Prior Works
Programming Language Ciil
Programming Language Scpi
Pulse Delay Normal
Pt Trig Penn
Pulse Delay Trigd
Function Group Menu Map Description IhnoD1
Pulse Menu
Function Group MOD
Pulse an/Off Ext
Pulse h/Off Extrnl
Pulse On/Off Intrnl
Pulse On/Off Scalar
MOD
Pulse Period
Pulse Rate
Pulse Rise Time klto
Pulse Rise Time Fast
Pulse Rise Time SlQW
Pulse Width
Pwr Mtr Range
Function Group Ialc Menu Map
Ref Osc Menu
Rotary Knob
Programming Codes Scpi *SAV num
Save User Preset
Save Lock
Mode MODE? Span
User’s Handbook Scpi Conformance Information
Auto AUTO?
Operating and Programming Reference S-3
Mode MODE?
SPAN?
Stop STOP?
Aoff
Step STEP? Time Auto AUTO?
Operating and Programming Reference S-5
TIME?
Gpib
Abus
ABUS?
Operating and Programming Reference S-7
Mode MODE? Type TYPE?
TINT?
A4VCO
Agvco
Zero Type
Save Zero ALL
Code
Span Auto AUTO?
Step Auto AUTO?
List
Msib
Slew SLEW? Auto AUTO?
Xfer
KEY
Save Type
Ieee 488.2 Common Commands
Introduction
Scpi Command Summary
Listmodeauto
Operating and Programming Reference S-17
Scpi Command Summary
Table S-l. HP 8360 Scpi Command Summary
Parameter Type1 Allowed Values
Page
Operating and Programming Reference S-21
Span
Table S-l. HP 8360 SCPl Command Summary
Aoff
Gate
Operating and Programming Reference S-25
Xfer
Operating and Programming Reference S-27
Sets and queries the automatic modulator calibration switch
User
Operating and Programming Reference S-29
OFF
Operating and Programming Reference S-31
Returns the following information
DIAGnosticsTESTCONTinue
Selects and queries the raw data logging ON/OFF switch. Both
Frequency Subsystem
No error is generated
Operating and Programming Reference S-37
Page
LISTMODE?
Operating and Programming Reference User’s
BNC
Power Subsystem
MODulat ion STATe?
POWerATTenuationAUTO ONlOFFlllO POWerATTenuationAUTO?
Operating and Programming Reference S-43
Sets and queries the RF slope setting dB per Hz
Step
Operating and Programming Reference S-45
*RST value is 500 kHz
Pulse Subsystem
PULSeFREQuency? MAXimum IMINimum
After STATusPRESet, all used bits are set, to 1’s
Sweep Subsystem
Operating and Programming Reference S-49
SWEepGENeration STEPpedlANALog SWEepGENeration?
SWEep MANual RELat ive mm SWEep MANual RELat ive ?
Operating and Programming Reference S-51
Attempting to set a sweep time faster than allowed
23, Numeric Overflow YOU PUT in a Number TOO BIG
Page
Operating and Programming Reference S-55
Scpi Status Register Structure
Scpi Status Register Structure
Security Menu
Save Lock
Set Atten
Software Rev
Cont
Span
See Also CENTER,ETxq,STOP
Page
Start Sweep Trigger Bus
Start Sweep Trigger Auto
See Also CONT, -1, Sweep Menu
Start Sweep Trigger Ext
Step Control Master
See Also Step Control Slave, Step Swp Menu
Step Control Slave
Step Point3
Step Dwell
Function Group Frequency
Step Size
Step Swp Menu
Dwell Coupled Step Control Master
Trig Auto
Trig Bus
Stop
Step Swp Pt Trig Ext
Sweep @ii
Manual Sweep
Sweep Mode List
Sweep Mode Ramp
Sweep Mode Step
See Also E, Manual Sweep,SINGLE, Step Swp Menu
Swp Span Cal Once
Swp Span Cal Always
See Also Freq Cal Menu
Sweep
SwpTime Auto
System
Operating and Programming Reference S-77
UsrMenu Clear
MHz Freq Std Auto
MHz Freq Std Extml
MHz Freq Std Intrnl
MHz Freq Std None
See Also Ref Osc Menu
See Also Ref #SC Menu
TrigOut Delay
Tracking Menu
Programming Codes Scpi TRIGgerODELay numtime suffix
Unlock Info
Uncoupl Atten
Status Messages
Up/Down Power
Up/b Size CV
Up/Dn Size Swept
User Defined Giij
UsrKey Clear
UsrMenu Clear
ASSIGN, User Defined e, UsrKey Clear
Waveform Menu
Zero Freq
Function Group Lmod Menu Map
See Also m,SPAN
Zoom
2Operating and Programming Reference
Introduction Front Panel Error Messages AlDhabetical.Order
Error Messages 2a-1
2a-2 Error Messages
Invalid Language on Rear Panel Switch
Error Messages 2a-3
2a-4Error Messages
Scpi Error Messages Numerical Order
Error Messages 2a-5
Universal Scpi Error Messages
Error Messages From -499 To
Error Messages From -399 To
Error Messages From -299 To
Error Messages From 199 to
Error Messages 2a-7
2a-8 Error Messages
Menu Maps 2b-1
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Specifications
Specifications
Range Resolution
Frequency Bands for CW signals
Frequency
Frequency Modes CW and Manual Sweep
Synthesized List Mode Accuracy Same as time base
Synthesized Step Sweep
RF Output
Output Power
204
Frequency GHz
Accuracy dB4
Flatness dB
Analog Power Sweep External Leveling Source Match
N g e
Spurious Signals
Spectral Purity
2c-8
Residual FM RMS, 50 Hz to 15 kHz bandwidth
Single-Sideband Phase Noise DBc/Hz
Offset from Carrier
Pulse
2010
Internal Pulse Generator
Simultaneous Modulations
2c-12
Internal Modulation Generator Option
Specifications 2013
Pulse Modulation Meter
Environmental
General
~14
Inputs & Outputs
MHz Reference Input
MHz Reference Output
Sweep Output
Stop Sweep Input/Output
Options
Option 008 1 Hz Frequency Resolution
Option W30 Two Years Additional Return-To-HP Service
Option 700 Mate System Compatibility
Option 806 Rack Slide Kit
Installation
Initial Inspection
Options Available
Preparation for Use
Line Voltage and Fuse Selection
Power Cable
AC Power Cables Available Specifications
Language Selection Remember
Option not Installed
Language HP-IB Addresses
HP-IB Address Selection
Factory-Set HP-IB Addresses
How to View or Change an HP-IB address from the Front Panel
How to Prevent a Front Panel Change to an HP-IB Address
Operating Environment
Installation Procedure
Rack Mount Slide Kit Contents
Chassis Kits
Removing the Side StraPs and Feet
\NSTALLATION
Chassis Slide Kit
Option
Kit
Rack Mount Flanges for Synthesizers with Handles Removed
Installation
Rack Mount Flanges for Synthesizers with Handles Attached
Storage Shipment
Environment
Package the Synthesizer for Shipment
Converting HP 6340141 Systems to HP 8360 Series Systems
Instrument Preset Conditions for the HP 6360/8340/8341
Manual Operation
Compatibility
Front Panel Operation
System Connections
HP 8510 Network Analyzer
HP 83550 Series Millimeter-wave Source Modules
HP 8757C/E Scalar Network Analyzer
HP 89708 Noise Figure Meter
Remote Operation
Converting from Network Analyzer Language to Scpi
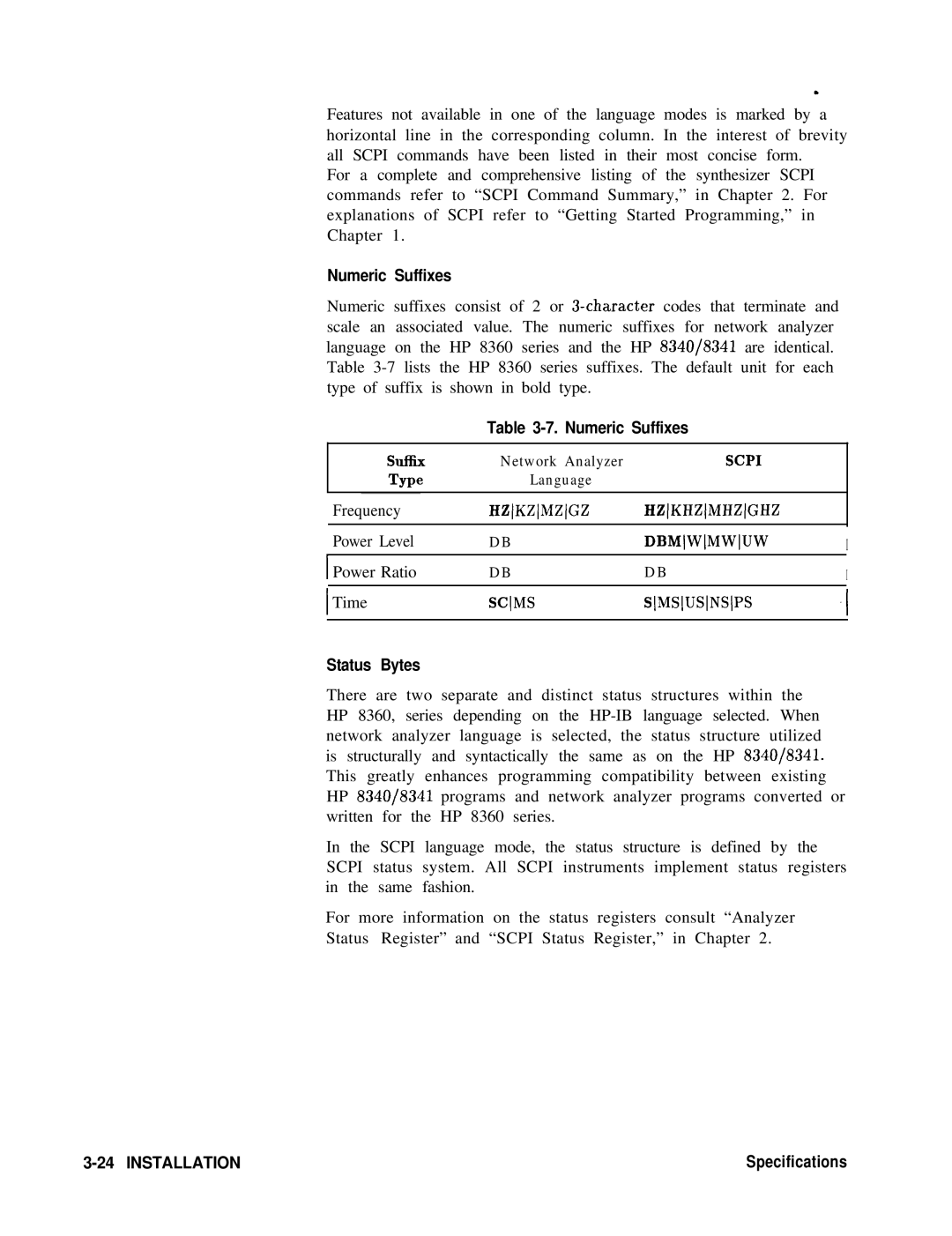
Numeric Suffixes
Numeric Suffixes Sllsx
Hzkhzmhzghz
Scms
Programming Language Comparison
ALC
Network Analyzer Language
Instrument State
Power Set power level
Description Sweep
Service Information
Operator’s Checks
Operator’s Check/Routine Maintenance
Local Operator’s Check
Main Check 1. Press Service
Routine Maintenance
Fuse Part Numbers
How to Clean the Fan Filter
Removing the Fan Filter Specifications
How to Clean the Cabinet How to Clean the Display Filter
Instrument History
Page
Change B
Change B
Change B User’s
On/Off Ratio
Internal Pulse Generator
Change a
Change a S-7
Change a User’s
IO MHz to 26.5 GHz
Range
Band
Change a
RF Output
Accuracy dBa
Flatness dB
HP836SOA
Outputkeq
Ty&al HP K5623A Harmonics
OWliequencies
Modulation
Pulse HP 8363o~
AIClevelsnoWcanbcof&etusingstepattektor
Internal Modulation Option
Weight & Dimensions Net weight 27 kg 60 lb
ExmJa.lALcIllput
VoWGHz Output
AuxmryJJltelface
Puke viiii ootptlt @ption 002 only
Optioll9l3RackFhgeKit
Index
Index-l
Index-2
Index-3
BUS
Index-4
Index-5
Index-6
Index-7
Index-6
Index-9
Index-10
Index
GP-IB
Index-12
Ieee
Index-13
Key
Index-14
Index-15
Index-16
Index-17
Index-16
Index-19
Index-20
Index-2
Index-22
SRQ
Index-23
Index-24
Index-25
Index-26
Index-27