Contents
HP E1429A/B Digitizer User’s Manual Contents
ARM
Data
Period Value Table
ESR?
Contents HP E1429A/B Digitizer User’s Manual
HP E1429A/B Digitizer User’s Manual Contents
HP E1429A/B 20 MSa/s 2-Channel Digitizer User’s Manual
Documentation History
According to ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN
March 1
HP E1429A/B 20 MSa/s 2-Channel Digitizer User’s Manual
HP E1429A/B Features and VXIbus Configuration
Chapter Contents
Getting Started Chapter
HP E1429A/B VXIbus Configuration
HP E1429A/B VXIbus Configuration
Assigning the Digitizer to a Commander
Preparation for Use
Digitizer Logical Address
HP E1429A/B Logical Address Switch Location
Installing the Digitizer
Digitizer Bus Request Level
Bus Request Level Guidelines
Addressing the Digitizer over HP-IB
Addressing the Digitizer using an Embedded Controller
Sending the *IDN? Command
Introductory Programs
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1429A,0,A.02.00
TST?
IOOUTPUTSADDR, *IDN?
Repeat Output 70905SYSTERR?
SLFTST.C
IOOUTPUTSADDR, *TST?
Resetting Clearing Digitizer
IOOUTPUTSADDR, SYSTERR?
IOOUTPUTSADDR, DIAGTEST?
IOOUTPUTSADDR, *RST*CLS
Subend
LRN?
Querying Digitizer Configuration
Integer
Repeat
LRN.C
Chapter Getting Started
TRIGSTARTIM1 10E-6
Instrument and Programming Languages
OUTPEXT1STAT Ontrigsour EXT1OUTPEXT1STAT OFF
Language Programs
Microsoft QuickC clhpib.lib
Command Line Compiling
∙ Microsoft QuickC
∙ Turbo C++
CLHPIB.LIB
Compiling in the Integrated Environment
Other subsystems
Introduction to Programming
Using the MEASure CONFigure Commands
Port
HP E1429A Programming Sequence
Programming Sequence
Using MEASure
Configuring the Channels
How to Make Measurements
MEAS.C
Can be used to set the desired number of pre-arm readings
SENS1SWEOFFSPOIN
Taking Readings After Using CONFigure
CONF.C
IOOUTPUTSADDR, FETC1?
Querying Command Settings
QUERY.C
Enable Intr
ERRORCHK.C
Abort
Digitizer Command Module Deadlock
Where to go Next
Programming Language
Using the Digitizer
INPUT.C
Configuring the Digitizer Input
ARMCNT.C
Taking a Burst of Readings
ARMLEVEL.C
Level Arming
Pre- and Post-Arm Readings
PREPOST.C
ARMSOUR1 EXT
SAMPLE.C
Specifying a Sample Rate
ARMSOUR1 IMM
Trigsour TIM
DUALSAMP.C
Dual Rate Sampling
ARMSLOP1 POS
Senssweoffspoin
Using Multiple Digitizers
MULTAD.C
OUTPTTLT0STAT on
OUTPTTLT0IMM
FETC2?
PACKED.C
Using the Packed Data Format
Diagchanlab
Form Pack
For i = 0 i 20 i++
IOOUTPUTSADDR, SYSTERR?
VMEREAL.C
VME Bus Data Transfers
Trigstarsour VME
Vinsconfvmemode GEN
Vinsconfvmefeed ’CONVCHAN1’
On Next
Using the Digitizer Chapter
VMESEG1.C
Armstarcoun
Armstarsour IMM
On Next
IOOUTPUTSADDR, *RST*CLS
IOOUTPUTSADDR, SYSTERR?
DOS
VME Bus Data Transfers Using an Embedded Controller
On Next
Using the Digitizer Chapter
On Next
On Next
INST.H
#include Files
Inst
INST.CPP
On Next
Chapter Using the Digitizer
E1429.CPP
E1429.H
Local Bus Data Transfers
Vinslbusmode GEN
Vinslbusres
Vinslbusfeed ’CONVBOTH’
Formdata Pack
IOOUTPUTSADDR, Init
IOOUTPUTSADDRMEM, Init
Using the Digitizer Chapter
Chapter Using the Digitizer
On Next
Vinslbusmode APP
Vinslbusfeed ’MEMCHAN1’
IOOUTPUTSADDRA, Init
IOOUTPUTSADDRG, Init
IOOUTPUTSADDRG, *OPC?
On Next
Using the Digitizer Chapter
On Next
Vinslbusfeed ’CONVCHAN1’
Armstarsour TTLT0
Vinslbusmode INS
OUTPTTLT0FEED ’READY’
IOOUTPUTSADDRG, Init
IOOUTPUTSADDRG, *OPC?,5
IOOUTPUTSADDRI, Init
Using the Digitizer Chapter
Chapter Using the Digitizer
Using the Digitizer Chapter
STATUS.C
Using the Digitizer Status Registers
Using the Digitizer Chapter
Understanding the Digitizer
HP E1429 Digitizer Block Diagram
Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer Chapter
Message and Register Interfaces
Digitizer Command Paths
Digitizer Input Section
Scpi Command Control
SENSechan VOLTage Range range
Setting the Input Impedance
Enabling the 10 MHz Input Filter
Inverting and Non-inverting Differential Input Ports
Digitizer Attenuators
Setting the Signal Range
Sensvoltrang
Using the Single-Ended Input 1V Range
Arming and Triggering
HP E1429 Digitizer State Diagram
ARM-TRIG State Diagram
HP E1429 Digitizer Arming and Triggering
ARM STARtSEQuence1
Set positive or negative transition
Arm Window Boundaries
Arm Level Range
ARM Synchronization Signals
OUTPutEXTernal1FEED source
Enabling the Synchronization Signal
Routing the Signal to a Source
Offset
Triggering Digitizer
TRIGgerSTARtTIMer1 period
Chapter Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer
Digitizer Reference Clock
Source
Specifying the External Reference Frequency
TRIGgerSTARtCOUNt count SENSechan SWEepPOINts count
Trigger Synchronization Signals
OUTPutEXTernal1FEED source
Routing the Signal to a Source
Data Flow, Storage, and Conversions
Analog-to-Digital Converter
HP E1429 Digitizer Data Flow
HP E1429 Digitizer Reading Storage
10. Memory Segments with Pre and Post-arm Readings
MEMory Subsystem
Digitizer Data Formats
Determining the Battery Charge
Definite Length Arbitrary Block Header
Packed Reading Conversions
HP Basic Example
Removing the Arbitrary Block Header
Language Example 16-bit readings
Readings
READ?
11. Retrieving Readings from Digitizer Memory
Retrieving Readings Using FETCh?
Retrieving Readings Using
READ?
FETChing Readings from Memory
Separating Pre- and Post-Arm Readings
Determining Number of Readings FETChed
Using DIAGnosticUPLoad SADDress?
DIAGnostic Subsystem
Memory Management
Locating Unsegmented Readings
Locating Segmented Readings
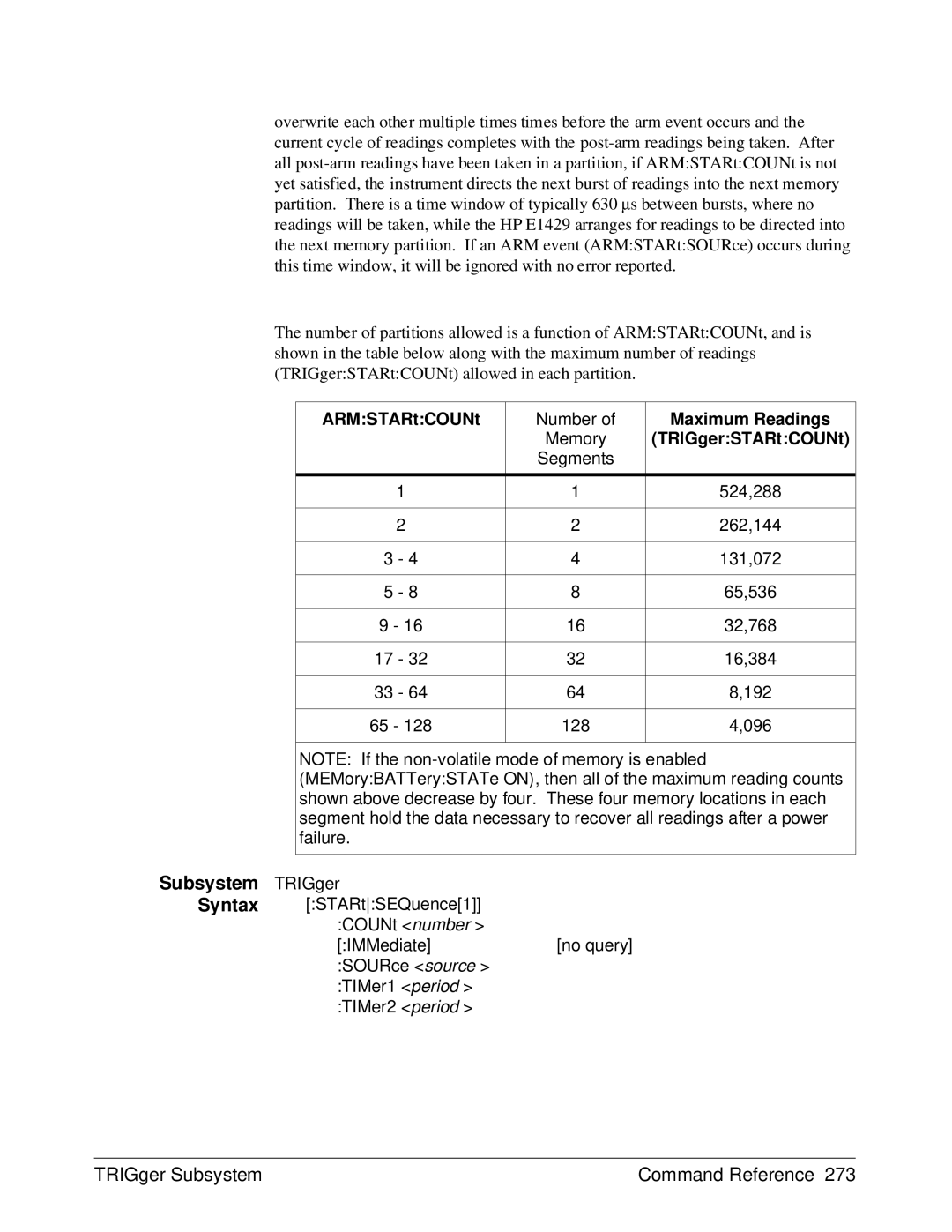
ARMSTARtCOUNt
Maximum Readings
Ending segment address = segmentnumber * 65536
Therefore, the DIAGnosticFETCh? command would be executed as
Locating the Data Register
12. Digitizer Registers in A16 and A24 Address Space
Base Address
Execute the following HP E1406 Command Module command
On Next
Data Register Offset
VINStrument Subsystem
VME
DATA?
Setting the VME bus Data Source
Segmented Reading Transfers
Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer Chapter
Multiple VME Bus Data Transfers
Local Bus Description
14. Local Bus Signal Line Definitions
15. HP E1429B Local Bus Data Transfer Protocol
How Data is Transferred
Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer Chapter
Local Bus Transfer Configurations
Digitizer Local Bus Commands
Lbus
Send
Multiple Digitizers and Serial Transfers
EOF EOB D3 D3 D3
EOF EOB D1 D1 D1
Digitizer Configuration Restrictions
Setting the Local Bus Transfer Mode
Setting the Local Bus Data Source
Multiple Local Bus Data Transfers
Status Subsystem Commands
Digitizer Status Registers
Status System Registers
16. HP E1429 Status Groups and Associated Registers
Questionable Signal Status Group
Condition Register
Reading the Condition Register
Operation Status Group
Enable Register
STATusOPERationCONDition?
Standard Event Status Register
Standard Event Status Group
PON
CME EXE DDE QYE
Reading the Standard Event Status Register
Standard Event Status Enable Register
ESR?
ESE?
Status Byte Status Group
Status Byte Register
Oper RQS ESB MAV Ques
Service Request Enable Register
Presetting the Enable Register and Transition Filter
Reading the Status Byte Register
STB? Spoll
Saving Digitizer Configurations
Synchronizing the Digitizer
OPC OPC? WAI
RST
How to Save and Recall a Configuration
Understanding the HP E1429 Digitizer Chapter
Command Reference
Common Command Format
Command Types
Abbreviated Commands
Scpi Command Format
ARM
Armlevneg
Scpi Command Parameters
Implied Optional Keywords Variable Command Syntax
Parameter Types Explanations, Examples
OUTPECLT0FEED ’EXT’ OUTPECLT0FEED \EXT\
Querying Parameter Settings
Scpi Command Execution
Optional Parameters
Definite length block
Executable When Initiated Commands
MIN and MAX Parameters in Coupled Commands
Armcoun Trigcoun MAX
Scpi Command Reference
Linking Ieee 488.2 Common Commands
Linking Multiple Scpi Commands
ABORt
∙ Executable when initiated Yes ∙ Coupled Command No
ABORt
Example Aborting a measurement
ARM
STARtCOUNt
ARMSTARtCOUNt
Syntax
Subsystem
Parameters
Parameter Range Default Name Type Values
ARMSTARtCOUNt
STARtDELay
ARMSTARtDELay
Parameter Range Default Name Type Values
MINimumMAXimum
ARMSTARtIMMediate
Example Setting the arming delay
STARtIMMediate
∙ *RST Condition none
STARtLEVelchanNEGative voltage
ARMSTARtLEVelchanNEGative voltage
Example Arming for measurement
Comments ∙ Executable while initiated No
STARtLEVelchanPOSitive voltage
ARMSTARtLEVelchanPOSitive voltage
STARtSLOPen
ARMSTARtSLOPen
Example Setting the arm slope
ARMSTARtSOURcen
Example Setting two arm start sources
∙ Related Commands ARMSTARtSLOPen , ARMSTARtLEVelchan
COUNt?
CALibrationchan
Subsystem Syntax
Numeric None
Data
CALibrationchanDATA
Assign @X to 70905FORMAT OFF
Comments ∙ Executable when initiated No ∙ Coupled Command No
DELay
CALibrationchanDELay
Gain
CALibrationchanGAIN
Seconds
Confarrvolt 100,4.8,DEF,@1
∙ *RST Condition none Example Performing a gain calibration
CALibrationchanSECureCODE
CALibrationchanSECureSTATe
CALibrationchan SECureSTATe mode ,code enables or disables
CALibrationchanSTORe
CALibrationchanSTOReAUTO
CALibrationchan STOReAUTO mode selects whether or not
VALue
Example Turn automatic storage of calibration values off
∙ Related commands CALibrationGAIN
CALibrationchanVALue
Numeric 101.80 to Volts
Example Setting the calibration value
CALibrationchanZERO
Zero
CAL1ZERO DEF,DEF,ALL
CONFigurechan
CONFigurechanARRayVOLTageDC size,expected
ARRayVOLTageDC
CONFigurechanARRayVOLTageDC
Range Volts Value
Maximum Voltage Resolution
CONFARRayVOLT 20,1.5,@3
CALibrationchan CONVerge?
DIAGnostic
DIAGnosticCALibrationchan GAINSENSitivity?
CALibrationchan ZEROSENSitivity?
CHANnelchan LABel
DIAGnosticFETCh?
∙ Coupled Command No ∙ Related Commands ABORt, FETCh?
Example 1 Tagging the data with channel number
Example 2 Reading back PACKed data HP Basic program
DIAGnosticMEMorychanFILL
DIAGnosticMEMorychan Fill numsegments, count sets up
MEMorychanADDResses?
DIAGnosticPEEK?
PEEK?
Thru Ffffff None
Example Examining the setting of the traffic register
DIAGnosticPOKE
Example Changing the contents of the traffic register
Poke
SGET?
DIAGnosticSGET?
Sput
TEST?
FETChchan
Command Reference FETChchan Subsystem
FETChchan Subsystem Command Reference
FETC1COUN?
FETChchanCOUNt?
∙ *RST Condition none Example Recovering readings in memory
FETChchanRECover?
Subsystem FORMat
FORMat
∙ Related Commands READ?, FETCh?
Example 1 Setting the data format to 64 bit reals
FORMatDATA
IMMediate
INITiate
Example Placing the HP E1429A in the wait-for-arm state
INITiateIMMediate
Subsystem INPutport
INPutport
INPutportFILTerLPASsSTATe
INPutportFILTerLPASsSTATe mode enables or disables
IMPedance
Example Enabling the 10 MHz low-pass filter
Example Setting 75 Ω input impedance
INPutportSTATe
STATe
Example Disabling input port
MEASurechan
ARRayVOLTageDC?
MEASurechanARRayVOLTageDC size,expected
MEASurechanARRayVOLTageDC?
Maximum Voltage Resolution
MEAS1ARRayVOLT? 20,1.5,@3
Example Enable memory to be non-volatile
BATTerySTATe
MEMory
∙ *RST Condition not affected
∙ *RST Condition none Example Check the battery charge
MEMoryBATTeryCHARge?
ECLTrgnFEED
OUTPut
OUTPutECLTrgnSTATe
Example Setting the ECLTrg0 sync pulse source
ECLTrgnSTATe
∙ *RST Condition
OUTPutEXTernal1FEED
Parameter Range Default Name Type Values Units
EXTernal1FEED
Boolean
TRIGgerSTARtSEQuence1
ARMSTARtSEQuence1 None RFTRigger SENSe12ROSCillator
OUTPutEXTernal1STATe
Example Setting the sync pulse source
EXTernal1STATe
TTLTrgnFEED
Numeric Through None
OUTPutTTLTrgnFEED
ARMSTARtSEQuence1 None
Example Enabling sync pulse for READy on TTLTrg5
Example Enabling sync pulse output to TTLTRG0* and TTLTRG5
OUTPutTTLTrgnSTATe
READchan
READchan Subsystem Command Reference
Command Reference READchan Subsystem
SENSe
SENSechanFUNCtion
SENSechanFUNCtion
Example Selecting the single ended input on channel
SENSechanFUNCtion SENSechanFUNCtion
EXTernalFREQuency
SENSechanROSCillator
SOURce
SENSechanROSCillatorSOURce
Example Setting the Reference Oscillator Source
SENSechan SWEep
SENSechan SWEepOFFSetPOINts count
OFFSetPOINts count
Number Maximum Number Memory Segments
Example Setting 50 pre-arm readings on channel 1, input port
MINimum selects 1 reading
SENSechan SWEepPOINts count
Example Setting 500 readings
SENSechanVOLTageDC
RANGe
SENSechan VOLTageDCRANGe range selects the range for
Range Measurement Resolution Allowable Setting Volts Ports
Comments ∙ Executable when initiated Yes
SENSechanVOLTageDC RANGe
SENSechanVOLTageDC RESolution?
RESolution?
Example Selecting the 102.35 Volt range on channel
Operation Status Register
STATus
Subsystem Syntax Questionable Signal Status Register
STATusOPCINITiate
OPCINITiate
OPERationQUEStionableENABle
STATusOPERationQUEStionableCONDition?
OPERationQUEStionableCONDition?
STATusOPERationQUEStionableEVENt?
Example Setting the Operation register enable mask
OPERationQUEStionableEVENt?
Through +32767 None Non-decimal Numeric
OPERationQUEStionablePTRansition
STATusOPERationQUEStionableNTRansition
PRESet
STATusPRESet
Example Reading the error queue
ERRor?
SYSTem
VERSion?
TRIGger
Command Reference TRIGger Subsystem
TRIGger Subsystem Command Reference
TRIGgerSTARtCOUNt
Example Taking 20 readings 8 pre-arm and 12 post-arm
STARtSOURce
TRIGgerSTARtIMMediate
Bushold
TRIGgerSTARtSOURce
STARtTIMer1
TRIGgerSTARtTIMer1
Example Setting the start trigger source
Reference period to
TRIGgerSTARtTIMer1
Period Value Table
STARtTIMer2
∙ *RST Condition 5.0E-8 seconds
Multiple Period
TRIGgerSTARtTIMer2
∙ *RST Condition 1.0E-7 seconds
Local Bus transfers
VINStrument
Data voltagelist
VME VXI data transfer Bus transfers
VINStrument CONFigureLBUSFEED
CONFigureLBUSMEMoryINITiate
VINStrumentCONFigureLBUSMEMoryINITiate
CONFigureLBUSMODE
VINStrumentCONFigureLBUSMODE
CONFigureLBUSRESet
VINStrumentCONFigureLBUSRESet
Example Setting the Local Bus operation mode
APPendGENerate None INSertOFF PIPeline
CONFigureLBUSSENDPOINts
VINStrumentCONFigureLBUSSENDPOINts
VINStrumentCONFigureLBUSSENDPOINtsAUTO
CONFigureLBUSSENDPOINtsAUTO
Boolean On OFF None
VINStrumentCONFigureTESTDATA
CONFigureTESTDATA
VINStrumentCONFigureTESTDATA voltagelist configures
∙ *RST Condition none Example Testing Local Bus operation
VINStrumentCONFigureVMEFEED
CONFigureVMEMEMoryINITiate
VINStrumentCONFigureVMEMEMoryINITiate
CONFigureVMEMODE
VINStrumentCONFigureVMEMODE
CONFigureVMESENDADDRessDATA?
VINStrumentCONFigureVMESENDADDRessDATA?
Example Setting the VXIbus data transfer bus operation mode
GENerateOFF None
HEWLETT-PACKARD Virtual INSTRUMENT,ANY ATOD,0,A.01.00
VINStrumentIDENtity?
Category Command Title
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
∙ Executable when initiated Yes
CLS
DMC
EMC and *EMC?
ESE and *ESE?
Example Define macro to start measurement
ESR?
Example Enable all error events
GMC?
String
LMC?
IDN?
Example Query macro definition
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1429,0,A.01.00
OPC
LRN?
OPC?
PMC
PUD and *PUD?
Block Through 63 characters None Data String
RCL
RST
RMC
SRE and *SRE?
SAV
TRG
STB?
WAI
TST?
Command Quick Reference Chapter
Chapter Command Quick Reference
Unmask
VINStrument
Scpi Conformance Information
Scpi Confirmed Commands
Chapter Scpi Conformance Information
Scpi Conformance Information Chapter
Appendix Contents
Specifications
To VME Bus
Read-Out
To Local Bus E1429B only
Number of Partitions
Total Readings per Partition
Amplitude Characteristics Signal Conditioning
Output Formats
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Gain and Offset 4.3.1, note
Filtering
Single-ended inputs Connector BNC
Converter Supplemental Characteristics
Word Error Rate 4.15 qualified error level word error rate
Integral Nonlinearity 4.4.3, Note
Analog Bandwidth 4.6.1 filter off
Single-ended inputs, supplemental characteristics
Effective bits on different ranges
Crosstalk between channels
Appendix a Specifications
Effective bits, relative to 1V single-ended range
Differential Inputs, supplemental characteristics
Frequency Sample Rate Characteristics Internal Timer
Trigger Sample Clock Subsystem
Crosstalk
Timebase and Trigger additional supplemental characteristics
Bus Access and Connectors
General Characteristics
EMC
Specifications Appendix a
Useful Tables
IDN.C HP BASIC, C
ERRORCHK.C
SLFTST.C
RSTCLS.C
LBUS2PST.C
LOCALAD.C
LBUSAUTO.C
STATUS.C
EMC
Mode OFF
Calstorauto
CAL1VAL
Sour
DEL
SLOP1
POS
Table B-3. HP E1429A/B Error Messages Code Description
Appendix B Useful Tables
Useful Tables Appendix B
Appendix B Useful Tables
Local bus test data size not
Register Programming
System Configuration
Register reads and writes are 8-bits
Reading and Writing to the Registers
Figure C-1. HP E1429A/B A24 Address Space
Addressing the Registers
Determining the A24 Base Address
Appendix C Register Programming
A24READ.C
Register Descriptions
See
A24 Register Table
Base +
A/D Status Register
Input Configuration Registers
A/D Serial Register
Base +0316
A/D Parallel Strobe Register
A/D Shift Register
Base +0B16
Bit Name Function
Abort and Arm Immediate Register
Arm and Trigger Configuration Registers
Arm Status Register
Base +
Timebase Initiation Registerbase +
Arm Source Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Arm Internal Bus Registerbase +
Arm Source Register
Arm Control Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Arm Control Register
Base + 4B16
Trigger Source Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Trigger Source Register
Base + 4D16
Register Programming Appendix C
Reference Oscillator Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Reference Oscillator Register
Base + 4F16
Arm delay Register Base + 5116 and base +5316
Arm Count Register Base + 5516 and base +
Arm Count Latch Register
Decade Division Register
Trigger Immediate Registerbase + 5D16
Binary Division Register
Base +6116
Post-Arm Reading Count Register power-On/Reset Settings
Pre-Arm Reading Count Register power-On/Reset Settings
Pre-Arm Reading Count Registers
Base + 7316 and base +
Memory Control Registers
Traffic Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Traffic Register
Base +0216
Pulse Register
Channel ID Register
Data Register
Memory Control Register Power-on/Reset Settings
Memory Control Register
Base +2116
Base +2316 to base +2716
Memory Address Registers
Base Address Registers
Terminal Address Register
Base +2B16
Base +2D16 and base +2F16
Figure C-2. Accessing the A/D Shift Register
Using the A/D Shift Register
Bit Name Setting
Setting the Input Impedance
Setting Measurement Range
Procedure
Enabling the 10 MHz Filter
Input Post 14 dB Attenuator Bits Bits 34 Bits 35 37,45 38,46
Checking the Idle State
Setting the Arm Sources
Setting the Digitizer Configuration
Setting the Arm Delay
Setting the Arm Count
Setting the Reference Source
Sending an Arm Immediate Signal
Setting the Trigger Source
Aborting Measurements
Sending a Trigger Immediate Signal
Initializing Digitizer Memory
Re-initiating the Digitizer
Appendix C Register Programming
MSB LSB
Initializing Initiating Timebase Processor
Trigger count
Timebase reset
Sample rate
Data source
Count is 1 and the post-arm count is y-3
Midsb LSB
Register Programming Appendix C
Initializing Digitizer Memory to Retrieve Data
Retrieving Data from Memory
Register Programming Appendix C
MSB LSB
Example Program
Appendix C Register Programming
REGPROG.C
IOOUTPUTSADDR, READ?
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
On Next
Void checkerrorchar *function Char Into161 Length =
Register Programming Appendix C
Interleaved Transfers
Local Bus Interleaved Transfers
Local Bus Interleaved Transfers Appendix D
Setting Interleaved Transfer Mode
Procedure
LBUSINTR.C
Trigstarsour TIM
Trigstarsour ECLT0
Trigstartim 1E-6
OUTPECLT0FEED ’TRIG’
Tracdef SET1 Store readings 80 bytes in SET1
IOOUTPUTSADDRMEM, *OPC?
IOOUTPUTSADDRG, Abor
IOOUTPUTSADDRI, Abor
Local Bus Interleaved Transfers Appendix D
Appendix D Local Bus Interleaved Transfers
Local Bus Interleaved Transfers Appendix D
HP E1429A/B User’s Manual Index
Index
Index HP E1429A/B User’s Manual
HP E1429A/B User’s Manual Index
Index HP E1429A/B User’s Manual
Scpi
Index HP E1429A/B User’s Manual