SPRS292A − OCTOBER 2005 − REVISED NOVEMBER 2005
RESET TIMING
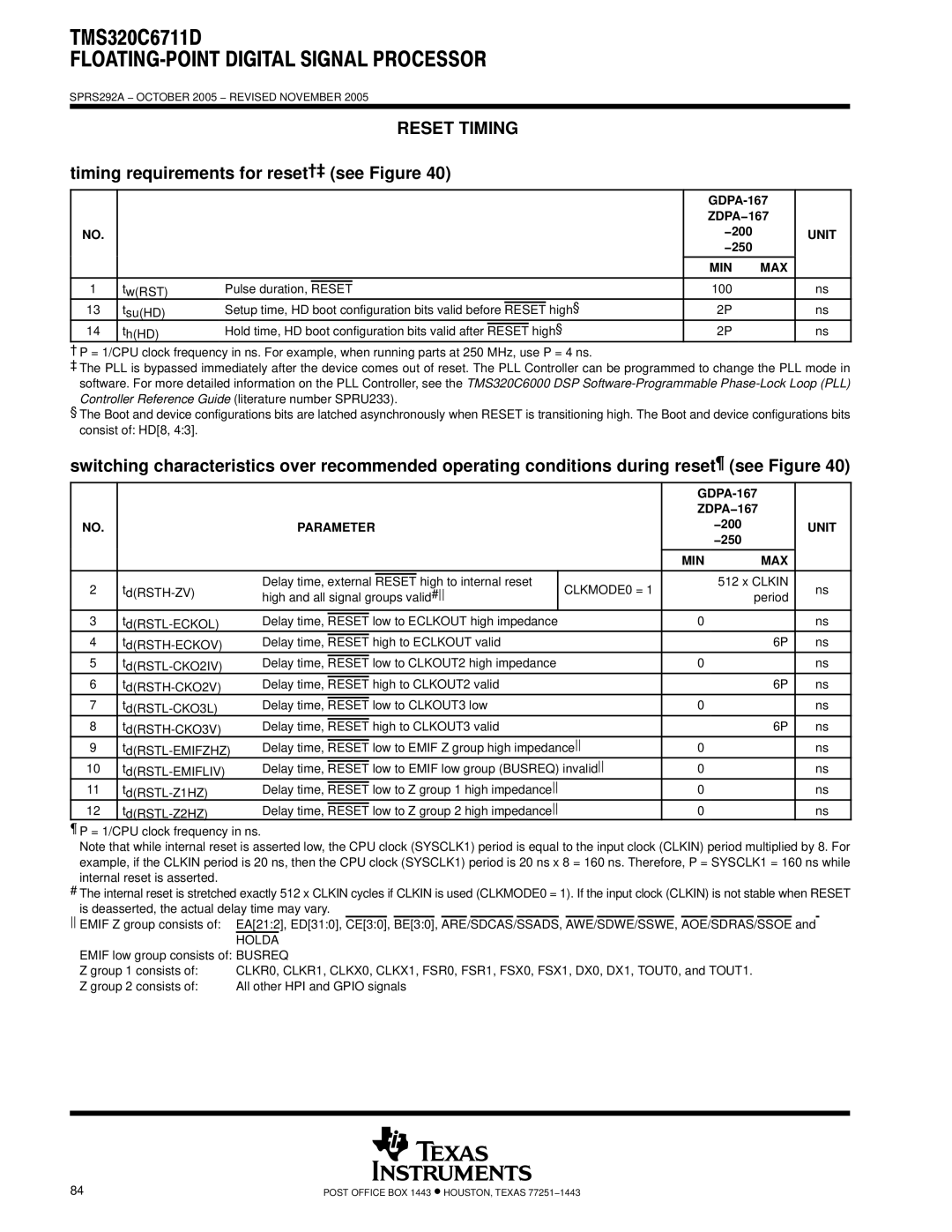
timing requirements for reset†‡ (see Figure 40)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ZDPA−167 |
| |
NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| −200 |
| UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| −250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MIN | MAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
1 | tw(RST) | Pulse duration, |
|
|
|
|
|
| 100 |
| ns |
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
13 | tsu(HD) | Setup time, HD boot configuration bits valid before |
|
| high§ | 2P |
| ns | |||
RESET |
| ||||||||||
14 | t | Hold time, HD boot configuration bits valid after |
|
| high§ | 2P |
| ns | |||
RESET |
| ||||||||||
| h(HD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
†P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns. For example, when running parts at 250 MHz, use P = 4 ns.
‡The PLL is bypassed immediately after the device comes out of reset. The PLL Controller can be programmed to change the PLL mode in software. For more detailed information on the PLL Controller, see the TMS320C6000 DSP
Controller Reference Guide (literature number SPRU233).
§The Boot and device configurations bits are latched asynchronously when RESET is transitioning high. The Boot and device configurations bits consist of: HD[8, 4:3].
switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions during reset¶ (see Figure 40)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ZDPA−167 |
| |
NO. |
| PARAMETER |
|
| −200 | UNIT | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| −250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| MIN | MAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
2 | Delay time, external | RESET | high to internal reset |
| CLKMODE0 = 1 |
| 512 x CLKIN | ns | |||||
# |
|
| period | ||||||||||
|
| high and all signal groups valid |
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
3 | Delay time, | RESET |
|
| low to ECLKOUT high impedance |
| 0 |
| ns | ||||
4 | Delay time, |
|
|
| high to ECLKOUT valid |
|
| 6P | ns | ||||
RESET |
|
|
| ||||||||||
5 | Delay time, |
|
|
| low to CLKOUT2 high impedance |
| 0 |
| ns | ||||
RESET |
|
|
| ||||||||||
6 | Delay time, |
|
|
| high to CLKOUT2 valid |
|
| 6P | ns | ||||
RESET |
|
|
| ||||||||||
7 | Delay time, |
|
|
| low to CLKOUT3 low |
| 0 |
| ns | ||||
RESET |
|
|
| ||||||||||
8 | Delay time, |
|
|
| high to CLKOUT3 valid |
|
| 6P | ns | ||||
RESET |
|
|
| ||||||||||
9 | t | Delay time, |
|
|
| low to EMIF Z group high impedance | 0 |
| ns | ||||
RESET |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
10 | Delay time, |
|
| low to EMIF low group (BUSREQ) invalid | 0 |
| ns | ||||||
RESET |
| ||||||||||||
11 | Delay time, |
|
|
| low to Z group 1 high impedance |
| 0 |
| ns | ||||
RESET |
|
| |||||||||||
12 | t | Delay time, |
|
|
| low to Z group 2 high impedance |
| 0 |
| ns | |||
RESET |
|
| |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
¶P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns.
Note that while internal reset is asserted low, the CPU clock (SYSCLK1) period is equal to the input clock (CLKIN) period multiplied by 8. For
example, if the CLKIN period is 20 ns, then the CPU clock (SYSCLK1) period is 20 ns x 8 = 160 ns. Therefore, P = SYSCLK1 = 160 ns while internal reset is asserted.
#The internal reset is stretched exactly 512 x CLKIN cycles if CLKIN is used (CLKMODE0 = 1). If the input clock (CLKIN) is not stable when RESET is deasserted, the actual delay time may vary.
EMIF Z group consists of: EA[21:2], ED[31:0], CE[3:0], BE[3:0], ARE/SDCAS/SSADS, AWE/SDWE/SSWE, AOE/SDRAS/SSOE and
| HOLDA |
EMIF low group consists of: BUSREQ | |
Z group 1 consists of: | CLKR0, CLKR1, CLKX0, CLKX1, FSR0, FSR1, FSX0, FSX1, DX0, DX1, TOUT0, and TOUT1. |
Z group 2 consists of: | All other HPI and GPIO signals |
84 | POST OFFICE BOX 1443 • HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251−1443 |