Powerware 9395 UPS and Plus 1 UPS 650-825 kVA
Consignes DE Sécurité Importantes Conserver CES Instructions
Table of Contents
Status Indicators System Events
Battery Power Wiring
Single UPS Modes Normal Mode Bypass Mode Battery Mode
Using the Menu Mimic Screen
UPS Maintenance
ENotify Service
Terminal Mode
Starting the UPMs
10.2.1 UPS Input 10−1 10.2.2 UPS Output 10−2 10.2.3
Product Specifications 10−1 10.1
10.2
List of Figures
34. Repo Switch
Optional X−Slot Cards
This page intentionally left blank
UPS Standard Features
Installation Features
Control Panel
Customer Interface
Advanced Battery Management
Power Management Software
Inherent Redundancy
Options and Accessories
Field Installed UPM
Sync Control
Single−Feed Kit
Battery System
Input Output Module Configuration
Separate Rectifier Input
Conventions Used in This Manual
Basic System Configurations
Using This Manual
Symbols, Controls, and Indicators
For More Information
Getting Help
Chapter Safety Warnings
E R T I S S E M E N T
Section
Page
Preparing the Site
Creating an Installation Plan
Environmental and Installation Considerations
95%, noncondensing
UPS Cabinet Weights
UPS Cabinet Clearances
Dimensions are in millimeters inches
Isbm Section Dimensions Front View
Front
Isbm Section Center of Gravity
114.3 115.8 Front View
UPS System Power Wiring Preparation
Common Battery
DC Input from Each Battery Disconnect to Each UPS
AC Input to UPS Bypass Five Wire Full Load Current
Phases, 1 Neutral, 1 Ground Minimum Conductor Size
AC Output to Critical Load Five Wire Full Load Current
Input Voltage
275
250
480
Supplied Intercabinet Wiring Terminal Hardware Kit
Battery UPM 4 FI−UPM
Battery
Battery UPM
Terminal Function Bus Landings Tightening Torque Bolt Size
10. Supplied External Wiring Terminal Hardware Kit
13. Power Cable Conduit Requirements
UPS Model Voltage Terminal Number of Wires Minimum Conduit
UPS Model Input Rating
13.Power Cable Conduit Requirements
14. Recommended Input Circuit Breaker Ratings
500A
UPS Model Input Rating for Each UPM
480V
400A
700A
UPS Model
UPS Model Each UPM 400V 480V
UPS System Interface Wiring Preparation
Distributed Bypass Power Wiring Preparation
Inspecting and Unpacking the UPS Cabinets
11. UPS Cabinet as Shipped on Pallet Isbm Section
12. UPS Cabinet as Shipped on Pallet UPM Section
This page intentionally left blank
Preliminary Installation Information
Unloading the UPS Sections from the Pallet
Front Door Shipping Bracket Bolts Pallet Left Side Shipping
Removing the Isbm Section Right Side Shipping Bracket
Bolts
Mechanically Joining the Sections
Right Side Shipping Bracket Bolts
U T I O N
UPM Wireway
Section Top Screw from Kit
Electrically Connecting the Sections
Screw from Kit Bracket from Kit
Back
UPS System Installation
−10
−11
UPM 2 Cable 2G1 & 2G2 Brown UPM 1 Cable 1G1 & 1G2 Orange
Phase a E1A UPM 2 Cable 2G1 & 2G2 Orange
Phase B E2A Phase C E3A AC Input to UPMs
UPM 3 Cable 3G1 & 3G2 Orange
−13
UPM 3 Cable 3G1 & 3G2 Yellow Phase B Phase a
UPM 1 Cable 1G1 & 1G2 Yellow UPM 2 Cable 2G1 & 2G2 Yellow
Cable 2G3 Black Cable 3G3 Black UPM 3 3E5A
Cable 1G3 Red UPM 1 1E4A
DC Input to UPMs UPM 2 2E4A
UPM 1 Cable 1G4 & 1G5 Orange UPM 2 Cable 2G4 & 2G5 Orange
Location of J50
Wiring Access
Protective Cage
J51, J61, and J70
Pl1 Interface Board J39 Inverter can Connector
Distributed Bypass Tie Cabinet Installation
Field Installed UPM Installation
Battery System Installation
Installing UPS External and Battery Power Wiring
Isbm Section
UPM Section Front
TOP View Bottom View
U T I O N
1A = 2A = 3A = 4A 1B = 2B = 3B = 4B
Critical Load
DC Input from Battery + E4 See -25or
AC Output to
Front Phase a E6 Phase B E7 AC Input to
Phase C E8 Section A-A
Isbm
Phase a E6 Phase B E7
Ground Terminals Front UPM Rectifier Input Terminal Block
UPS System Installation UPM
Battery Power Wiring
DC Input from Battery + E4 DC Input from Battery E5
Section B-B
UPM
UPM 4 FI−UPM
Installing Interface Connections
4−38 for detail
TB1, TB2, and TB3 Interface Connections
For terminal
Assignments
Battery Shunt Trip +
Battery Aux
Battery Aux Common
Battery Shunt Trip
2 TB1 Battery Interface Connections
Battery Aux Battery Aux Return
Battery Aux Battery Aux Common
Battery Disconnect 48 Vdc
Battery Disconnect
3 X−Slot Connections
−Slot Communication Bay
Installing a Repo Switch
Repo Switch Front View
Return
Repo Wire Terminations
Either Block
Wires
Twisted
Completing the Installation Checklist
Initial Startup
Installation Checklist
Distributed Bypass Installation Checklist
−45
−46
Installing an Optional Powerware Hot Sync can Bridge Card
Plug−in Terminal Block J3
Installing Options and Accessories
Normally-open contact closes when UPS is on bypass
J3 Terminal Name Description Alarm
Normally-closed contact opens when UPS is on bypass
Bypass contact return
Installing Distributed Bypass Control Wiring
From
If Installed
Shielded Twisted Pair
Twisted Pair
AUX
UPS 3 can Bridge Card J3-1 Alarm MOB 3 Aux 1 NC
Pull−Chain Wiring Terminations with MOBs
UPS 2 can Bridge Card J3-1 Alarm MOB 2 Aux 1 NC
UPS 4 can Bridge Card J3-1 Alarm MOB 4 Aux 1 NC
Installing an Optional Remote Monitor Panel
RMP II, RIM II, or SCM Nm lb
Ground Terminal Terminal TB3 Vac Power
From Tightening Torque Remarks
Installing an Optional Relay Interface Module
J1 through J4 Interface Connectors
Terminal TB1 Signal
Installing an Optional Supervisory Contact Module
Terminal TB3 Vac Power Ground Terminal TB2 Customer
11. Supervisory Contact Module II TB2
Accessory Mounting Dimensions
13. Relay Interface Module II Dimensions
14. Supervisory Contact Module II Dimensions
This page intentionally left blank
Operation
−20
UPS Cabinet
Battery System
UPS System Overview
Modes
Normal Mode
Single UPS
Inverter
Battery Converter
Rectifier
Bypass Mode
Battery Mode
Path of Current Through the UPS in Battery Mode
Single UPS Unit System Oneline Configurations
Service Connector
Fuse Battery Contactor K2
E4. E5 Battery Breaker
E1, E2, E3 E6, E7 Interface Board E8, E12 Single−feed Kit
Rotation
Load
Battery Breaker
Contactor K5
E4. E5
Battery System
Converter Fuse
E1, E2, E3 Interface Board Input Breaker CB1 Optional
Rectifier Fuse Inverter
Converter Fuse Battery Contactor K2
Rectifier Fuse Inverter Output
Rotation Bypass
CB4
Inverter Output
E6, E7 Interface Board E8, E12 Backfeed
Fuse Inverter
Contactor K5 Fuse
Fuse Inverter Output Contactor
AC Input to UPS Rectifiers 3 Wire −B−C Rotation
UPS Cabinet
Bypass Input Breaker
AC Input
Rectifier Input Breaker
Multiple UPS Distributed Bypass System
Multiple UPS Parallel System Modes
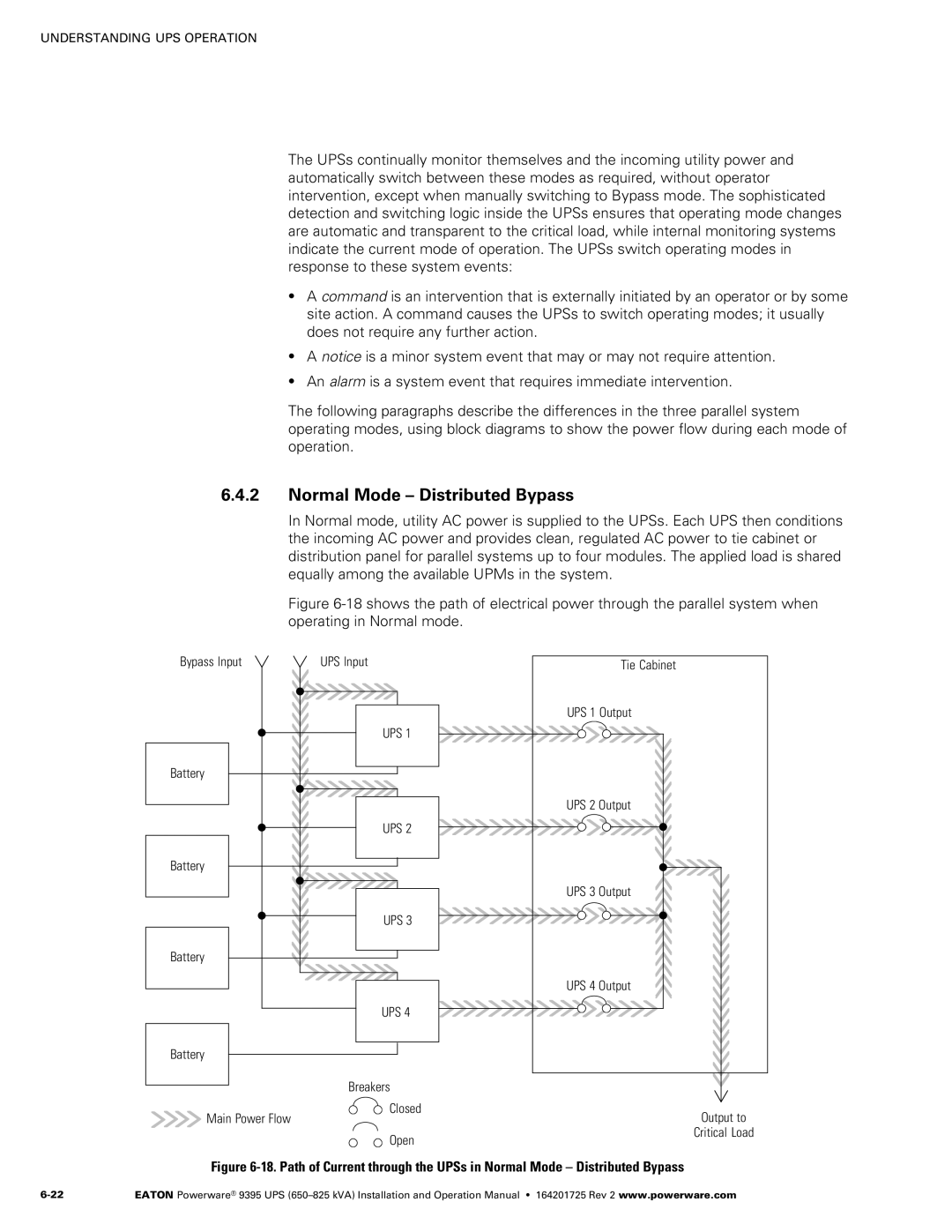
Normal Mode Distributed Bypass
Bypass Mode Distributed Bypass
Battery Mode Distributed Bypass
Main Power Flow Open
+1 and 4+0 Configurations
+1 and 2+0 Configurations
+1 and 3+0 Configurations
Multiple UPS Distributed Bypass
TIE
Rectifier Static Switch
Fuse Inverter Battery Converter E4. E5
This page intentionally left blank
UPS Controls and Indicators
Control Panel
Using the Control Panel
Circuit Breaker
System Events
Status Indicators
Status Indicators
Events Meters Controls Setup
Using the LCD and Pushbuttons
Using the Menu
Mimic Screen
Display Menu Operation
Display Menu Operation
System Level 1 Setup Password
Function Subfunction Operation Contrast Adjust
System Setup screen, press the return arrow pushbutton
Password is L1
Control See paragraph 7.2.7 for details
System Status Screen and Controls
Function Subfunction Operation Com Port Selection
Command Menu Operation
Typical System Status Messages
Cancel Load OFF
Load Off Screen
Starting the UPS in Normal Mode
Single UPS Operation
Starting the UPS in Bypass Mode
Starting the UPMs
−13
Power is present inside the UPS cabinet sections
Transfer from Normal to Bypass Mode
Transfer from Bypass to Normal Mode
Transfer from Normal to Bypass Mode and Shut Down UPS
Single UPM Shutdown
UPS and Critical Load Shutdown
Charger Control
Using the UPS Load OFF Pushbutton or Command
Using the Remote Emergency Power−off Switch
Repo Operation
Starting the Distributed Bypass System in Normal Mode
Multiple UPS Distributed Bypass Operation
Starting the Distributed Bypass System in Bypass Mode
Starting the UPSs UPMs
−22
R N I N G
Transfer from Normal to Bypass Mode and Shut Down all UPSs
UPS and Critical Load Shutdown
U T I O N
Using the Remote Emergency Power−off Switch
−28
Chapter Communication
X−Slot Cards
Installing eNotify Service
ENotify Service
ENotify Service Features
ConnectUPS−X Web/SNMP Card Modbus Card Modem Card
Powerware LanSafe Power Management Software
Remote Notification
Terminal Mode
Display UPS Control Panel
Event History Log
CSB Bootloader Display
CTO TF12710000000
Remote Monitor Panel
Building Alarm Monitoring
General Purpose Relay Contact
RMP II Status Indicators
System Normal
Pins 6 Contacts are closed when Utility Failure is detected
Customer Interface Connectors
Pins 3 Contacts are open when the UPS is offline
Relay Interface Module
SCM II Status Indicators and Connections
Supervisory Contact Module
Chapter UPS Maintenance
Important Safety Instructions
Monthly Maintenance
Performing Preventive Maintenance
Daily Maintenance
Isbm Section Air Filter Locations
Isbm Air Filters
Verify washed filter is thoroughly dry before reinstalling
UPM Air Filters
Annual Maintenance
Installing Batteries
Periodic Maintenance
Battery Maintenance
Recycling the Used Battery or UPS
Maintenance Training
UPS Input
Specifications
Model Numbers
UPS Output
UPS Environmental
Warranty
Warranty
Page
1642017252