6. Configuring the Gateway
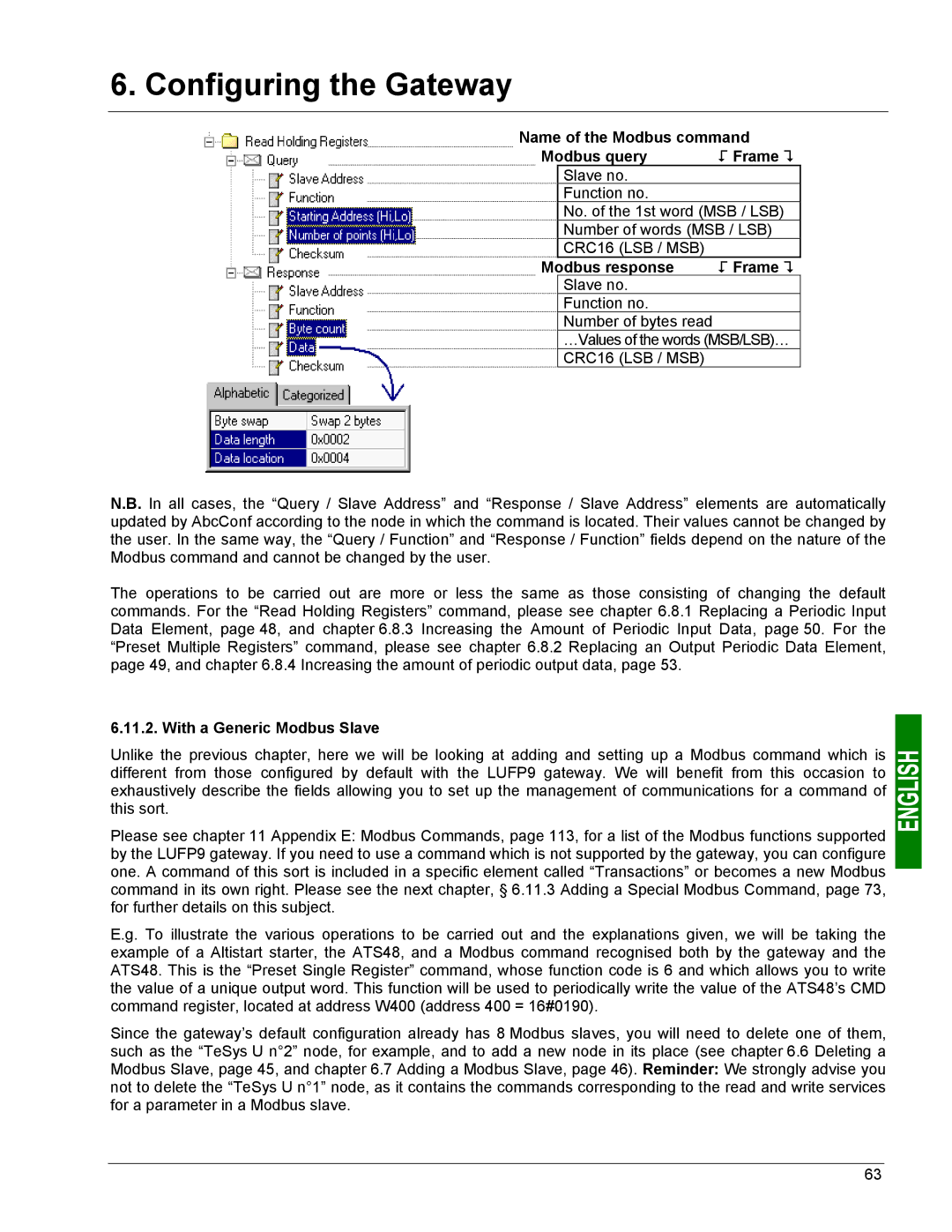
Name of the Modbus command
Modbus query | ! Frame " |
Slave no.
Function no.
No. of the 1st word (MSB / LSB)
Number of words (MSB / LSB)
CRC16 (LSB / MSB)
Modbus response | ! Frame " |
Slave no.
Function no.
Number of bytes read
…Values of the words (MSB/LSB)…
CRC16 (LSB / MSB)
N.B. In all cases, the “Query / Slave Address” and “Response / Slave Address” elements are automatically updated by AbcConf according to the node in which the command is located. Their values cannot be changed by the user. In the same way, the “Query / Function” and “Response / Function” fields depend on the nature of the Modbus command and cannot be changed by the user.
The operations to be carried out are more or less the same as those consisting of changing the default commands. For the “Read Holding Registers” command, please see chapter 6.8.1 Replacing a Periodic Input Data Element, page 48, and chapter 6.8.3 Increasing the Amount of Periodic Input Data, page 50. For the “Preset Multiple Registers” command, please see chapter 6.8.2 Replacing an Output Periodic Data Element, page 49, and chapter 6.8.4 Increasing the amount of periodic output data, page 53.
6.11.2. With a Generic Modbus Slave
Unlike the previous chapter, here we will be looking at adding and setting up a Modbus command which is different from those configured by default with the LUFP9 gateway. We will benefit from this occasion to exhaustively describe the fields allowing you to set up the management of communications for a command of this sort.
Please see chapter 11 Appendix E: Modbus Commands, page 113, for a list of the Modbus functions supported by the LUFP9 gateway. If you need to use a command which is not supported by the gateway, you can configure one. A command of this sort is included in a specific element called “Transactions” or becomes a new Modbus command in its own right. Please see the next chapter, § 6.11.3 Adding a Special Modbus Command, page 73, for further details on this subject.
E.g. To illustrate the various operations to be carried out and the explanations given, we will be taking the example of a Altistart starter, the ATS48, and a Modbus command recognised both by the gateway and the ATS48. This is the “Preset Single Register” command, whose function code is 6 and which allows you to write the value of a unique output word. This function will be used to periodically write the value of the ATS48’s CMD command register, located at address W400 (address 400 = 16#0190).
Since the gateway’s default configuration already has 8 Modbus slaves, you will need to delete one of them, such as the “TeSys U n°2” node, for example, and to add a new node in its place (see chapter 6.6 Deleting a Modbus Slave, page 45, and chapter 6.7 Adding a Modbus Slave, page 46). Reminder: We strongly advise you not to delete the “TeSys U n°1” node, as it contains the commands corresponding to the read and write services for a parameter in a Modbus slave.
63