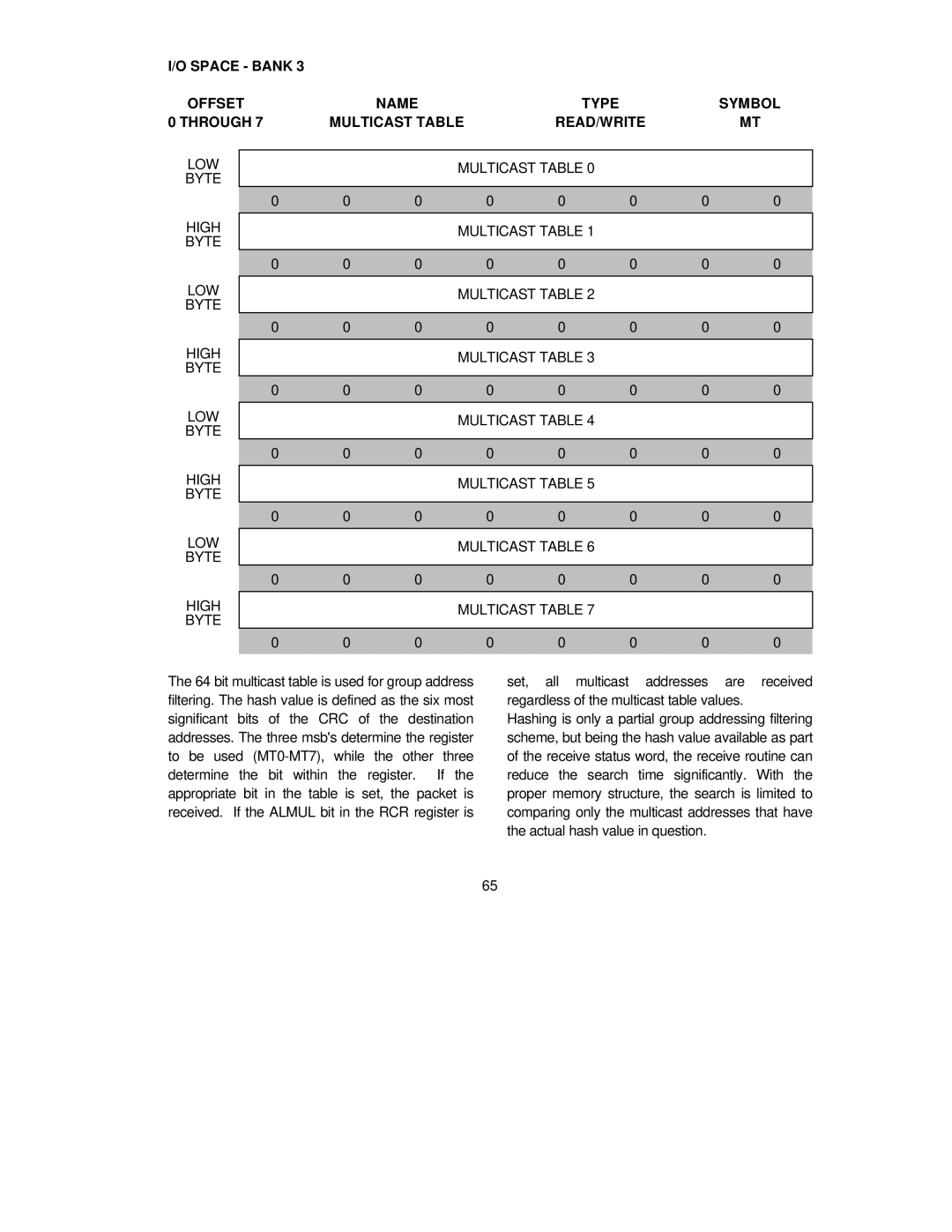
I/O SPACE - BANK 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
OFFSET |
| NAME |
| TYPE |
|
| SYMBOL | |
0 THROUGH 7 | MULTICAST TABLE |
| READ/WRITE |
| MT | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
LOW |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 0 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
HIGH |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 1 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
LOW |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 2 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
HIGH |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 3 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
LOW |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 4 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
HIGH |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 5 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
LOW |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 6 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
HIGH |
|
| MULTICAST TABLE 7 |
|
|
| ||
BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 64 bit multicast table is used for group address filtering. The hash value is defined as the six most significant bits of the CRC of the destination addresses. The three msb's determine the register to be used
set, all multicast addresses are received regardless of the multicast table values.
Hashing is only a partial group addressing filtering scheme, but being the hash value available as part of the receive status word, the receive routine can reduce the search time significantly. With the proper memory structure, the search is limited to comparing only the multicast addresses that have the actual hash value in question.
65