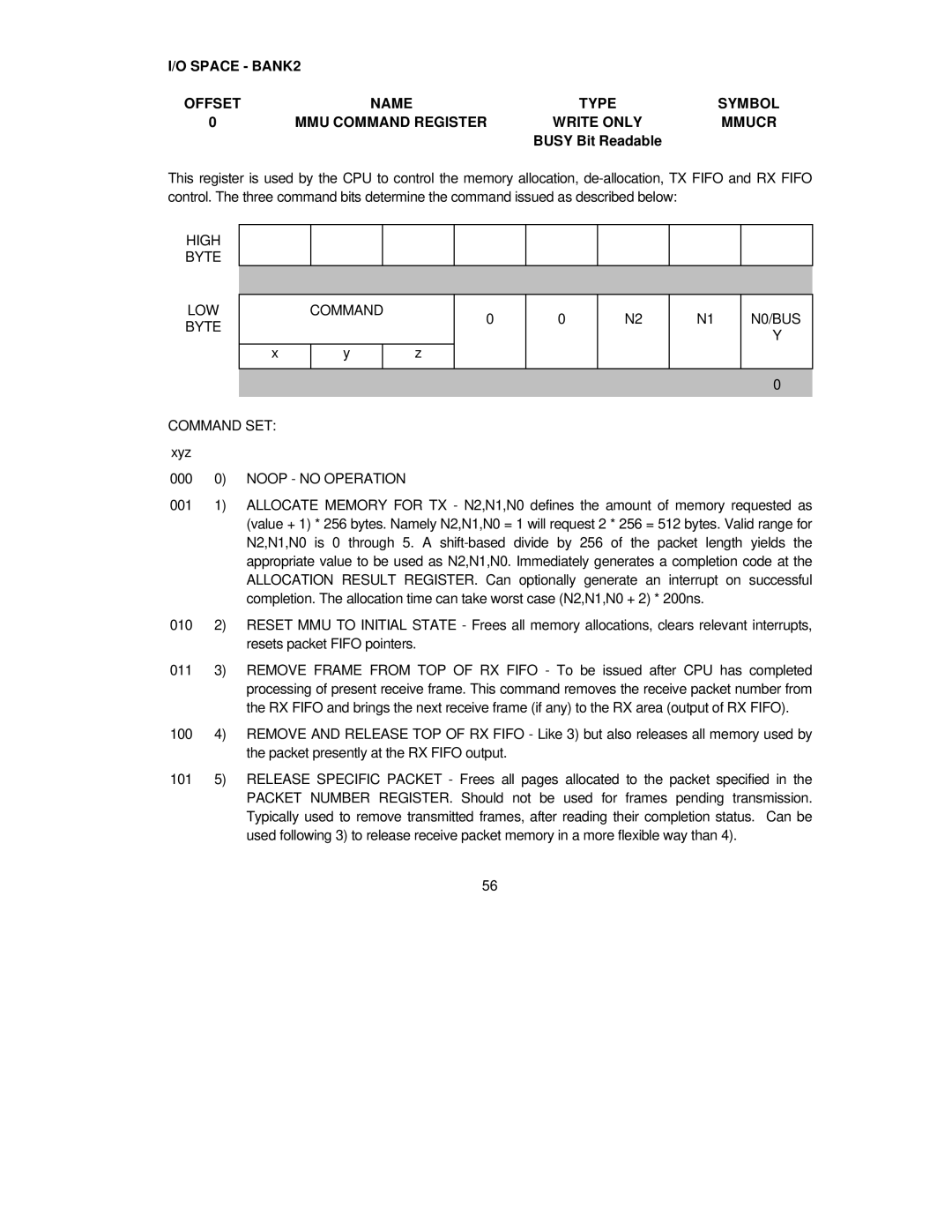
I/O SPACE - BANK2 |
|
| |
OFFSET | NAME | TYPE | SYMBOL |
0 | MMU COMMAND REGISTER | WRITE ONLY | MMUCR |
|
| BUSY Bit Readable |
|
This register is used by the CPU to control the memory allocation,
HIGH
BYTE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOW |
| COMMAND |
| 0 | 0 | N2 | N1 | N0/BUS | |
BYTE |
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Y | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| x | y |
| z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMMAND SET: xyz
000 0) NOOP - NO OPERATION
0011) ALLOCATE MEMORY FOR TX - N2,N1,N0 defines the amount of memory requested as (value + 1) * 256 bytes. Namely N2,N1,N0 = 1 will request 2 * 256 = 512 bytes. Valid range for N2,N1,N0 is 0 through 5. A
0102) RESET MMU TO INITIAL STATE - Frees all memory allocations, clears relevant interrupts, resets packet FIFO pointers.
0113) REMOVE FRAME FROM TOP OF RX FIFO - To be issued after CPU has completed processing of present receive frame. This command removes the receive packet number from the RX FIFO and brings the next receive frame (if any) to the RX area (output of RX FIFO).
1004) REMOVE AND RELEASE TOP OF RX FIFO - Like 3) but also releases all memory used by the packet presently at the RX FIFO output.
1015) RELEASE SPECIFIC PACKET - Frees all pages allocated to the packet specified in the PACKET NUMBER REGISTER. Should not be used for frames pending transmission. Typically used to remove transmitted frames, after reading their completion status. Can be used following 3) to release receive packet memory in a more flexible way than 4).
56