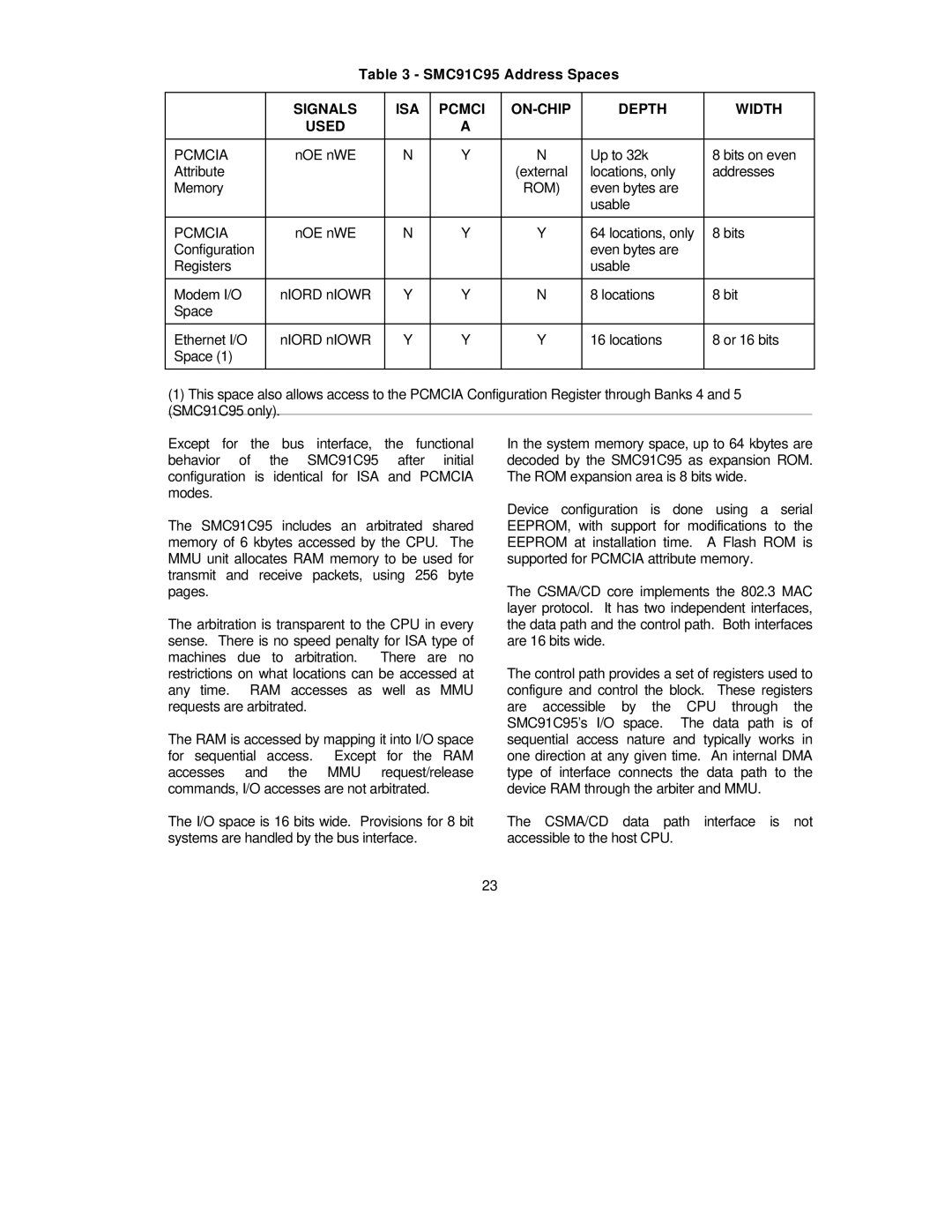
Table 3 - SMC91C95 Address Spaces
| SIGNALS | ISA | PCMCI |
| DEPTH | WIDTH |
| USED |
| A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCMCIA | nOE nWE | N | Y | N | Up to 32k | 8 bits on even |
Attribute |
|
|
| (external | locations, only | addresses |
Memory |
|
|
| ROM) | even bytes are |
|
|
|
|
|
| usable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCMCIA | nOE nWE | N | Y | Y | 64 locations, only | 8 bits |
Configuration |
|
|
|
| even bytes are |
|
Registers |
|
|
|
| usable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modem I/O | nIORD nIOWR | Y | Y | N | 8 locations | 8 bit |
Space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethernet I/O | nIORD nIOWR | Y | Y | Y | 16 locations | 8 or 16 bits |
Space (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)This space also allows access to the PCMCIA Configuration Register through Banks 4 and 5 (SMC91C95 only).
Except for the bus interface, the functional behavior of the SMC91C95 after initial configuration is identical for ISA and PCMCIA modes.
The SMC91C95 includes an arbitrated shared memory of 6 kbytes accessed by the CPU. The MMU unit allocates RAM memory to be used for transmit and receive packets, using 256 byte pages.
The arbitration is transparent to the CPU in every sense. There is no speed penalty for ISA type of machines due to arbitration. There are no restrictions on what locations can be accessed at any time. RAM accesses as well as MMU requests are arbitrated.
The RAM is accessed by mapping it into I/O space for sequential access. Except for the RAM accesses and the MMU request/release commands, I/O accesses are not arbitrated.
The I/O space is 16 bits wide. Provisions for 8 bit systems are handled by the bus interface.
In the system memory space, up to 64 kbytes are decoded by the SMC91C95 as expansion ROM. The ROM expansion area is 8 bits wide.
Device configuration is done using a serial EEPROM, with support for modifications to the EEPROM at installation time. A Flash ROM is supported for PCMCIA attribute memory.
The CSMA/CD core implements the 802.3 MAC layer protocol. It has two independent interfaces, the data path and the control path. Both interfaces are 16 bits wide.
The control path provides a set of registers used to configure and control the block. These registers are accessible by the CPU through the SMC91C95’s I/O space. The data path is of sequential access nature and typically works in one direction at any given time. An internal DMA type of interface connects the data path to the device RAM through the arbiter and MMU.
The CSMA/CD data path interface is not accessible to the host CPU.
23