User’s Guide
Products Applications
Important Notice
Preface
Glossary
Register Bit Conventions
Register Bit Accessibility and Initial Condition
Page
Introduction
Risc 16-Bit CPU
Basic Clock Module
Flash Memory Controller
Supply Voltage Supervisor
TimerA
Watchdog Timer
Usart Peripheral Interface, SPI Mode
18 ADC10
Chapter
Flexible Clock System
Architecture
−1. MSP430 Architecture
Embedded Emulation
Address Space
Flash/ROM
2 RAM
Peripheral Modules
Special Function Registers SFRs
Memory Organization
6Introduction
Chapter
−1. Power-On Reset and Power-Up Clear Schematic
System Reset and Initialization
−2. POR Timing
Power-On Reset POR
−3. Brownout Timing
Brownout Reset BOR
Software Initialization
Device Initial Conditions After System Reset
−4. Interrupt Priority
Interrupts
Non-Maskable Interrupts NMI
Reset/NMI Pin
−5. Block Diagram of Non-Maskable Interrupt Sources
Oscillator Fault
Flash Access Violation
Maskable Interrupts
Example of an NMI Interrupt Handler
Interrupt Acceptance
Interrupt Processing
Interrupt Nesting
Return From Interrupt
−1. Interrupt Sources,Flags, and Vectors
Interrupt Vectors
Operating Modes
−10. MSP430x1xx Operating Modes For Basic Clock System
Mode CPU and Clocks Status
Extended Time in Low-Power Modes
Entering and Exiting Low-Power Modes
Principles for Low-Power Applications
Connection of Unused Pins
−2. Connection of Unused Pins
18System Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes
Chapter
CPU Introduction
−1. CPU Block Diagram
Program Counter PC
CPU Registers
−3. Stack Pointer
Stack Pointer SP
Status Register SR
−1. Description of Status Register Bits
Bit Description
Register Constant Remarks
Constant Generator Registers CG1 and CG2
−2. Values of Constant Generators CG1, CG2
Constant Generator − Expanded Instruction Set
−7. Register -Byte/Byte-Register Operations
General−Purpose Registers R4 R15
As/Ad Addressing Mode Syntax Description
Addressing Modes
−3. Source/Destination Operand Addressing Modes
Register Mode
−4. Register Mode Description
Assembler Code Content of ROM
−5. Indexed Mode Description
Indexed Mode
−6. Symbolic Mode Description
Symbolic Mode
−7. Absolute Mode Description
Absolute Mode
−8. Indirect Mode Description
Indirect Register Mode
−9. Indirect Autoincrement Mode Description
Indirect Autoincrement Mode
−10.Immediate Mode Description
Immediate Mode
Instruction Set
Double-Operand Format I Instructions
−11. Double Operand Instructions
Mnemonic Reg Operation Status Bits
−12.Single Operand Instructions
Single-Operand Format II Instructions
Jumps
−13.Jump Instructions
Mnemonic Reg, D-Reg Operation
ADC.B
ADC.W
ADD.B
ADD.W
ADDC.B
ADDC.W
AND.B
AND.W
BIC.B
BIC.W
BIS.B
BIS.W
BIT.B
BIT.W
BR, Branch
Call
CLR.B
Clrc
Clrn
Clrz
CMP.B
CMP.W
DADC.B
DADD.B
DADD.W
DEC.B
−12. Decrement Overlap
DECD.B
Dint
Disable Interrupt
Incd
Eint
INC.B
INCD.B
INV.B
JHS
JEQ, JZ
JGE
Jump if less
Hint
JMP
SUB R5,COUNT Count − R5 − Count
JLO
JNC
JNZ
JNE
MOV.B
MOV.W
NOP
POP.B
PUSH.B
PUSH.W
RET
Reti
−13. Main Program Interrupt
RLA.B
−14. Destination Operand-Arithmetic Shift Left
RLC.B
−15. Destination Operand-Carry Left Shift
RRA.B
RRA.W
RRC.B
RRC.W
SBC.B
Setc
Setn
Setz
SUB.B
SUB.W
Borrow Implementation
Swpb
−18. Destination Operand Byte Swap
SXT
−19. Destination Operand Sign Extension
TST.B
XOR.B
XOR.W
Format-III Jump Instruction Cycles and Lengths
Interrupt and Reset Cycles
Instruction Cycles and Lengths
Format-II Single Operand Instruction Cycles and Lengths
−16.Format 1 Instruction Cycles and Lengths
Format-I Double Operand Instruction Cycles and Lengths
−20. Core Instruction Map
Instruction Set Description
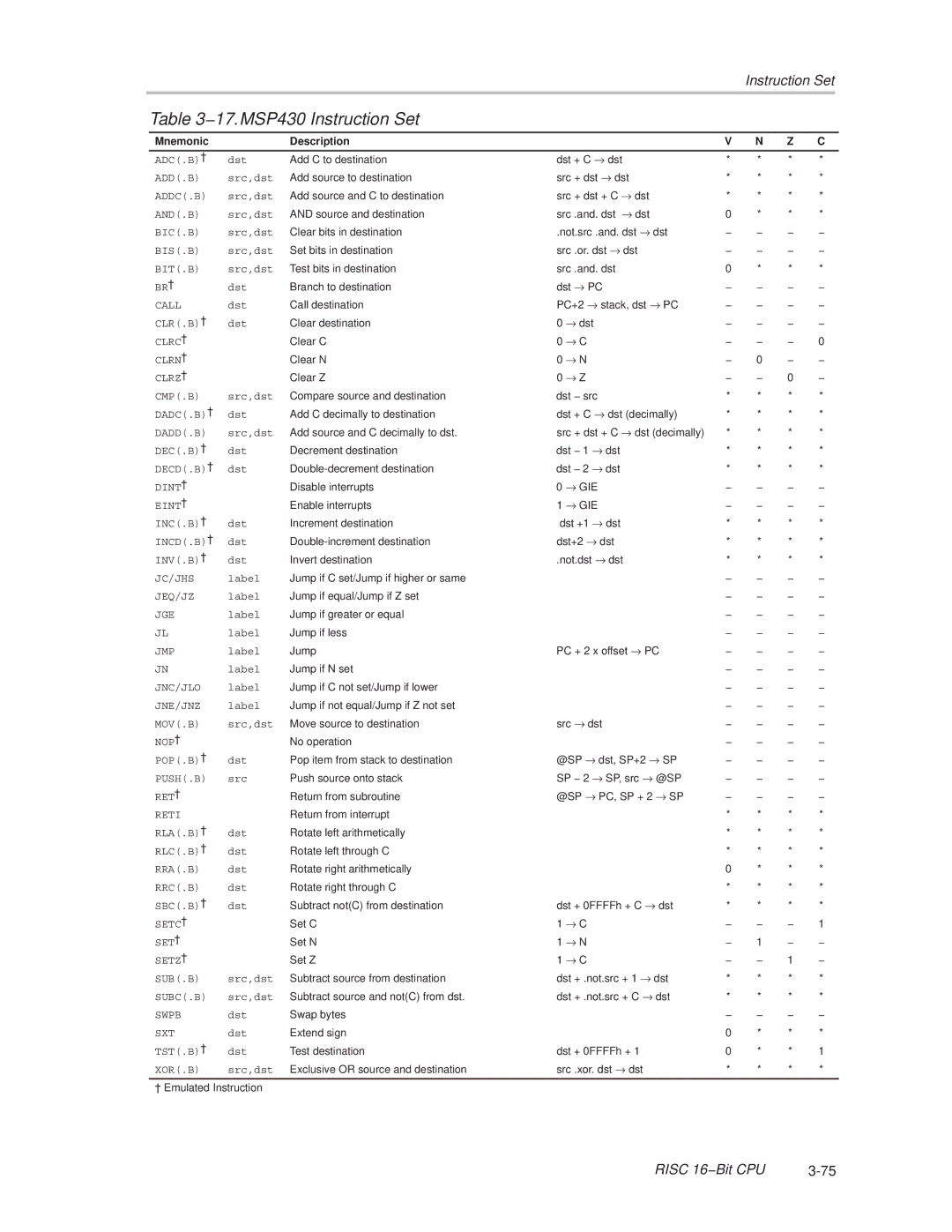
Mnemonic Description
−17.MSP430 Instruction Set
Page
Chapter
Basic Clock Module Introduction
−1. Basic Clock Block Diagram
Basic Clock Module Operation
Basic Clock Module Features for Low-Power Applications
LFXT1 Oscillator
−2. Off Signals for the LFXT1 Oscillator
3 XT2 Oscillator
Digitally-Controlled Oscillator DCO
Disabling the DCO
−5. Typical DCOx Range and RSELx Steps
Adjusting the DCO frequency
−6. DCO Frequency vs. Temperature
Using an External Resistor Rosc for the DCO
−7. Modulator Patterns
DCO Modulator
Basic Clock Module Fail-Safe Operation
−9. Oscillator-Fault Signal
−10. Oscillator-Fault-Interrupt
Oscillator Fault Detection
Sourcing Mclk from a Crystal
−11. Switch Mclk from Dcoclk to LFXT1CLK
Synchronization of Clock Signals
Basic Clock Module Registers
−1. Basic Clock Module Registers
Register Short Form Register Type Address Initial State
BCSCTL1, Basic Clock System Control Register
DCOCTL, DCO Control Register
DIVSx
BCSCTL2, Basic Clock System Control Register
SELMx
DIVMx
IFG1, Interrupt Flag Register
IE1, Interrupt Enable Register
18Basic Clock Module
Chapter
Flash Memory Introduction
−1. Flash Memory Module Block Diagram
−2. Flash Memory Segments, 4-KB Example
Flash Memory Segmentation
Flash Memory Timing Generator
Flash Memory Operation
Erase Mode
Erasing Flash Memory
−1. Erase Modes
−5. Erase Cycle from Within Flash Memory
Initiating an Erase from Within Flash Memory
−6. Erase Cycle from Within RAM
Initiating an Erase from RAM
Byte/Word Write
Write Mode
Writing Flash Memory
−2. Write Modes
−8. Initiating a Byte/Word Write from Flash
Initiating a Byte/Word Write from Within Flash Memory
−9. Initiating a Byte/Word Write from RAM
Initiating a Byte/Word Write from RAM
−10. Block-Write Cycle Timing
Block Write
−11. Block Write Flow
Block Write Flow and Example
KHz Smclk 952 kHz Assumes Accvie = Nmiie = Ofie =
Result
Flash Memory Access During Write or Erase
−3. Flash Access While Busy =
Flash
Programming Flash Memory Devices
Configuring and Accessing the Flash Memory Controller
Stopping a Write or Erase Cycle
Flash Memory Controller Interrupts
Programming Flash Memory via Jtag
−12. User-Developed Programming Solution
−4. Flash Memory Registers
Flash Memory Registers
FCTL1, Flash Memory Control Register
Reserved
Erase Cycle
FNx
FCTL2, Flash Memory Control Register
FWKEYx
FSSELx
FCTL3, Flash Memory Control Register FCTL3
Rather than MOV.B or CLR.B instructions
Flash Memory Controller
SVS Introduction SVS Operation SVS Registers
SVS Introduction
−1. SVS Block Diagram
Configuring the SVS
SVS Operation
SVS Comparator Operation
Changing the VLDx Bits
−2. Svson state When Changing VLDx
SVS Operating Range
−3. Operating Levels for SVS and Brownout/Reset Circuit
SVSCTL, SVS Control Register
Read/write 055h Reset with BOR
SVS Registers
−1. SVS Registers
Supply Voltage Supervisor
Chapter
Hardware Multiplier Introduction
−1. Hardware Multiplier Block Diagram
OP1 Address Register Name Operation
Hardware Multiplier Operation
Operand Registers
−1. OP1 addresses
Macs Underflow and Overflow
−2. Reshi Contents
−3. Sumext Contents
Result Registers
Process results
Software Examples
Indirect Addressing of Reslo
Using Interrupts
−4. Hardware Multiplier Registers
Hardware Multiplier Registers
Hardware Multiplier
DMA Introduction DMA Operation DMA Registers
DMA Introduction
−1. DMA Controller Block Diagram
DMA Addressing Modes
DMA Operation
DMADTx Transfer Description Mode
DMA Transfer Modes
−1. DMA Transfer Modes
Single Transfer
−3. DMA Single Transfer State Diagram
Block Transfers
−4. DMA Block Transfer State Diagram
Burst-Block Transfers
−5. DMA Burst-Block Transfer State Diagram
Halting Executing Instructions for DMA Transfers
Initiating DMA Transfers
Edge-Sensitive Triggers
Level-Sensitive Triggers
DMAxTSELx Operation
−2. DMA Trigger Operation
Stopping DMA Transfers
DMA Channel Priorities
DMA Priority Transfer Occurs New DMA Priority
CPU Operating Mode Clock Source Maximum DMA Cycle Time
DMA Transfer Cycle Time
−3. Maximum Single-Transfer DMA Cycle Time
DMA Controller Interrupts
Using DMA with System Interrupts
Using the I2C Module with the DMA Controller
Using ADC12 with the DMA Controller
Using DAC12 With the DMA Controller
−4. DMA Registers
DMA Registers
TSELx
DMACTL0, DMA Control Register
DMACTL1, DMA Control Register
Reserved DMADTx DMA DSTINCRx DMA SRCINCRx
DMAxCTL, DMA Channel x Control Register
DMAxSAx
DMAxSA, DMA Source Address Register
DMAxSZ, DMA Size Address Register
DMAxDA, DMA Destination Address Register
Page
Chapter
Digital I/O Introduction
Direction Registers PxDIR
Digital I/O Operation
Input Register PxIN
Output Registers PxOUT
Function Select Registers PxSEL
Interrupt Flag Registers P1IFG, P2IFG
5 P1 and P2 Interrupts
Interrupt Enable P1IE, P2IE
Configuring Unused Port Pins
Interrupt Edge Select Registers P1IES, P2IES
−1. Digital I/O Registers
Digital I/O Registers
Digital I/O
Watchdog Timer Introduction 10-2
Watchdog Timer Operation 10-4
Watchdog Timer Registers 10-7
Watchdog Timer Introduction
−1. Watchdog Timer Block Diagram
Interval Timer Mode
Watchdog Timer Operation
Watchdog Timer Counter
Watchdog Mode
Watchdog Timer Interrupts
Operation in Low-Power Modes
−1.Watchdog Timer Registers
Watchdog Timer Registers
WDTISx
WDTCTL, Watchdog Timer Register
Nmiie
Nmiifg
TimerA Introduction 11-2
TimerA Operation 11-4
TimerA Registers 11-19
TimerA Introduction
−1. TimerA Block Diagram
TimerA Operation
11.2.1 16-Bit Timer Counter
Clock Source Select and Divider
MCx Mode Description
Starting the Timer
Timer Mode Control
−1. Timer Modes
−2. Up Mode
Up Mode
−4. Continuous Mode
Continuous Mode
−6. Continuous Mode Time Intervals
Use of the Continuous Mode
−7. Up/Down Mode
Up/Down Mode
−9. Output Unit in Up/Down Mode
Use of the Up/Down Mode
Capture/Compare Blocks
Capture Mode
−11. Capture Cycle
Compare Mode
−2. Output Modes
OUTMODx Mode Description
Output Unit
Output Modes
−12.Output Example-Timer in Up Mode
−13.Output Example-Timer in Continuous Mode
−14.Output Example-Timer in Up/Down Mode
TimerA Interrupts
TACCR0 Interrupt
TAIV, Interrupt Vector Generator
Taiv Software Example
−3. TimerA Registers
TimerA Registers
IDx
TACTL, TimerA Control Register
Unused
TASSELx
TARx
TAR, TimerA Register
OUTMODx
TACCTLx, Capture/Compare Control Register
CMx
CCISx
Interrupt
TAIV, TimerA Interrupt Vector Register
Taiv Contents Interrupt Source Interrupt Flag Priority
TAIVx
11-24TimerA
TimerB Introduction 12-2
TimerB Operation 12-4
TimerB Registers 12-20
Similarities and Differences From TimerA
TimerB Introduction
−1. TimerB Block Diagram
TimerB Operation
12.2.1 16-Bit Timer Counter
TBR Length
−1.Timer Modes
Changing the Period Register TBCL0
Way as the other capture/compare registers
12-8TimerB
TBCL0−1 TBCL0 TBCL0−1 TBCL0−2
Changing the Value of Period Register TBCL0
−10. Capture Signal SCS=1
−11.Capture Cycle
CLLDx Description
TBCLGRPx Grouping Update Control
−2.TBCLx Load Events
−3.Compare Latch Operating Modes
−4.Output Modes
−12. Output Example-Timer in Up Mode
−13. Output Example-Timer in Continuous Mode
−14. Output Example-Timer in Up/Down Mode
TBIV, Interrupt Vector Generator
TimerB Interrupts
TBIV, Interrupt Handler Examples
−5.TimerB Registers
TimerB Registers
TimerB Control Register Tbctl
CNTLx
TBSSELx
TBRx
TBR, TimerB Register
CLLDx
TBCCTLx, Capture/Compare Control Register
12-24TimerB
TBIV, TimerB Interrupt Vector Register
Tbiv Contents Interrupt Source Interrupt Flag Priority
TBIVx
12-26TimerB
Usart Introduction Uart Mode 13-2
Usart Operation Uart Mode 13-4
Usart Registers Uart Mode 13-21
−1 shows the Usart when configured for Uart mode
Usart Introduction Uart Mode
−1. Usart Block Diagram Uart Mode
Usart Operation Uart Mode
Usart Initialization and Reset
Character Format
Idle-Line Multiprocessor Format
Asynchronous Communication Formats
13-6USART Peripheral Interface, Uart Mode
−4. Address -Bit Multiprocessor Format
Address-Bit Multiprocessor Format
Automatic Error Detection
−1.Receive Error Conditions
Error Condition Description
−5. State Diagram of Receiver Enable
Usart Receive Enable
−6. State Diagram of Transmitter Enable
Usart Transmit Enable
−7. MSP430 Baud Rate Generator
Uart Baud Rate Generation
Determining the Modulation Value
Baud Rate Bit Timing
Brclk =
Transmit Bit Timing
Receive Bit Timing
−9. Receive Error
Brclk
−2.Commonly Used Baud Rates, Baud Rate Data, and Errors
Typical Baud Rates and Errors
Usart Transmit Interrupt Operation
Usart Interrupts
−11.Receive Interrupt Operation
Usart Receive Interrupt Operation
Receive-Start Edge Detect Operation
−12. Glitch Suppression, Usart Receive Not Started
Usart Registers Uart Mode
−3.USART0 Control and Status Registers
−4.USART1 Control and Status Registers
UxCTL, Usart Control Register
SSELx
UxTCTL, Usart Transmit Control Register
UxRCTL, Usart Receive Control Register
UxMCTL, Usart Modulation Control Register
UxBRx
UxMCTLx
UxTXBUFx Bits
UxRXBUF, Usart Receive Buffer Register
UxTXBUF, Usart Transmit Buffer Register
UxRXBUFx Bits
ME2, Module Enable Register
ME1, Module Enable Register
IE2, Interrupt Enable Register
IFG2, Interrupt Flag Register
UTXIFG0 ‡
Usart Peripheral Interface, Uart Mode 13-31
Usart Introduction SPI Mode 14-2
Usart Operation SPI Mode 14-4
Usart Registers SPI Mode 14-13
Usart Introduction SPI Mode
−1. Usart Block Diagram SPI Mode
Simo
Usart Operation SPI Mode
Four-Pin SPI Master Mode
Master Mode
Four-Pin SPI Slave Mode
Slave Mode
Transmit Enable
SPI Enable
−6. SPI Master Receive-Enable State Diagram
Receive Enable
−8. SPI Baud Rate Generator
Serial Clock Control
−9. Usart SPI Timing
Serial Clock Polarity and Phase
SPI Transmit Interrupt Operation
SPI Interrupts
SPI Receive Interrupt Operation
−12. Receive Interrupt State Diagram
Usart Registers SPI Mode
−1.USART0 Control and Status Registers
−2.USART1 Control and Status Registers
I2C †
Ckph
Undefined
Baud-rate generator uses the content of UxBR1+UxBR0 to set
MSB is always reset
USPIE0 †
14-20USART Peripheral Interface, SPI Mode
USART0
14-22USART Peripheral Interface, SPI Mode
Usart Peripheral Interface, SPI Mode 14-23
2C Module Introduction 15-2
2C Module Operation 15-4
2C Module Registers 15-20
START/RESTART/STOP
15.1 I2C Module Introduction
−1. Usart Block Diagram I 2C Mode
15.2 I2C Module Operation
−2. I 2C Bus Connection Diagram
15.2.1 I2C Module Initialization
−3. I 2C Module Data Transfer
15.2.2 I2C Serial Data
15.2.3 I2C Addressing Modes
Bit Addressing
Repeated Start Conditions
15.2.4 I2C Module Operating Modes
−1.Master Operation
Condition Or Bus Activity
−8. Master Transmitter Mode
−9. Master Receiver Mode
−10. Arbitration Procedure Between Two Master Transmitters
Automatic Data Byte Counting
−11.Slave Transmitter
−12. Slave Receiver
Receive Overrun
I2C Data Register I2CDR
−2.I2CDR Register Function
Transmit Underflow
−13. I 2C Module SCL Generation
15.2.6 I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
Using the I2C Module with Low Power Modes
15.2.8 I2C Interrupts
−3.I 2C Interrupts
Interrupt Interrupt Condition Flag
I2CIV Software Example
I2CIV, Interrupt Vector Generator
−4.I 2C Registers
15.3 I2C Module Registers
U0CTL, USART0 Control Register-I2C Mode
I2CSSELx
I2CTCTL, I2C Transmit Control Register
I2CDCTL, I2C Data Control Register
I2CDRW, I2CDRB, I2C Data Register
I2CNDAT, I2C Transfer Byte Count Register
I2CNDATx Bits
I2CPSCx
I2CPSC, I2C Clock Prescaler Register
I2CSCLLx Bits
I2CSCLH, I2C Shift Clock High Register
I2CSCLL, I2C Shift Clock Low Register
I2CSCLHx Bits
I2COA, I2C Own Address Register, 7-Bit Addressing Mode
I2COA, I2C Own Address Register, 10-Bit Addressing Mode
I2COAx
I2CSA, I2C Slave Address Register, 7-Bit Addressing Mode
I2CSA, I2C Slave Address Register, 10-Bit Addressing Mode
I2CSAx
I2CIE, I2C Interrupt Enable Register
I2CIFG, I2C Interrupt Flag Register
I2CIV, I2C Interrupt Vector Register
I2CIV
I2CIVx
15-32USART Peripheral Interface, I2C Mode
ComparatorA Introduction 16-2
ComparatorA Operation 16-4
ComparatorA Registers 16-9
ComparatorA Introduction
−1. ComparatorA Block Diagram
Input Analog Switches
ComparatorA Operation
Comparator
Voltage Reference Generator
Output Filter
ComparatorA Interrupts
ComparatorA, Port Disable Register Capd
ComparatorA Used to Measure Resistive Elements
−5. Temperature Measurement System
−6. Timing for Temperature Measurement Systems
−1.ComparatorA Registers
ComparatorA Registers
CACTL1, ComparatorA Control Register
CAPD, ComparatorA, Port Disable Register
CACTL2, ComparatorA, Control Register
CAPDx
16-12ComparatorA
ADC12 Introduction 17-2
ADC12 Operation 17-4
ADC12 Registers 17-20
17.1 ADC12 Introduction
−1. ADC12 Block Diagram
17.2 ADC12 Operation
17.2.1 12-Bit ADC Core
Conversion Clock Selection
Analog Port Selection
17.2.2 ADC12 Inputs and Multiplexer
Auto Power-Down
Sample and Conversion Timing
Extended Sample Mode
−4. Pulse Sample Mode
Pulse Sample Mode
−5. Analog Input Equivalent Circuit
Sample Timing Considerations
17.2.7 ADC12 Conversion Modes
−1.Conversion Mode Summary
CONSEQx Mode Operation
Conversion Memory
−6. Single-Channel, Single-Conversion Mode
Single-Channel Single-Conversion Mode
−7. Sequence-of-Channels Mode
Sequence-of-Channels Mode
−8. Repeat-Single-Channel Mode
Repeat-Single-Channel Mode
−9. Repeat-Sequence-of-Channels Mode
Repeat-Sequence-of-Channels Mode
Stopping Conversions
Using the Multiple Sample and Convert MSC Bit
−10. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function
Using the Integrated Temperature Sensor
−11.ADC12 Grounding and Noise Considerations
17.2.9 ADC12 Grounding and Noise Considerations
ADC12IV, Interrupt Vector Generator
17.2.10 ADC12 Interrupts
ADC12IFG15
ADC12 Interrupt Handling Software Example
−2.ADC12 Registers
17.3 ADC12 Registers
ADC12CTL0, ADC12 Control Register
SHT1x
SHT0x
Bit Reference generator voltage. Refon must also be set
ADC12DIVx
ADC12CTL1, ADC12 Control Register
ADDx
SHSx
Results
ADC12MEMx, ADC12 Conversion Memory Registers
CONSEQx
Conversion
ADC12MCTLx, ADC12 Conversion Memory Control Registers
SREFx
INCHx
ADC12IFGx Bits
ADC12IE, ADC12 Interrupt Enable Register
ADC12IFG, ADC12 Interrupt Flag Register
ADC12IEx
Contents Interrupt Source Interrupt Flag Priority
ADC12IV, ADC12 Interrupt Vector Register
ADC12IVx Bits
17-28 ADC12
ADC10 Introduction 18-2
ADC10 Operation 18-4
ADC10 Registers 18-24
18.1 ADC10 Introduction
−1. ADC10 Block Diagram
18.2.1 10-Bit ADC Core
18.2 ADC10 Operation
Analog Port Selection
18.2.2 ADC10 Inputs and Multiplexer
Internal Reference Low-Power Features
−3. Sample Timing
−4. Analog Input Equivalent Circuit
Conversion Modes
−5. Single-Channel Single-Conversion Mode
−6. Sequence-of-Channels Mode
−7. Repeat-Single-Channel Mode
−8. Repeat-Sequence-of-Channels Mode
Using the MSC Bit
18.2.7 ADC10 Data Transfer Controller
−9. One-Block Transfer
One-Block Transfer Mode
=0 ADC10DTC1 DTC reset Wait for write to
−11.Two-Block Transfer
Two-Block Transfer Mode
ADC10CT=1
−2.Maximum DTC Cycle Time
CPU Operating Mode Clock Source Maximum DTC Cycle Time
Continuous Transfer
DTC Transfer Cycle Time
−14. Typical Temperature Sensor Transfer Function
−16. ADC10 Grounding and Noise Considerations
18.2.9 ADC10 Grounding and Noise Considerations
−17. ADC10 Interrupt System
18.2.10 ADC10 Interrupts
−3.ADC10 Registers
18.3 ADC10 Registers
SHTx
ADC10CTL0, ADC10 Control Register
Bit Reference-generator voltage. Refon must also be set
ADC10CTL1, ADC10 Control Register
ADC10AE, Analog Input Enable Control Register
ADC10DIVx
ADC10AEx Bits
ADC10MEM, Conversion-Memory Register, 2’s Complement Format
ADC10MEM, Conversion-Memory Register, Binary Format
ADC10DTC0, Data Transfer Control Register
ADC10SAx
ADC10DTC1, Data Transfer Control Register
ADC10SA, Start Address Register for Data Transfer
Transfers
18-32 ADC10
DAC12 Introduction 19-2
DAC12 Operation 19-4
DAC12 Registers 19-10
19.1 DAC12 Introduction
−1. DAC12 Block Diagram
DAC12 Port Selection
19.2 DAC12 Operation
19.2.1 DAC12 Core
−1.DAC12 Full-Scale Range Vref = V eREF+ or VREF+
19.2.2 DAC12 Reference
DAC12 Reference Input and Voltage Output Buffers
Updating the DAC12 Voltage Output
19.2.4 DAC12xDAT Data Format
−4. Negative Offset
19.2.5 DAC12 Output Amplifier Offset Calibration
Grouping Multiple DAC12 Modules
−6. DAC12 Group Update Example, TimerA3 Trigger
19.2.7 DAC12 Interrupts
−2.DAC12 Registers
19.3 DAC12 Registers
LSELx
DAC12xCTL, DAC12 Control Register
AMPx
DAC12AMPx Input Buffer Output Buffer
DAC12xDAT, DAC12 Data Register
DAC12 Data
DAC12 Data Format
19-14 DAC12