LogiCORE IP Gigabit Ethernet MAC
UG144 April 24
Gigabit Ethernet MAC v8.5 User Guide
Revision History
Date Version Revision
DIS Product
Table of Contents
Designing with the Core
Configuration and Status
Appendix C Calculating DCM Phase-Shifting
1Block Diagram
Schedule of Figures
2External Gmii Receiver Logic for Spartan-3, Spartan-3E,
Figure A-2Frame Transfer across LocalLink Interface
DIS Product
Schedule of Tables
Clocking and Resetting Interfacing to Other Cores
Guide Contents
About This Guide
Conventions
Typographical
Preface About This Guide
Convention Meaning or Use Example
Online Document
List of Acronyms
Conventions
Acronym Spelled Out
Preface About This Guide Acronym Spelled Out
Vhdl
Related Xilinx Ethernet Products and Services
Introduction
About the Core
Recommended Design Experience
Specifications
Technical Support
Feedback
Gemac Core
Core Architecture
System Overview
Core Components
Gmac Core with Optional Management Interface
Core Interfaces
Core Interfaces
Core Architecture
Core Interfaces
Client Side Interface
Transmitter Interface
Receiver Interface
Flow Control Interface
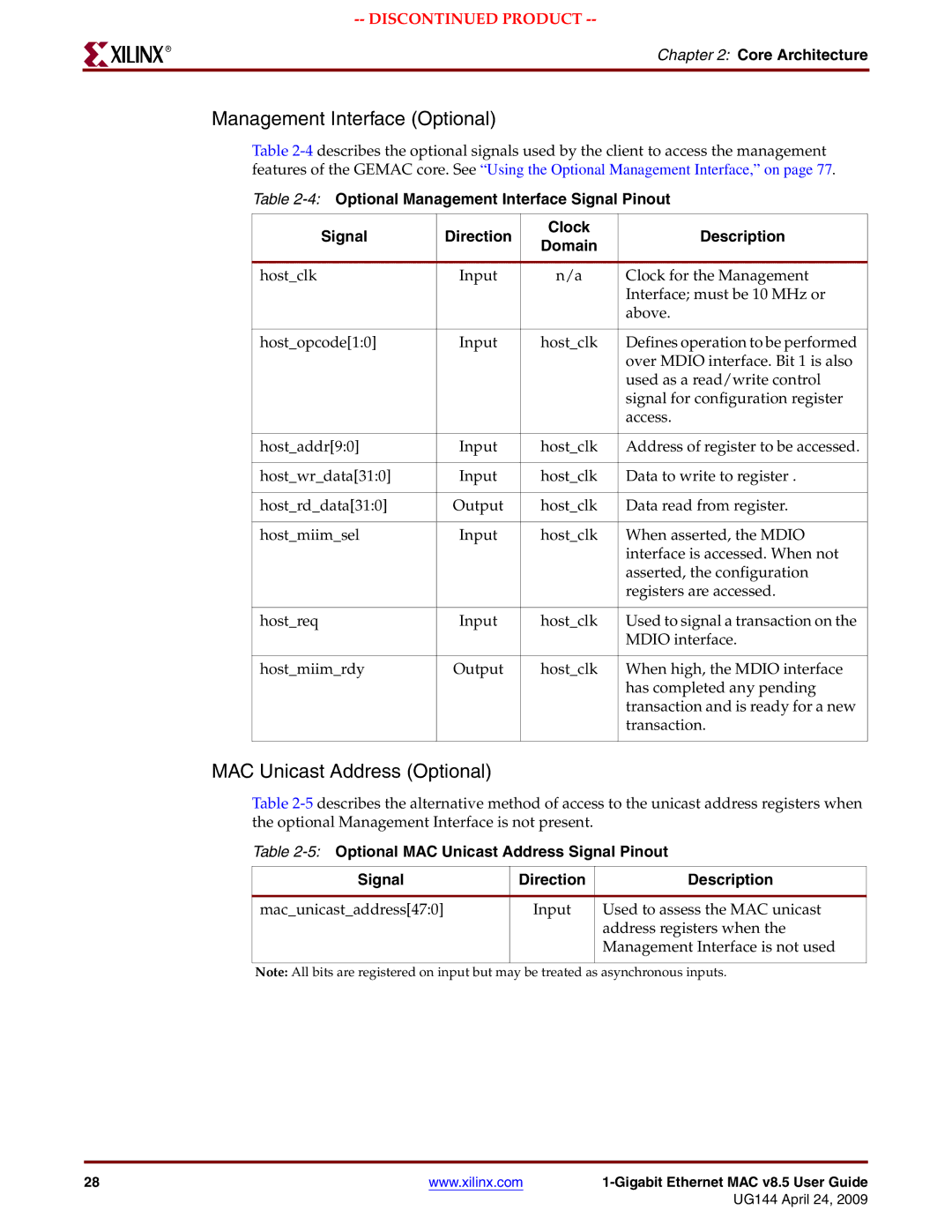
Management Interface Optional
MAC Unicast Address Optional
Configuration Vector Optional
Asynchronous Reset
7Reset Signal Direction Clock Domain Description
Physical Side Interface
Mdio Interface
Generating the Core
Graphical User Interface
Parameter Values in the XCO File
Output Generation
Generating the Core
Using the Example Design as a Starting Point
Designing with the Core
General Design Guidelines
Design Steps
Designing with the Core
11-Gigabit Ethernet MAC Core Example Design
Implementing the 1-Gigabit Ethernet MAC in Your Application
Know the Degree of Difficulty
General Design Guidelines
Recognize Timing Critical Signals
Keep it Registered
Use Supported Design Flows
Make Only Allowed Modifications
Using the Client Side Data Path
1Abbreviations Used in Timing Diagrams Definition
Receiving Inbound Frames
Normal Frame Reception
Using the Client Side Data Path
Rxgoodframe, rxbadframe timing
Frame Reception with Errors
Receiving Inbound Frames
Client-Supplied FCS Passing
Vlan Tagged Frames
Length/Type Field Error Checks
Enabled
Disabled
Maximum Permitted Frame Length
Receiver Statistics Vector
5Receiver Statistics Vector Timing
DIS Product
Length see Maximum Permitted Frame
Transmitting Outbound Frames
Normal Frame Transmission
Padding
Transmitting Outbound Frames
Client Underrun
7Frame Transmission with Client-supplied FCS
Inter-Frame Gap Adjustment
9Transmission of a Vlan Tagged Frame
10Inter-Frame Gap Adjustment
Transmitter Statistics Vector
Name
Bit 31 is equivalent to bit
Overview of Flow Control
Using Flow Control
Flow Control Requirement
Using Flow Control
Flow Control Basics
Pause Control Frames
Overview of Flow Control
Flow Control Operation of the Gemac
Transmitting a Pause Control Frame
Core-initiated Pause Request
Client Initiated Pause Request
Receiving a Pause Control Frame
Core Initiated Response to a Pause Request
Client Initiated Response to a Pause Request
Flow Control Operation of the Gemac
Flow Control Implementation Example
Method
Flow Control Implementation Example
4Flow Control Implementation Triggered from Fifo Occupancy
Using Flow Control
Implementing External Gmii
Using the Physical Side Interface
Gmii Transmitter Logic
Using the Physical Side Interface
1External Gmii Transmitter Logic
Spartan-3, Spartan-3E, Spartan-3A and Virtex-4 Devices
Gmii Receiver Logic
Implementing External Gmii
DCM Reset circuitry
Virtex-5 Devices
3External Gmii Receiver Logic for Virtex-5 Devices
Implementing External Rgmii
Rgmii Transmitter Logic
Virtex-4 Devices
Implementing External Rgmii
5External Rgmii Transmitter Logic in Virtex-4 Devices
6External Rgmii Transmitter Logic in Virtex-5 Devices
Rgmii Receiver Logic
7External Rgmii Receiver Logic
Virtex-4 Devices
8External Rgmii Receiver Logic for Virtex-4 Devices
9External Rgmii Receiver Logic for Virtex-5 Devices
Rgmii Inband Status Decoding Logic
10RGMII Inband Status Decoding Logic
Connecting the Mdio to an Internally Integrated PHY
Using the Mdio interface
Connecting the Mdio to an External PHY
Using the Optional Management Interface
Configuration and Status
Host Clock Frequency
Configuration and Status
Configuration Registers
2Configuration Registers Address Description
Receiver Configuration
Using the Optional Management Interface
3Receiver Configuration Word Bit Default Description
Receiver Configuration Word
Transmitter Configuration
Interframe Gap Adjust Enable If ‘1,’ the transmitter will
Flow Control Configuration
6Flow Control Configuration Word Bit Default Description
Mdio Configuration
Address Filter Configuration
Writing and Reading to and from the Configuration Registers
10Address Table Configuration Word Bits Default Description
11 Address Table Configuration Word
12Address Filter Mode Bits Default Description
1Configuration Register Write Timing
Accessing the Address Table
3Address Table Write Timing
Mdio Interface
Introduction to Mdio
Write Transaction
5Typical MDIO-managed System
Accessing Mdio With Gemac
Read Transaction
8MDIO Access through Management Interface
Access without the Management Interface
Pause frame MAC Source Address470
Transmitter Interframe Gap Adjust Enable
Receive Flow Control Enable . When this bit
Constraining the Core
Required Constraints
Period Constraints for Clock Nets
Constraining the Core
Timespecs for Critical Logic within the Core
Required Constraints
Timespecs for Reset Logic within the Core
Constraints when Implementing an External Gmii
Gmii IOB Constraints
Gmii Input Setup/Hold Timing
1Input Gmii Timing Symbol Min Max Units
Virtex-5 Devices
Virtex-5 devices with Delayed Data/Control
Understanding Timing Reports for Gmii Setup/Hold Timing
Non-Virtex-5 devices
Virtex-5 Devices with Delayed Clock
Constraints when Implementing an External Rgmii
Rgmii IOB Constraints
Rgmii Input Setup/Hold Timing
2Input Rgmii Timing Symbol Min Typical Units
Spartan-3, Spartan-3E, Spartan-3A, and Virtex-4 Devices
Rgmii DDR Constraints
Understanding Timing Reports for Rgmii Setup/Hold timing
106
4Timing Report Setup/Hold Illustration
108
Clocking and Resetting
Clocking the Core
With Internal Gmii
With External Gmii
Clocking and Resetting
Multiple Cores
With Rgmii
Standard Clocking Scheme
Multiple Cores
3Clock Management Logic with External Gmii Multiple Cores
Reset Conditions
4Clock Management Logic with External Rgmii Multiple Cores
Interfacing to Other Cores
Ethernet 1000Base-X PCS/PMA or Sgmii Core
Integration to Provide 1000BASE-X PCS with TBI
Interfacing to Other Cores
Ethernet 1000Base-X PCS/PMA or Sgmii Core
116
Virtex-5 LXT and SXT Devices
GTP
Virtex-5 FXT Devices
Clkdv
Integration to Provide Sgmii Functionality
Ethernet Statistics Core
Ethernet Statistics Core
120
Configuration Miim access Statistics Read
122
Using the Simulation Model
Implementing Your Design
Pre-implementation Simulation
Synthesis
Implementation
XST-Verilog
Generating the Xilinx Netlist
Mapping the Design
Post-Implementation Simulation
Placing-and-Routing the Design
Static Timing Analysis
Generating a Bitstream
Using the Model
Other Implementation Information
Using the Client-Side Fifo
GMII/RGMII
Interfaces
Appendix a Using the Client-Side Fifo
Transmit Fifo
Receive Fifo
Interfaces
Overview of LocalLink Interface
Data Flow
Clock Requirements
Functional Operation
Functional Operation
Expanding Maximum Frame Size
User Interface Data Width Conversion
Verification by Simulation
Core Verification, Compliance, and Interoperability
Hardware Verification
134
DCM Phase-Shifting
Calculating DCM Phase-Shifting
Finding the Ideal Phase-Shift
Appendix C Calculating DCM Phase-Shifting
Transmit Path Latency
Core Latency
Receive Path Latency
Appendix D Core Latency