MODEL 3081 pH/ORP | SECTION 16.0 | |
| GLOSSARY | |
Combination electrode | In a combination electrode, the measuring electrode and reference electrode are | |
| combined in a single body. Often the temperature element is included in the body | |
| as well. | |
Common | A point in a circuit against which voltages are measured. | |
Diagnostics | Diagnostics, also called advanced sensor diagnostics, automatically and continu- | |
| ously monitor the condition of the sensor. Diagnostics warn the user of impending | |
| or existing problems with the sensor. The most useful pH sensor diagnostics are | |
| glass impedance and reference impedance. | |
Electrode potential | Electrode potential is a measure of the tendency of a half reaction to occur as writ- | |
| ten. Electrode potentials are stated relative to a reference electrode, which by | |
| convention is the normal hydrogen electrode. The normal hydrogen electrode is | |
| assigned a potential of zero volts. | |
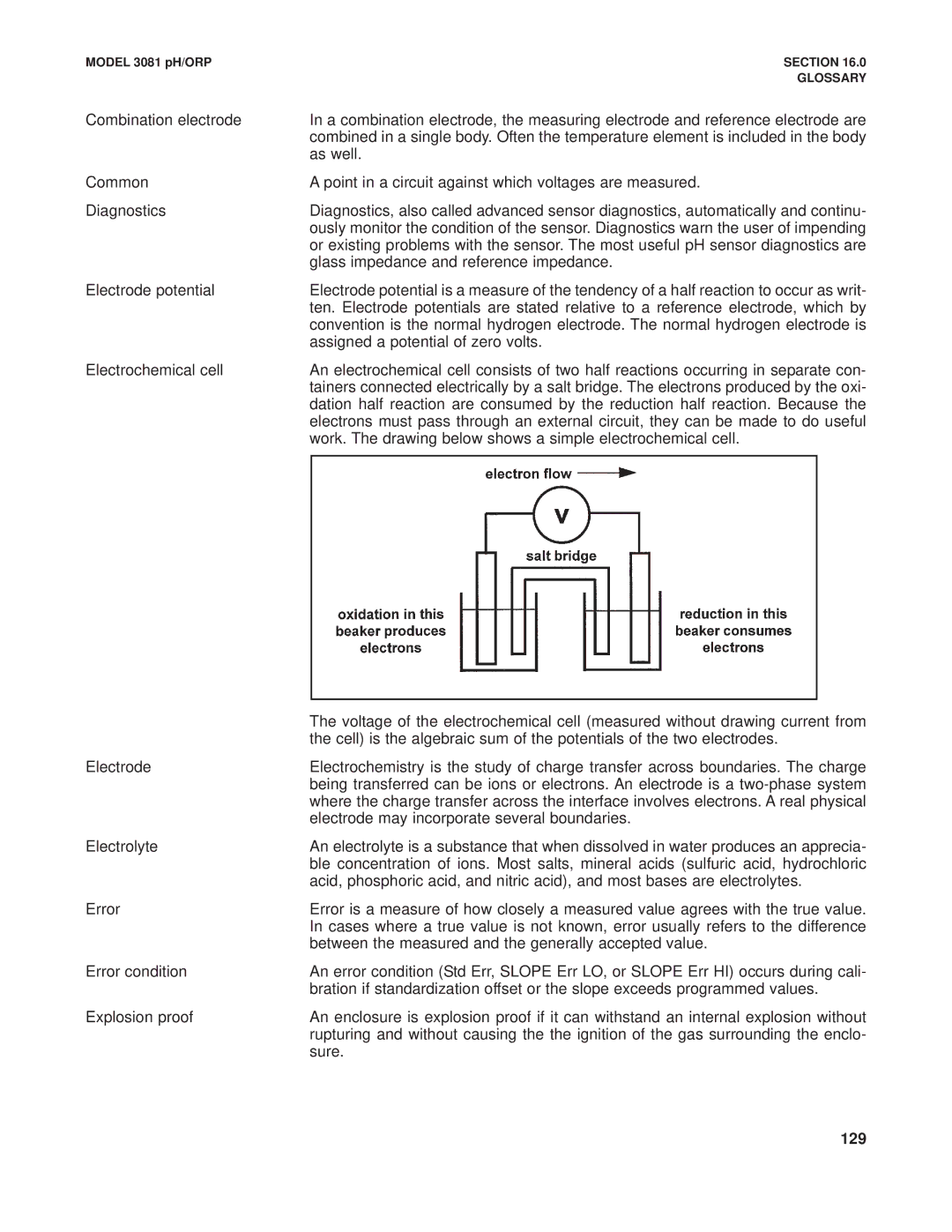
Electrochemical cell | An electrochemical cell consists of two half reactions occurring in separate con- | |
| tainers connected electrically by a salt bridge. The electrons produced by the oxi- | |
| dation half reaction are consumed by the reduction half reaction. Because the | |
| electrons must pass through an external circuit, they can be made to do useful | |
| work. The drawing below shows a simple electrochemical cell. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The voltage of the electrochemical cell (measured without drawing current from |
| the cell) is the algebraic sum of the potentials of the two electrodes. |
Electrode | Electrochemistry is the study of charge transfer across boundaries. The charge |
| being transferred can be ions or electrons. An electrode is a |
| where the charge transfer across the interface involves electrons. A real physical |
| electrode may incorporate several boundaries. |
Electrolyte | An electrolyte is a substance that when dissolved in water produces an apprecia- |
| ble concentration of ions. Most salts, mineral acids (sulfuric acid, hydrochloric |
| acid, phosphoric acid, and nitric acid), and most bases are electrolytes. |
Error | Error is a measure of how closely a measured value agrees with the true value. |
| In cases where a true value is not known, error usually refers to the difference |
| between the measured and the generally accepted value. |
Error condition | An error condition (Std Err, SLOPE Err LO, or SLOPE Err HI) occurs during cali- |
| bration if standardization offset or the slope exceeds programmed values. |
Explosion proof | An enclosure is explosion proof if it can withstand an internal explosion without |
| rupturing and without causing the the ignition of the gas surrounding the enclo- |
| sure. |