Version
3Com Telecommuting Module
Page
United States Government Legend
Page
Table of Contents
Page
Part I. Introduction to 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Page
Configuration alternatives
What is a Telecommuting Module?
Introduction to 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
DMZ/LAN Configuration
DMZ Configuration
Standalone Configuration
Quick guide to 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module installation
Introduction to 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
About settings in 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Introduction to 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Installation
Installing 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Installation with magic ping
Installation with a serial cable
Page
Page
Page
Page
Installation with a diskette
Page
Page
Remember to lock up the Telecommuting Module
Turning off a Telecommuting Module
Installing 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Log on again
Configuring 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Logging on
Site Map
Navigation
Log out
SIP Services
Administration
Basic Configuration
Network Configuration
Overview of configuration
Quality of Service
Failover
Virtual Private Networks
Preliminary and permanent configuration
Page
Mask/Bits
IP address
No. of computers Mask Bits
Name queries in 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Page
Configuring 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Part II. How To
Page
Networks and Computers
How To Configure SIP
DMZ Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the WAN
Surroundings
Interoperability
Basic Settings
Routing
Filtering
Save/Load Configuration
DMZ Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the LAN
Networks and Computers
Basic Settings
Routing
Standalone Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the WAN
Basic Settings
Filtering
Standalone Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the LAN
Client Settings
Basic Settings
Interoperability
DMZ/LAN Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the WAN
Basic Settings
Filtering
DMZ/LAN Telecommuting Module, SIP server on the LAN
Interoperability
Filtering
LAN Telecommuting Module
Surroundings
Filtering
Remote SIP Connectivity
Firewall
How To Configure SIP
Outgoing Calls
How To Configure Advanced SIP
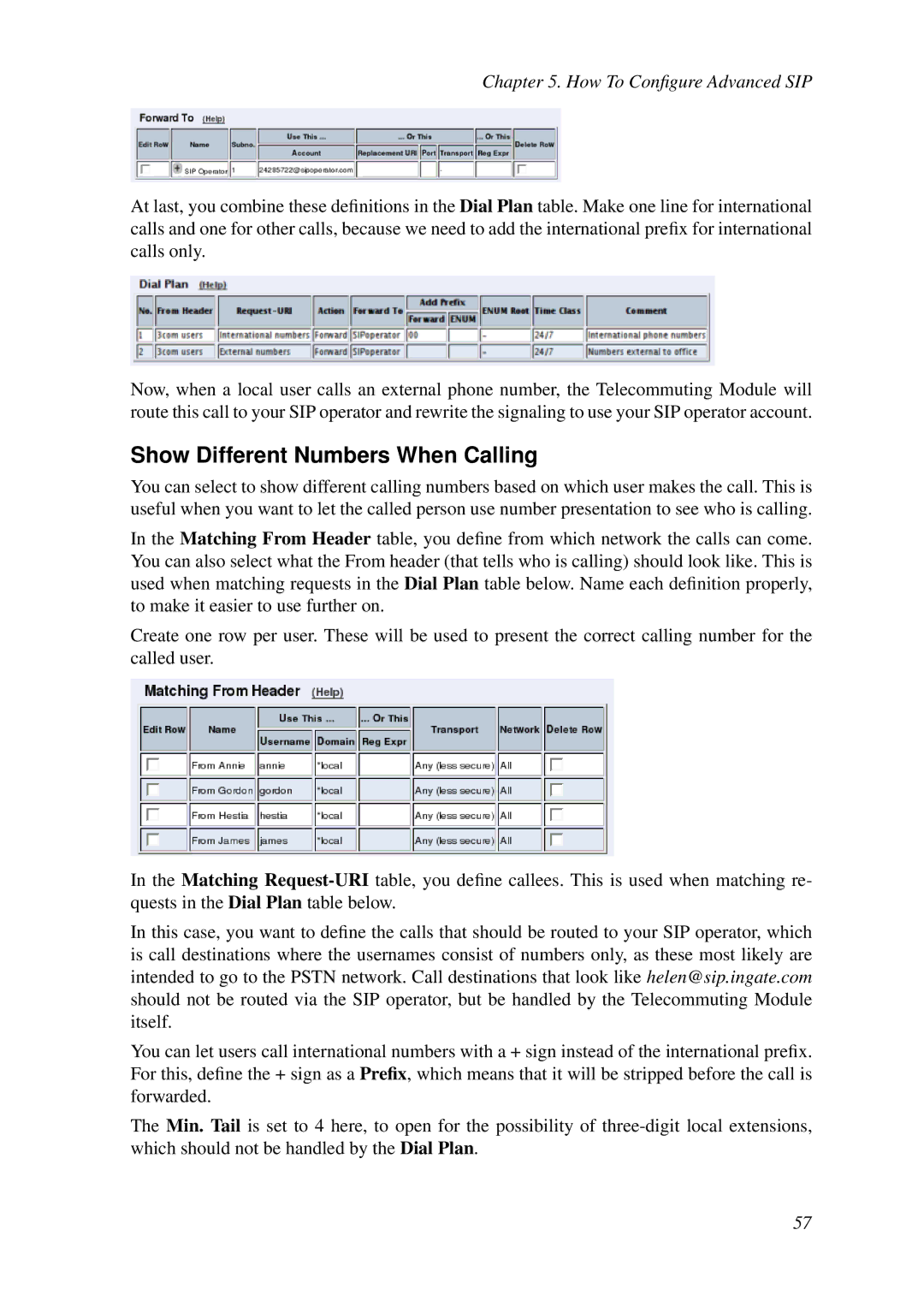
Show One Number When Calling
Show Different Numbers When Calling
Incoming Calls
Page
Authentication by Accounts a.k.a SIP Trunk via SIP accounts
Page
Page
Page
Incoming Calls
Page
Multiple Operators Least Cost Routing
Page
Multiple PBXs
How To Configure Advanced SIP
How To Configure Advanced SIP
Page
Page
Page
Page
Basic Configuration
Basic Configuration
General
Name of this Telecommuting Module
Policy For Ping To Your 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Default domain IP Policy
DNS Servers
Cancel
Access Control
Save
Look up all IP addresses again
Configuration Transport
User Authentication For Web Interface Access
Configuration Allowed Via Interface
Configuration via Https
Configuration via Http
DNS Name Or Network Address
Configuration Computers
Configuration via SSH
Netmask/Bits
Network address
Range
Via IPsec Peer
Radius
Radius server
Radius Servers
Port
Secret
Status for Radius Servers
Identifier
Contact IP Address
Sent requests
Score
Received replies
Consecutive sends
Value
Configuration of a Radius server
Telecommuting Module IP address to respond to Snmp requests
Snmp v1 and v2c
Contact person
Node location
Access via SNMPv3
Access via SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c
Snmp
Community
Authentication
Password
Snmp Traps
User
Trap sending function
Resource Monitoring
Trap receiver
Version
SIP Sessions Trap Levels
Download the 3Com MIB
SIP User Registrations Trap Levels
CPU Load Trap Levels
DynDNS service
Dynamic DNS update
DynDNS General Configuration
Use DynDNS
User, Smtp Server
IP address for updates
Wildcard hostnames Offline URL redirection
Username
Smtp server is backup
DNS Names to Update at DynDNS
Smtp server
DNS Name
Private Certificates
Certificates
Name
Certificate
Create certificate or certificate request
CA Certificates
CA Certificate
Timeouts
Advanced
Timeout for two-way UDP connections
Timeout for one-way UDP connections
Timeout for established TCP connections
Timeout for Icmp connections
DMZ/LAN Configuration
Change Telecommuting Module Type to
Telecommuting Module Type configuration
Current Telecommuting Module Type
Change type
Duration of limited test mode
Administration
Save/Load Configuration
Test Preliminary Configuration
Apply configuration
Backup
Show Message About Unapplied Changes
Save/Load CLI Command File
Revert to Old Configurations
Show Configuration
Abort All Edits
Reload Factory Configuration
Old password
User Administration
Password For the ’admin’ Account
Change administration password
New password, Confirm password
Other Accounts
Account Type
Currently Logged In Administrators
Upgrade
Upgrade
Log Out
Step
Accept upgrade
Try the upgrade
Abort upgrade
Table Look
Edit Column
Change Time Zone
Date and Time
Date
Change Date and Time Manually
Time
Set date and time manually
Synchronize time with NTP
NTP Servers To Use If NTP Is Enabled
Change Date and Time With NTP
Restart
Reboot Your 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Restart the SIP Module
Automatic Restart of the SIP Module
Administration
Administration 118
Networks and Computers
Network Configuration
Lower Limit
Name
Subgroup
Interface/VLAN
Upper Limit
Delete Row
Create
Main Default Gateways
Default Gateway
Priority
Interface
Gateway Reference Hosts
Policy For Packets From Unused Gateways
Interface name
Interface Network Interface 1
Physical device
Obtain IP Address Dynamically
Directly Connected Networks
Broadcast address
Alias
Vlan Id
Vlan Name
Static Routing
Router
Routed network
Named VLANs
Vlan
Interface Status
Interface Status
PPPoE Client Status
Dhcp Client Status
Keep Alive
Authentication
PPPoE
Log class for PPPoE negotiations
Surroundings
LCP echo-request interval
Additional Negotiators
Data Interfaces
Network
Select a data interface here
Network Configuration 136
Display Log
Logging
Search the Log
Display log
Packet Selection
Support Report
IP Address Selection
Packet Type Selection
Protocol/Port Selection
All IP protocols
Icmp
Call-ID
SIP Packet Selection
SIP Methods
IP addresses
Time Limits
Show newest at top
Show This
Export the Log
Clear form
Log
RST
Display Load
Time Period
Packet Load
Direction
Unit
Value
Diagram Size
Diagram
Diagram Heading
View diagram
Log class for non-SIP packets
Inbound Traffic
Log class for spoofed packets
Log class for broadcast packets
Log class for Radius errors
Log class for email errors
Log class for Snmp errors
Log class for Dhcp requests
Log class for IPsec key negotiations
VPN Events
Log class for IPsec key negotiation debug messages
Log class for ESP packets
SIP Events
Other
Local Log
Log Classes
Email Address
Syslog
Log Sending
Syslog Servers
Smtp Server
Status for Outbound Email
Reverts the fields to the previous configuration 157
Logging 158
Administration of SIP
SIP Services
Basic Settings
SIP Module
Provisioning Relay
Additional SIP Signaling Ports
Transport
Comment
SIP Servers To Monitor
SIP Media Port Range
Public IP address for NATed Telecommuting Module
Server
SIP Logging
Log class for SIP signaling
Relaxed Refer-To
Interoperability
Loose Routing
Translation Exceptions
Remove Via Headers
SIP Server
Except this from translation
Always Translate This
Expires Header
Force Translation
URI Encoding
User Matching
Signaling Order of Re-INVITEs
Loose Username Check
Transmit RTP/AVP With sdescriptions
Accept RTP/AVP With sdescriptions
Force Record-Route for Outbound Requests
Force Record-Route for All Requests
Accept TCP Marked As TLS
Force Remote TLS Connection Reuse
Remove Headers in 180 Responses
Allow Large UDP Packets
Preserve RFC 2543 Hold
Forward Cancel Body
Use Cancel Body In ACK
Convert Escaped Whitespaces in URIs
Allow RFC 2069 Authentication
Open Port 6891 For File Transfer
Ports and the maddr Attribute
Keep User-Agent Header When Acting as B2BUA
Strip ICE Attributes
Timeout for SIP over TCP/TLS
Session timer
Sessions and Media
Session Configuration
Limitation of sender of media streams
Media Configuration
Allowed number of concurrent sessions
Limitation of RTP Codecs
Type
Codecs
Name
This Codec Is Allowed
Music on Hold Redirection
Local Ringback
Local Ringback Played at Call Transfer
Ring Tone for Local Ringback
Maximum timeout for Invite requests
Default timeout for Invite requests
Requests
SIP blacklist interval
Remote SIP Connectivity
Base retransmission timeout for SIP requests
Maximum number of retransmissions for Invite requests
Maximum number of retransmissions for non-INVITE requests
Stun server
Stun Server
Stun server IP addresses
Stun ports
Remote NAT Traversal
Remote Clients Signaling Forwarding
Remote NAT traversal
IP Address for Remote Clients
NAT timeout for TCP
NAT timeout for UDP
Forward Signaling from IP Address
NAT keepalive method
SIP Methods
SIP Traffic
Traffic To
Method
Allow
Auth
Sender IP Filter Rules
Filtering
From Network
Action
Default Policy For SIP Requests
Content Types
Content Type
Allow
Header Filter Rules
Local SIP Domains
Default Header Filter Policy
Local Registrar
Domain
Local SIP User Database
Register From
Authentication and Accounting
Authentication Name
SIP User Database
Authentication settings
Use P-Asserted-Identity
Asserted-Identity
Trusted Domains
Network
Radius Accounting
Dial Plan
Use Dial Plan
Emergency Number
Reg Expr
Matching From Header
Prefix
Matching Request-URI
Head
Tail
Min. Tail
Forward To
Subno
Replacement URI
Dial Plan
Forward To
Request-URI
Add Prefix
Enum Root
Register in Dial Plan
Methods in Dial Plan
Method
Enum Root
Routing
DNS Override For SIP Requests
SIP Routing Order
Weight
Relay To
Port
Routing Function
Class 3xx Message Processing
Requests To User
Static Registrations
Also Forward To
User
Always handle Refer locally
Local Refer Handling
For clients not supporting Refer
Sip/sips
For dialogs with specified From URI
For clients not supporting replaces
For dialogs with specified User-Agent header
From URIs For Which Refer is Handled Locally
Restrict Incoming Callers
User Routing
Alias
Action
Forward
Send To Voice Mail
Voice Mail Server
From Domain
Outbound Proxy
Request-URI Domain
Domain or IP Address
Gateway
Tel URIs
Monitored SIP Servers
Registrar and Session Status
Active Sessions
Monitored SIP server
Registered Users
Monitored SIP server status
Registered from
Packet Capture
Tools
Network Interface Selection
IP Address Selection
Tools Any
Icmp
Collect data
Check Network
Check Network
Test Results
Page
Tools 222
DMZ type
Firewall and Client Configuration
SIP over UDP
SIP over TCP/TLS
SIP clients
DMZ/LAN type
Standalone type
SIP clients
Part IV Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module Serial Console
Page
Main Menu
Basic Administration
Connecting to the serial console
Command line interface
Set password
Exit admin
Wipe email logs
Deactivate other interfaces
Physical device name
Configure from multiple computers
Configure from a single computer
Password
Wipe email logs
Exit admin
Set password
Basic Administration 236
Help and Troubleshooting
Command Line Reference
Command Reference
Modifying Tables
Load-factory
List-tables
Modify-row
Revert-edits
Table Definitions
Config.authlogclass
Config.allowconfig
Config.allowviainterface
Config.httpservers
Config.authentication
Config.httpsservers
Config.mgmtlogclass
Fent.alwaysfent
Failover.ifacerefhosts
Fentalwaysfentexceptions
Fentalwaysfentinterfaces
Field Name Field Type Explanation Enabled OnOffToggle
Fent.mapsignaladdress
Fent.fentkeepalive
Fent.mediarelease
firewall.blindroutepolicy
firewall.defaultpolicy
firewall.broadcastlogclass
firewall.dhcplogclass
firewall.pingpolicy
firewall.networkgroups
firewall.ownlogclass
firewall.policylogclass
firewall.services
firewall.spoofinglogclass
firewall.timeclasses
Idsips.predefinedipsrules
Idsips.active
Ipsec.cryptodef
Idsips.ratelimitedips
Ipsec.espproposals
Ipsec.espahlogclass
Ipsec.ikeproposals
Ipsec.ikelogclass
Ipsec.ipsecnets
Ipsec.nattkeepalive
Ipsec.plutoverboselogclass
Ipsec.plutologclass
Ipsec.radiusauthserver
Field Name Field Type
Ipsec.x509cacerts
Ipsec.tunnelednets
Ipsec.userauthlogclass
Ipsec.x509cert
Misc.conntracktimeouts
Misc.dnsservers
Misc.dyndns
Misc.fversion
Misc.dyndnsname
Misc.ntpservers
Field Name Field Type Explanation DomainName
Misc.unitname
Monitor.cpuloadlevelalarm
Misc.usentp
Monitor.emailalertlogclass
Monitor.radiuserrorslogclass
Monitor.memorylevelalarm
Monitor.hardwarelogclass
Monitor.logclasses
Monitor.snmpagentlogclass
Monitor.siplevelalarms
Monitor.snmpagentaddress
Monitor.snmpmanagementstations
Monitor.snmpcontactperson
Monitor.snmpnodelocation
Monitor.snmppacketlogclass
Monitor.snmpv3access
Monitor.snmpv1v2caccess
Monitor.snmptrapsending
Monitor.snmpv1v2cauth
Monitor.syslogservers
Network.extradefaultgateways
Monitor.watchdogs
Network.aliasaddresses
Network.pppoe
Network.interfaces
Network.localnets
Network.routes
Network.routetestservers
Network.vlans
Field Name Field Type Explanation Server DnsIpAddress
Pptp.pptpenable
Password.adminusers
Pptp.grelogclass
Pptp.pptplogclass
Pptp.pptpusers
Pptp.pptpserverip
Pptp.pptpneglogclass
Field Name Field Type Explanation PPTPOwnIpReference
Qos.classes
Qos.bandwidths
Qos.egressqueueing
Qos.egressdefaultqueueing
Qos.ingressdefaultqueueing
Qos.sipcac
Qos.ingressqueueing
Qos.status
Qos.tagging
Sip.active
Sip.acceleratedtls
Sip.addexpireheader
Sip.allowedcodecs
Sip.authmethods
Sip.defaultgateway
Sip.b2buaofferfromtemplate
Sip.codecfiltering
Sip.externradiusdb
Sip.emergency
Sip.externalrelay
Field Name Field Type Explanation DnsIpAddress
Sip.fixfiletransferport
Sip.forwardcancelbody
Sip.forcemodify
Sip.forwardtoheader
Sip.headerfilterrules
Sip.headerfilterdefault
Sip.ignoreuriportwhenmaddr
Field Name Field Type Explanation Action Sipfilteractionsel
Sip.lcscompanion
Sip.largeudp
Sip.listen
Sip.localdomains
Sip.looseusernamecheck
Sip.loosereferto
Sip.lrtrue
Sip.mediaencryptionpolicy
Sip.mediaencryptionsuite
Sip.mediaencryptionsettings
Sip.mediaports
Field Name Field Type Explanation Portslower PortNumber
Sip.mediarestriction
Sip.mediatimeouts
Sip.message
Sip.mfull
Sip.mimetypes
Sip.optiontimeout
Sip.monitorserver
Sip.musiconhold
Sip.outboundproxy
Field Name Field Type Explanation Timeout OptionTimeout
Sip.percent20towhitespace
Sip.preserve2543hold
Sip.recurseon3xxinb2bua
Sip.radiusacct
Sip.registrarlimits
Sip.relayrules
Sip.replyconfig
Sip.removevia
Sip.rewritetoforregisterindp
Sip.ringback
Sip.routingorder
Sip.routeusesport
Sip.rroutealways
Sip.rrouteoutbound
Sip.siperrorslogclass
Sip.signaladdressfordestination
Sip.sessionlimits
Sip.sipalias
Sip.siplicenselogclass
Sip.sipsignalinglogclass
Sip.sipmedialogclass
Sip.sipmessagelogclass
Sip.sttype
Sip.tcptimeout
Sip.stripiceattributes
Sip.surroundings
Sip.tlscacerts
Sip.tlssettings
Sip.tlsclientcfg
Sip.tlsservercfg
Sip.trusteddomain
Sip.transactionconfig
Sip.uriencoding
Field Name Field Type Explanation Uriencodingsel
Sipswitch.accounts
Sip.usecancelbodyinack
Sipswitch.b2buatransferenable
Sip.uaregister
Sipswitch.dialplan
Sipswitch.b2buatransferfromuser
Sipswitch.dialplanenable
Field Name Field Type Explanation User AliasAlias
Sipswitch.enumroot
Sipswitch.dialplanmethods
Sipswitch.forwardto
Field Name Field Type Explanation Enabled Fallbacksel
Sipswitch.requestfrom
Sipswitch.incomingunauth
Sipswitch.requestto
Field Name Field Type Explanation Url SipWildcardUrl
Sipswitch.users
Sipswitch.userrouting
Userdb.radiuslocalendpoint
Sipswitch.voicemail
Userdb.radiusservers
Voipsm.voipsm
AdminTypeSel
AdminPassword
Field Types
Voipsm.voipsmdomains
AliasAlias
AdminUser
AliasIpReference AliasUser
AuthData
CertReference
CaReference
CryptoDefReference DepUsableVlanInterface DnsDynIpAddress
DnsDynIpNetworkInterface DnsDynIpOtherHost
DyndnsServiceSel
DyndnsPassword
EnumReference
EspCryptoReference FirewallLogclassReference
InviteRetransmitCount
InterfaceSel
IpsRuleName
IpsecAuthSel
LogclassReference
IsakmpSALife
MaxMessageSizeInteger
MaxReg
OnOffButton
NonemptyString
OnOffToggle
OnOffToggleOn
OptComment
OptDnsAutoRuntimeReachableHost OptDnsIpAddress
OptDSCPInteger
OptDepOwnIpReference
OptIcmpRangeList
OptForwardToReference
OptIpsecNetReference
OptIpsecPeerReference
OptServicesReference
OptPassword
OptPercent
OptPercentFloat
OptSipUserDomain
OptionTimeout
OptString
OptTimeclassReference
RegTimeout
PptpPassword
PPTPOwnIpReference
Percent
SipUserDomainDefaultAll
SessionTimeout
SipUserPassword
SIPRadiusSel
TimerAFloat
SnmpPassword
SipWildcardUrl
SubGroup
Accountvoicemailsel
Accounttypesel
Autonegsel
Addexpireheadersel
Blindsel
Bypasstransportsel
Dpactionsel
Configauthsel
Fallbacksel
Fentkeepalivesel
Fwtypesel
Functionsel
Hitsnumber
Mediaencryptionsuitesel
Policysel
Pingpolicysel
Pqueuesel
Qostypesel
RegexpwithAt
Rfc2782weight
Restfuncsel
Rfc2782priority
Sipfilteractionsel
Sipauthdirsel
Sipfunctionsel
Sipsel
Snmpv3authsel
Snmptrapversionsel
Snmpv3privacysel
Sttypesel
Tlsservermethods
Sysloglevelsel
Tlsclientmethods
Trusteddomaintransportsel
Tlsconfsel
Uriencodingsel
Voipsmmethodsel
Windownumber
CLI command examples
Add and change firewall rules
Apply a configuration
Part V. Appendices
Page
SIP Protocol
Why use SIP?
Appendix A. More About SIP
Configuring the 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Managing Your Own SIP Domain
SIP and Firewalls
Page
Configuring the SIP Clients
Configuring the PBX
Configuring the DNS Server
Establishing a SIP session
SIP Sessions
SIP in 3Com VCX IP Telecommuting Module
Contact
SIP Packet Headers
Via
Content-Type
Record-Route
Route
Appendix A. More About SIP 328
Network troubleshooting
Appendix B. Troubleshooting
No traffic shown in the log
Traffic discarded as spoofed
SIP users can’t register on the Telecommuting Module
SIP troubleshooting
SIP users can’t register through the Telecommuting Module
SIP Trunking calls via SIP operator
Call is established, but there is no voice
Administration troubleshooting
Log Messages
SIP errors
SIP send failure -1 on socket -1 event number
Destination IP addressport is known bad. Skipping
Starting SIP TCP server at port
IPsec key negotiations
Starting SIP UDP server at port
Stopped SIP TCP server
Configuration server logins
Name Port/protocol Description
List of the most important reserved ports
WWW
Cmip
Krcmd Kerberos encrypted remote shell -kfall
Type Name
List of Icmp types
Icmp type Name Code Description
Icmp codes
Type Name Reference
Unreachable for Type
Protocol number Keyword
Internet protocols and their numbers
IP intervals
Set bits Mask IP address class
Class IP in- tervals
Reserved IP addresses
Page
ARP
Appendix D. Definitions of terms
DMZ
349
Https
NAT
Nntp
353
PPP
SIP
Uucp
357
Appendix D. Definitions of terms 358
Software developed by Peter Åstrand
Appendix E. License Conditions
BSD derived licenses
Terms
Software developed by Carnegie Mellon University
Software developed by Cisco Systems
Software developed by Gregory M Christy
Software developed by Digital Equipment Corporation
Software developed by Jason Downs
Dhcp license
Software developed by Brian Gladman
GNU General Public License GPL
Software developed by Google, Inc
Version 2, June
Preamble
GNU General Public License
367
368
No Warranty
IBM Public License
Software developed in the GIE Dyade cooperation
Software developed by Ingate Systems
Software developed by Tommi Komulainen
USA
GNU Library General Public License Lgpl v
374
GNU Library General Public License
376
377
Page
379
380
Version 2.1, February
GNU Lesser General Public License Lgpl v
382
GNU Lesser General Public License
384
385
386
Page
Glibc Tzdata 2006a 388
Software in the GNU C distribution
Appendix E. License Conditions
Appendix E. License Conditions
392
More software in the GNU C distribution
394
License exceptions for gcc/libgcc2.c
License for lilo
License exceptions for libstdc++
License
Disclaimer
Software developed by Paul Mackerras
Software developed at M I T
Software developed by Pedro Roque Marques
Part 1 CMU/UCD copyright notice BSD like
License for Net-SNMP
Part 4 Sun Microsystems, Inc. copyright notice BSD
Part 5 Sparta, Inc copyright notice BSD
Part 6 Cisco/BUPTNIC copyright notice BSD
License for OpenSSH
License for NTP
404
Appendix E. License Conditions
406
407
Snprintf replacement Copyright Patrick Powell
409
License for OpenSSL
License for OpenSWAN
Release Derived Year Owner GPL- compatible? From
Python license
Terms and Conditions for Accessing or Otherwise Using Python
Beopen Python Open Source License Agreement Version
Cnri License Agreement for Python
CWI License Agreement for Python 0.9.0 Through
License for Python Imaging Library
License for Rdisc
More software developed by RSA Data Security, Inc
Software developed by RSA Data Security, Inc
License for SSL
Software developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc
License for stunnel
License for Sun RPC
More software developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc
Software developed by Trusted Information Systems, Inc
License for termcap
Software developed by Paul Vixie
Software developed by Andrew Tridgell
Vovida Software License, Version
Vovida Software License v
Software developed by Rayan S Zachariassen
Software developed at University of California
License for zlib
Openswan-kernel
427
Appendix E. License Conditions
Appendix E. License Conditions Readlink
Appendix E. License Conditions 430
Solve Problems Online
Register Your Product to Gain Service Benefits
Purchase Extended Warranty Professional Services
Appendix F. Obtaining Support for Your 3Com Products
Contact Us
Access Software Downloads
Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Asia, Pacific Rim Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Country Telephone Number
Latin America Telephone Technical Support and Repair
US and Canada Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Index
For administration
Configuration logins
From the Telecommuting Module
MIBs