|
|
| Appendix C: Example Systems | |
|
|
|
| |
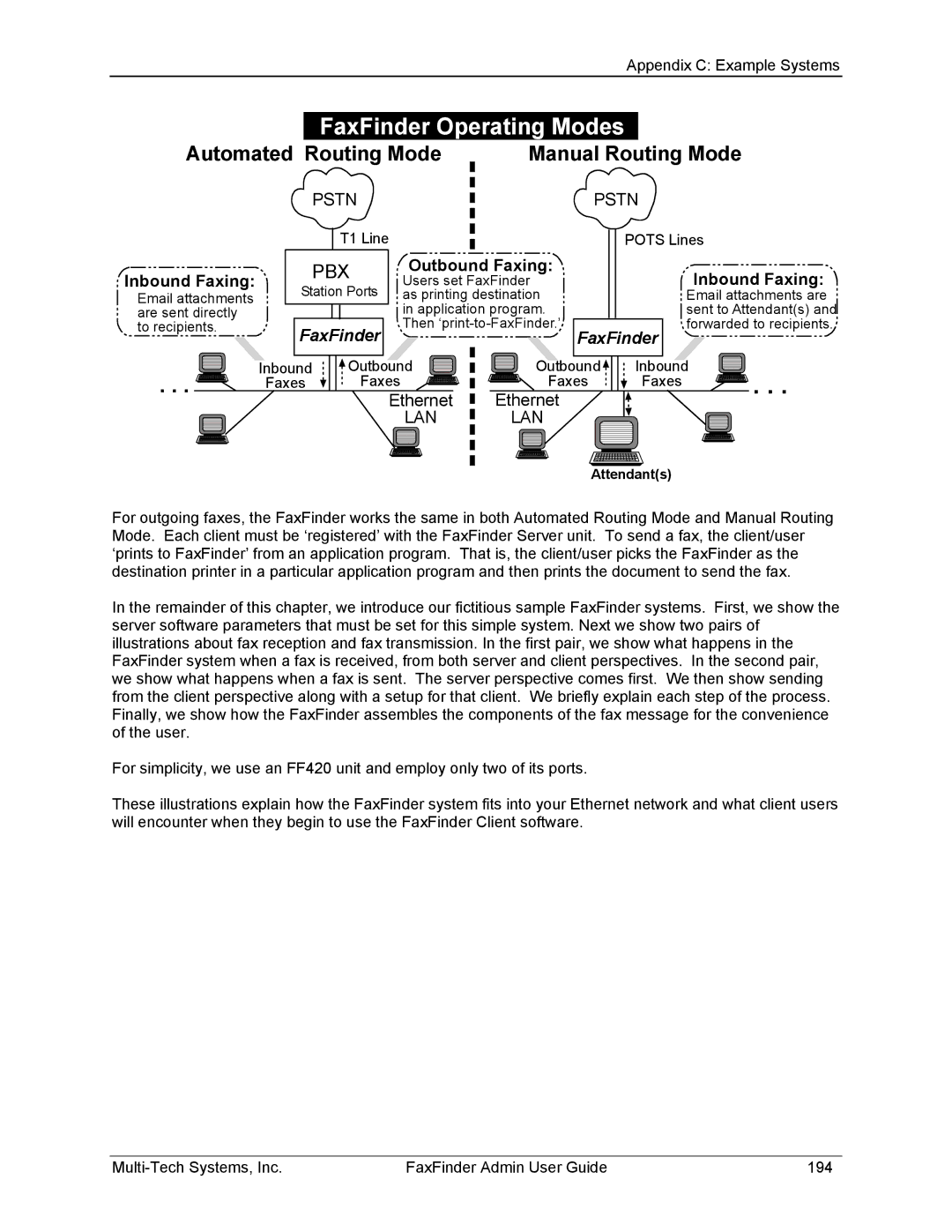
| FaxFinder Operating Modes | |||
Automated Routing Mode |
| Manual Routing Mode | ||
| PSTN |
| PSTN | |
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
T1 Line
POTS Lines
Inbound Faxing:
Email attachments are sent directly to recipients.
PBX
Station Ports
FaxFinder

 Outbound Faxing:
Outbound Faxing: 

Users set FaxFinder as printing destination in application program. Then ![]()
FaxFinder
![]()
![]() Inbound Faxing:
Inbound Faxing: ![]()
![]()
![]() Email attachments are
Email attachments are ![]() sent to Attendant(s) and
sent to Attendant(s) and ![]() forwarded to recipients.
forwarded to recipients.![]()
![]()
. . . | Inbound | Outbound | Outbound | Inbound | . . . |
Faxes | Faxes | Faxes | Faxes | ||
|
| Ethernet | Ethernet |
|
|
|
| LAN | LAN |
|
|
|
|
| Attendant(s) |
| |
For outgoing faxes, the FaxFinder works the same in both Automated Routing Mode and Manual Routing Mode. Each client must be ‘registered’ with the FaxFinder Server unit. To send a fax, the client/user ‘prints to FaxFinder’ from an application program. That is, the client/user picks the FaxFinder as the destination printer in a particular application program and then prints the document to send the fax.
In the remainder of this chapter, we introduce our fictitious sample FaxFinder systems. First, we show the server software parameters that must be set for this simple system. Next we show two pairs of illustrations about fax reception and fax transmission. In the first pair, we show what happens in the FaxFinder system when a fax is received, from both server and client perspectives. In the second pair, we show what happens when a fax is sent. The server perspective comes first. We then show sending from the client perspective along with a setup for that client. We briefly explain each step of the process. Finally, we show how the FaxFinder assembles the components of the fax message for the convenience of the user.
For simplicity, we use an FF420 unit and employ only two of its ports.
These illustrations explain how the FaxFinder system fits into your Ethernet network and what client users will encounter when they begin to use the FaxFinder Client software.
FaxFinder Admin User Guide | 194 |