USE 101
Momentum
Training
November
USE 101 10 Version
Document Set
Preface
Installing and using this product
Preface
Contents
Overview of Momentum Option Adapters
Part Communication Ports 109 Using the Modbus Ports 111
Assembling Momentum Components
181
Chapter Using the I/OBus Port 171
Chapter
141
Chapter Mapping an I/OBus Network with Modsoft 247
Saving to Flash in Modsoft 303
Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Modsoft
Part Concept 307 Configuring an M1 CPU with Concept 309
257
Mapping an I/OBus Network with Concept 361
Saving to Flash 399
Saving to Flash with Concept 399
Appendix B
417
Contents Xiv
Version Change
About This Book
Documentation
About Book
Related
You may find the following other manuals useful
This Part
Getting Started
At a Glance
Purpose
Getting Started
This Chapter This chapter contains the following sections
Overview of Momentum M1 Processor Adapters
To local and distributed I/O
This chapter describes the M1 Processor Adapters
Common communication bus
Characteristics of M1 Processor Adapters
Section Introducing the M1 Processor Adapters
Overview
Label Description
Front Panel illustration
Processor
Overview of Ports
Introduction
Ports Per
OBus Port
Internal Memory
Memory and Performance Characteristics
Flash RAM
Program Memory
Clock Speed
Below
Processor 984LL Flash RAM
References
Input and Output
984LL Executive IEC Executive Registers Discretes
Refer to 870 Use 002 00 V Momentum I/O Base User Guide
Power Supply
Supplied by
Base
Specifications for each Processor Adapter
Section Features of Each Processor Adapter
CCS 700
Features, an illustration and specifications
Overview
Input and Output References
Status Function
Servicing
Operating Conditions
Specifications
Safety Parameters
Mechanical
Overview
LED
Specifications
CCS 760
IEC Input and Output References
984LL Input and Output References
Temperature 40 ... +85 degrees C Humidity 95% noncondensing
CCC 760
LED
Specifications
CCS 780
LED
Specifications
CCC 780
LED
Specifications
CCC 960
Features, a illustration and specifications
RUN
Indicato Status Pattern
Specifications
Scantime Formula for 984LL Exec Example
CCC 960 30 will not operate in a
Processor Adapter, including key
Label Description
Indicator Status Pattern
Specifications
Scantime Formula for 984LL Exec Example
CCC 980
LED
Specifications
Scantime Formula for 984LL Exec Example
Overview
Label Description
LED
Specifications
Scantime Formula for 984LL Exec Example
This Chapter
Overview of Momentum Option Adapters
This chapter contains the following sections
Section Introducing the Momentum Option Adapters
Basic Features of Option Adapters
This section includes the following topics
Front panel components and specifications
Section Serial Option Adapter
This Section
Front Panel Components
An LED indicator
Battery compartment
Modbus Port 2 connector
Green
Modbus Port
Pinouts for
Pin For RS232 For RS485
Time-of-Day Clock
Specifications
Specifications
This section contains the following topics
Section Modbus Plus Option Adapter
Pin D-shell connector for Modbus Plus communications
Address switches
Connector, and battery compartment
Pattern Meaning
Address
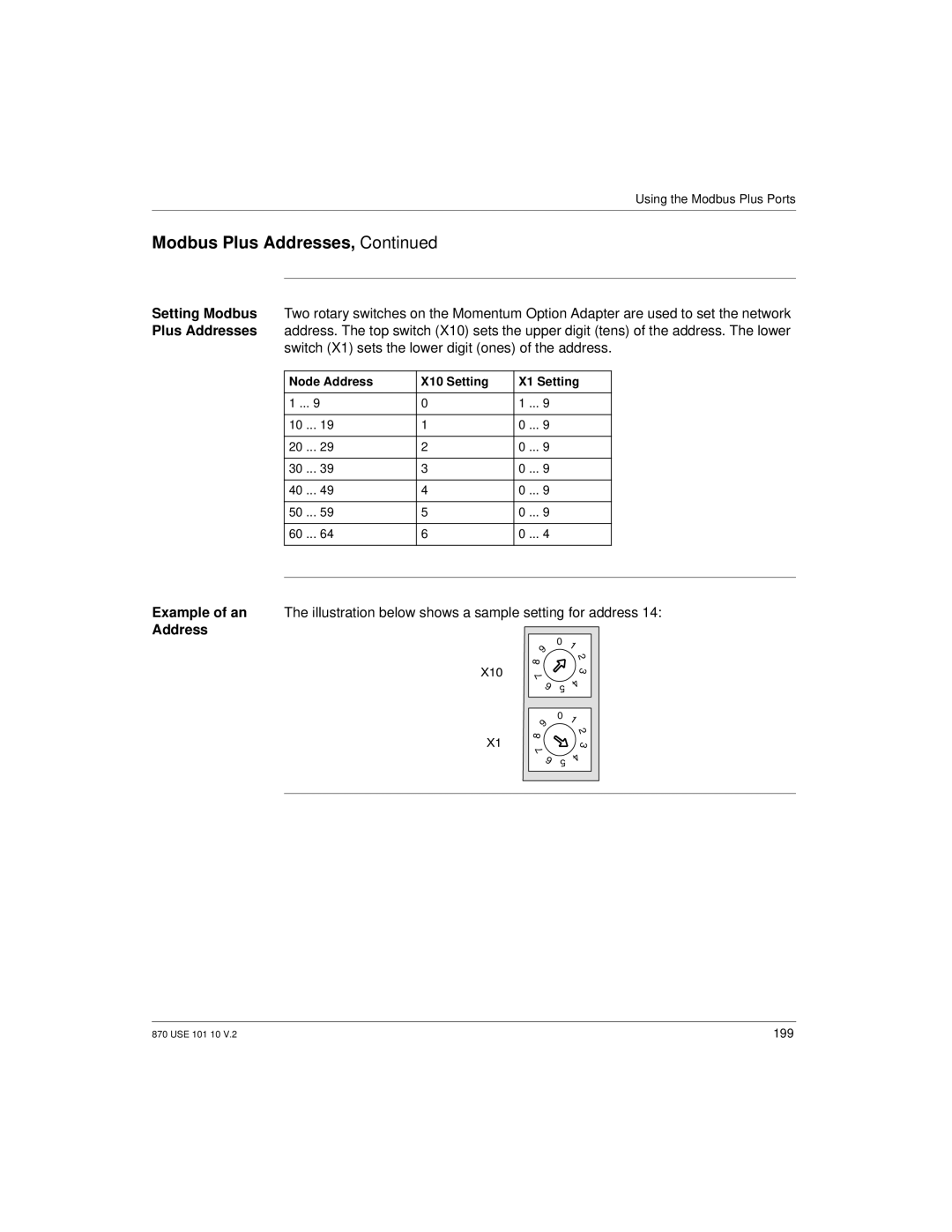
Switches
Switches in this illustration are set to address
Modbus Plus
Specifications
Specifications
Section Redundant Modbus Plus Option Adapter
Three LED indicators
Two 9-pin D-shell connectors for Modbus Plus communications
Compartment and Modbus Plus connectors
MB+ ACT
Patterns
MB+ ACT Flash
Status of the Modbus Plus node
Modbus Plus
Specifications
Option Adapters
Option Adapters
Assembling Momentum Components
Section Assembling a CPU
How to disassemble them
Connections at three points
Assembling a Processor Adapter and I/O Base
Assembling a Base Processor Adapter and an I/O Base
Procedure
Step
Next Step
Procedure Assembling a Processor Adapter and an Base
Personnel
Processor Adapter from an I/O base
Disassembling a Processor Adapter from an I/O Base
Step Action
Disassembling a Processor Adapter from an I/O Base
Section Assembling a CPU with an Option Adapter
Assembling a Processor Adapter and an Option Adapter
PIN Alignment
Assembling an Processor Option Adapter
Next Step
Two slots on the sides of the I/O base
Mounting the Assembled Adapters on the I/O Base
Assembled Processor and Option Adapter on an I/O base
Front of the I/O base
Procedure Mounting the Assembled Adapters on an I/O Base
Mounting the Assembled Adapters on the I/O Base
Tools Required
Disassembling a Module with an Option Adapter
Exposed Circuitry in Battery Compartment
Procedure Removing the Adapter Assembly from the I/O Base
103
Procedure Disassembling An Option Adapter and M1 Processor
While handling the equipment during battery maintenance
Section Installing Batteries in an Option Adapter
Installation Guidelines
Time-of-day clock in the event that the CPU loses power
For Concept
Battery
Removing
Replacing Following illustration Batteries Monitor
Guidelines for Labeling the CPU
Section Labeling the CPU
Fill-In Label
Example of a a fill-in label is illustrated below
Processor Adapters and Option Adapters
Communication Ports
Communication Ports 110
Accessories and pinouts
Using the Modbus Ports
Section Modbus Port
Accessories, and provides pinouts
Modbus Port
Connector Type
Stop Bit Modbus Address
Baud
Parity
Mode/Data Bits
Auto-Logout
Default
Feature
Parameters
Length Part Number
Cable Accessories for Modbus Port
Cables
Electric
Pinout
Pinouts for Modbus Port
118
Topics
RS485 Port
Features of an
Two Types
Port
Comm Protocol
RS232 protocol
Modbus network address
Four-Wire Cabling Schemes for Modbus RS485 Networks
Label Description Part Number
125
Potential for Multimaster Conflicts
Two-Wire Cabling Schemes for Modbus RS485 Networks
Slave Cabling
Cable
Require the special master communication cable
Multimaster
Two-Wire Cabling Schemes for Modbus RS485 Networks
Master
Scheme. This cable is 10 long and has a blue boot
Cable for Modbus RS485 Networks
Network for Momentum components
Interconnect
Boot
Crimping Tool
Other Premade
Custom Cable
Vendors
RS485 network for Momentum components
Connectors for Modbus RS485 Networks
Custom Cabling network
Shunt Plugs
Terminating Devices for Modbus RS485 Networks
Terminating
Resistor Plugs
Pin Function
Pinouts for Modbus RS485 Networks
For RS485. The metal shell is connected to chassis ground
Pin D-Shell
137
Modbus RS485
Connector T Base DB9 Base
Connector T Base RJ45 Base
Resistor Plugs Terminating RJ45 Resistor Plugs
Using the Ethernet Port
Section Ethernet Port
Ethernet Port
Control Networks Must be Isolated from MIS Data Networks
Network Design Considerations
Handling
Networks
Supervisory
Combined
Security
On a central Ethernet hub
Cabling Schemes
As shown in the following table
Components
Pinouts
Pin
Assigning Ethernet Address Parameters
150
151
Refer to the Bootp Lite user documentation for instructions
Using Bootp Lite to Assign Address Parameters
Specifying Addresses Stopping Processor
Follows
Reading Ethernet Network Statistics
By the user
Statistics
Description
Words 16, 17 High Word Not used, always
Framing Errors
Overflow Errors
CRC Errors
Words 26
Errors
Transmit Buffer
157
What’s in this
Section Establishing a Connection with an Ethernet Module
Section
Establishing a Connection with an Ethernet Module
Using the Network Options Ethernet Tester
160
161
Section Accessing Embedded Web Pages
Accessing the Web Utility Home
Section CCC 960 30 and 171 CCC 980 30 Web Pages
Link Results
Momentum M1E Web Pages
Its status. It has the following links
Configuration
M1E I/O Status
Links and LED indicators
Ethernet
Transmit Statistics Receive Statistics Functioning Errors
Following links
Technical Assistance
Contacting Schneider Automation
Table below
Momentum M1E Indicators
Indicators
Adapter LED
This chapter contains the following topics
Using the I/OBus Port
As many as 255 slave devices over an Interbus cable
Bus Port
How I/OBus Works
Network Status Indication in the M1 Ethernet Module
Distance
Guidelines for I/OBus Networks
Between Nodes Number
176
Low Profile
Cable Accessories
178
Pin Wire Color Ingoing Connection
Pin Wire Color
Using the I/OBus Port 180
Modbus Plus ports are available with
Using the Modbus Plus Ports
172 PNN 210 Option Adapter Single Port PNN 260
Introduction Cluster Mode Nodes
Modbus Plus Features for Momentum
Two Types of Modbus Plus Networks
184
Between Nodes
Standard Cabling Schemes
Network
Momentum
Used
Clusters in a
Cluster Mode Cabling Schemes
Minimum length of cable between clusters is 10 ft m
Cluster Scheme
Second cluster
Cable Within
Cable Accessories for Modbus Plus Networks
Clusters
192
Modbus Plus Connector T XTS 020 DB9 base
Plus network for Momentum components
Pinouts and Wiring Illustrations for Modbus Plus Networks
195
RJ45 Shielded Connector
Modbus Plus Connector T DB9 Base
DB9 Connector
197
Will be passed from device to device
Modbus Plus Addresses
Sequence
Node Address X10 Setting X1 Setting
Peer Cop
Received
Effect of Using
How Peer Cop
Data Is Sent
Using the Modbus Plus Ports 202
Modsoft
To Flash using Modsoft
For Information On
Page
Chapter contains the following topics
Configuring an M1 CPU with Modsoft
Modsoft
Section Configuring the Processor Adapter
Selecting an M1 Processor Adapter
Starting from the Configuration Overview editor
Follow the steps below to select an M1 Processor Adapter
208
Configuration
Which Type
Specifying an M1 Processor Type
Should Choose?
Push Enter
12.0K Adapter Parameters
Default Configuration Parameters
Adapter Parameters
Defaults for an
Parameter 4K Adapter 12.0K Adapter 18.0K Adapter
Default Values Here are the default parameters
Changing the Range of Discrete and Register References
Step Action
Words allocated the configuration extension memory
Fields in the Configuration Overview screen
Changing the Size of Your Application Logic Space
Cases
Changing the Number of Segments
For I/OBus
For All Other
Type the new number of segments
Processors
Changing the Size of the I/O Map
Your Processor Adapter supports an I/OBus network
All Other
I/O Map
How Much
Establishing Configuration Extension Memory
Configuration extension memory
Pull-down list
Clock features of the Momentum Option Adapters
Section Configuring Option Adapter Features
Reserving a
Reserving and Monitoring a Battery Coil
Configuration Overview editor in Modsoft
Battery Coil
225
Registers for TOD Clock
Setting up the Time-of-Day Clock
Block of eight 4 x registers
Reserving
Reserving Registers for the TOD Clock
Next Step Setting the time
Option
Setting the Time
Bits
Running while you are setting the bits
Setting
Status Bits
Clock
Clock Example
Describe how to interpret the time-of-day clock registers
Reading the Time-of-Day Clock
Reading
Parameters
Section Modifying Communication Port Parameters
Values shown for Port
Accessing the Port Editor Screen
Screen is accessed from the Configuration Overview editor
How To Get
Stop Bit
Parameters Which Should Not Be Changed
Head-Slot
Possible modes RTU or Ascii
Changing the Mode and Data Bits
If the mode is RTU, the number of data bits is always
If the mode is ASCII, the number of data bits is always
Step
Changing Parity
Checking. The factory-set default is Even parity
Changing the Baud Rate
Changing the Modbus Address
Default for both ports is address
Modbus networks
Values
Changing the Delay
Delay Timing
Valid Delay
Protocol on Modbus Port
Changing the Protocol on Modbus Port
Local base unit
Accessing and Editing the I/O Map
Section Mapping the Local I/O Points
Base are the local I/O for that processor
Map
Assign the appropriate state RAM references to the unit
Editing the Local I/O Map
Special Case
Bus a
Configuring an M1 CPU with Modsoft 246
Topics
Mapping an I/OBus Network with Modsoft
Screen
Settings
Parameter Setting
Supporting an I/O Map for an I/OBus Network
249
Accessing an I/O Map Screen for an I/OBus Network
Next Step Editing the I/OBus I/O Map
Processor Adapter Max. Modules Max. I/O Bits
Editing the I/OBus I/O Map
Move the cursor onto the desired model number and push Enter
254
Identifier Code Type
Codes
Its I/O type but not its specific model or name
Screens to define the parameters for these InterBus modules
Codes
Generic InterBus Module Identifier
Pages
For This Topic
Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Modsoft with Peer Cop
Section Getting Started
Describes the default screen
Accessing the Peer Cop Configuration Extension Screen
Reserve
Description
Default Peer Cop Screen
Networks
Section Using Modbus Plus to Handle I/O
Strategy
Devices on the Network
Strategy used to assign addresses
Momentum module on the network
Link and access a node
Defining the Link and Accessing a Node
Popup menu
Step Action Push Enter
Next Step Confirming the Peer Cop summary information
On Error
Timeout
Confirming the Peer Cop Summary Information
269
270
Next Step Specifying references for input data
Is required to handle this module
Specifying References for Input Data
Device
Requirements
273
274
Next Step Accessing the remaining devices
Address 3, using the AddNode command
Accessing the Remaining Devices
277
Completed
Completing the I/O Device Configuration in Peer Cop
Register
Assignments
Completed Peer Cop screen for node 3 should look like this
Screen Node Completed
Completed Peer Cop screen for node 4 should look like this
Completed Peer Cop screen for node 5 should look like this
Section Passing Supervisory Data over Modbus Plus
MB+ Address
Supervising device
Configuring a Node to Exchange Data
284
285
As an increment of 20 ms
For our example, we will use the default setting
Supervisor
Specifying References for Input and Output Data
Address 2. This device will
Modbus Plus address
Defining the Specific Output
Global Inputs
Defining
Specify the global input references
Defining the Global Inputs
Next Step Defining the references for the next node
Outputs
Defining the References for the Next Node
Link and Node
Defining Specific
Defining Specific Outputs
294
Inputs
Defining Global
Next Step Defining references for the supervisory computer
Will be received by both of the M1 CPUs
Defining References for the Supervisory Computer
Handle the M1 CPUs at addresses 2
Specific inputs
298
Specifying References for Node
300
Accesses node 3 and defines the references for that node
Node A Node setting Specifying
Completing the Configuration
References for that CPU
This Chapter This chapter contains the following topics
Flash using Modsoft
Saving to Flash in Modsoft
Application logic and state RAM values will be preserved
Preparing to Save to Flash
Saving to Flash
Saving to Flash
Save-to-Flash Procedure
Concept
To Flash using Concept
Page
This chapter explains how to configure a CPU using Concept
Configuring an M1 CPU with Concept
Concept
PLC
Using Concept
312
313
Step Action Choose your PLC type from the CPU/Executive menu
Defaults for a 2.4K Machine
Defaults for a 12.2K Machine
Parameter 4K Machine 12.2K Machine 18.4K Machine
Defaults for an 18.4K Machine
Maximum of state memory displayed at the top of the dialog
319
Changing the Size of the Full Logic Area
Configuration screen
Cop
Solved
Understanding the Number of Segments
Only the First
Segment is
Devices on the network bus
Area
Processors for
OBus Networks
From the Configure menu, select I/O Map
Establishing Configuration Extension Memory for Peer Cop
Adjust the amount of Configuration Extension memory
Result The Peer Cop dialog box appears
Step Action From the Configure menu, select Peer Cop
Clock features of the Momentum Option Adapters using Concept
Reserve a battery coil
Service release
Dialog box in Concept
Step Action Click the check box next to Battery Coil
Reserving a Battery Coil
Monitoring
Battery Coil When the battery is low
Setting up the Time-of-Day Clock
332
333
Time bits. The CPU must be running
Registers
Section Modifying Modbus Port Parameters
Default parameters
How to Get There
Accessing the Modbus Port Settings Dialog Box
Default Settings
Changing the Baud Rate
One of two possible modes RTU or Ascii
Changing Mode and Data Bits
Stop Bit Should Not Be Changed Changing Parity
Parity checking. The factory-set default is Even parity
Ms increments
Follow the steps in the table below to change the delay
To change the Modbus Address
Set the Stop Bit at Bridge mode is not supported
Step Address
To change the Protocol on Modbus Port
Overview
Ethernet / I/O Scanner dialog box in Concept
Accessing the Ethernet / I/O Scanner Screen
346
Use Bootp
Ethernet Configuration Options
Specify IP
IP Address
Setting Ethernet Address Parameters
Gateway
349
Parameters for I/O scanning
Configuring I/O
On the down arrow and selecting it, as shown
Unit ID Health Timeout Rep Rate
First address to write to
Read
First address to read to
Write
Description column
Copy, Cut, Paste, Delete, Sort and Fill Down buttons
Completing the I/O Configuration
Delete
Cut and Paste
Sort
Down button, following the steps in the table below
Fill Down
Result The I/O Map dialog box appears
Map Screen From the Configure menu
Module Selection
Map Local I/O Map
Editing the Local Map
Configuring an M1 CPU with Concept 360
Mapping an I/OBus Network with Concept
Segments
Reserved Words
From the Configure menu, select I/OMap
Result The Remote I/O Bus Drop dialog appears
Perform the steps in the following table
Network depends on your Processor Adapter and its executive
Processor Adapter Executive Max. Modules Max. I/O Bits
366
367
Mapping an I/OBus Network with Concept 368
Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Concept with Peer Cop
Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Concept with Peer Cop
Accessing the Peer Cop Dialog Box
Accessing the Screen
Memory Size Words
Adjusting the Amount of Extension Memory
Other Default Settings in the Peer Cop Dialog Box
Last Value
Modbus Plus communications have been restored
Option Effect
Section Using Modbus Plus to Handle I/O
Devices on the Network
Changing the Peer Cop Summary Information
Default Last Value setting to Hold on timeout
379
Required to handle this module
ADI 340 00 16-point input module
381
382
Next Step Specifying output references
170 AD0 340 00 16-point output module
Specifying References for Output Data
Specific output reference with a length of one word 16 bits
385
Specifying References for Output Data
Section Passing Supervisory Data over Modbus Plus
Devices on the Network
Peer Cop dialog box
Ms and Last Value Clear on timeout
Address 2 to
Outputs broadcast by the supervisory controller
390
Input reference
392
Defining the References for the Next Node
394
Supervisory PLC at Modbus Plus address
Peer Cop screens to handle the M1 CPUs at addresses 2
Defining References for the Supervisory PLC
Specific Inputs
Received by each of the M1 CPUs
Global Outputs
USE 101 10
Saving to Flash with Concept
Saving to Flash with Concept
Result The Online Control Panel appears
Saving to Flash
For Information On See Appendix
Appendices
Page
This Appendix
Ladder Logic Elements Instructions
This appendix contains the following topics
Ladder Logic
Symbols
Symbol Meaning Nodes Consumed
Standard Ladder Logic Elements
Integer Math Instructions
Symbol Meaning
Counter and Timer Instructions
Logic Instructions
Standard Ladder Logic Instructions
Symbol Meaning Nodes Consumed DX Matrix Instructions
Ladder Logic Subroutine Instructions
Other Special Purpose Instructions
Standard Ladder Logic
DX Loadable Support
Specify Length
Diagram of Stat
Special Stat Instruction
Avoid Discretes
Top Node
Content
Bottom Node
Word Description
Word
415
128
This Word Indicates the Status of These I/O Modules 112
Number of Blinks Code hex Error
Run LED Flash Patterns and Error Codes
Run LED Flash Pattern and Error
419
Run LED Flash Patterns and Error Codes 420
Index Numerics
Address strategy, 264, 282, 377, 388 two types, 257
423
Index 424
North Andover, MA Seligenstadt