TMS320C67x/C67x+ DSP CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide
Copyright 2005, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Read This First
Trademarks
Contents
Instruction Set
Contents Vii
Mvkl Move Signed Constant Into Register
Pipeline
Interrupts
SPRU733
Figures
−18
Tables
131
Tables
Examples
Introduction
TMS320C6000 DSP Family Overview
TMS320 DSP Family Overview
Automotive Consumer Control
−1. Typical Applications for the TMS320 DSPs
General-Purpose Graphics/Imaging Industrial
Instrumentation Medical Military
TMS320C67x DSP Features and Options
SPRU733
TMS320C67x DSP Features and Options
TMS320C67x DSP Architecture
−1. TMS320C67x DSP Block Diagram
Memory and Peripheral Options
Central Processing Unit CPU
Internal Memory
SPRU733
CPU Data Paths and Control
General-Purpose Register Files
Introduction
−1. TMS320C67x CPU Data Paths
Register Files Devices
−1 -Bit/64-Bit Register Pairs
−2. Functional Units and Operations Performed
Functional Units
Memory, Load, and Store Paths
Register File Cross Paths
Control Register File
Data Address Paths
−3. Control Registers
Acronym Register Name Section
Acronym Register Name Address Read/ Write
Register Addresses for Accessing the Control Registers
−4. Register Addresses for Accessing the Control Registers
Pipeline Stage
Pipeline/Timing of Control Register Accesses
Bit Field Value Description
Addressing Mode Register AMR
−5. Addressing Mode Register AMR Field Descriptions
B6 Mode
BK n Value Block Size
−6. Block Size Calculations
−4. Control Status Register CSR
Control Status Register CSR
Bit Field
−7. Control Status Register CSR Field Descriptions
DCC
−8. Interrupt Clear Register ICR Field Descriptions
Interrupt Clear Register ICR
−9. Interrupt Enable Register IER Field Descriptions
Interrupt Enable Register IER
−10. Interrupt Flag Register IFR Field Descriptions
Interrupt Flag Register IFR
−9. Interrupt Return Pointer Register IRP
Interrupt Return Pointer Register IRP
−11. Interrupt Set Register ISR Field Descriptions
Interrupt Set Register ISR
−11.Interrupt Service Table Pointer Register Istp
Interrupt Service Table Pointer Register Istp
Nonmaskable Interrupt NMI Return Pointer Register NRP
12 E1 Phase Program Counter PCE1
−13. Control Register File Extensions
Floating-Point Adder Configuration Register Fadcr
Control Register File Extensions
−14. Floating-Point Adder Configuration Register Fadcr
NAN2
Inexact results status for .L1
−15. Floating-Point Auxiliary Configuration Register Faucr
Floating-Point Auxiliary Configuration Register Faucr
UND
NaN select for .S2 src2
Signed infinity for .S1
−16. Floating-Point Multiplier Configuration Register Fmcr
Floating-Point Multiplier Configuration Register Fmcr
Inexact results status for .M2
Rounding mode select for .M1
Denormalized number select for .M1 src1
Topic
Instruction Set
−1. Instruction Operation and Execution Notations
Symbol Meaning
Instruction Operation and Execution Notations
Rotl
Occurs
Extu l,r
Greater than
−2. Instruction Syntax and Opcode Notations
Instruction Syntax and Opcode Notations
Ucstn Bit unsigned constant field Ucst n
SPRU733
Sdfpn
−3. Ieee Floating-Point Notations
−4. Special Single-Precision Values
Symbol Sign s Exponent e Fraction f
−2. Double-Precision Floating-Point Fields
Symbol Hex Value Decimal Value
−6. Special Double-Precision Values
Delay Slots
Instruction Type Slots Unit Latency Read Cycles†
−8. Delay Slot and Functional Unit Latency
−3. Basic Format of a Fetch Packet
Parallel Operations
Example 3−2. Fully Parallel p-Bit Pattern in a Fetch Packet
Example 3−1. Fully Serial p-Bit Pattern in a Fetch Packet
Cycle/Execute
Instructions
Cycle/Execute Packet Instructions
Example Parallel Code
Branching Into the Middle of an Execute Packet
−9. Registers That Can Be Tested by Conditional Operations
Conditional Operations
Specified
Conditional Bit Register
Resource Constraints
Constraints on Instructions Using the Same Functional Unit
Constraints on Cross Paths 1X
Following execute packets are valid
Constraints on Loads and Stores
Following code sequence is invalid
Constraints on Long 40-Bit Data
Constraints on Register Reads
However, this code sequence is valid
Constraints on Register Writes
MPYSP2DP
Constraints on Floating-Point Instructions
Intdp
Tional unit on cycle i + 4, i + 5, or i +
Addsp Subsp Spint Sptrunc Intsp Mpysp
Addressing Modes
Linear Addressing Mode
Example 3−4. LDW Instruction in Circular Mode
Circular Addressing Mode
Before LDW
Cycle after LDW Cycles after LDW
Syntax for Load/Store Address Generation
Example 3−5. Addah Instruction in Circular Mode
Before Addah
Cycle after Addah
−10. Indirect Address Generation for Load/Store
Mode Field Syntax Modification Performed
−11. Address Generator Options for Load/Store
Addressing Type Address Register
Instruction Descriptions
Instruction Compatibility
Example
Way each instruction is described
Opcode map field used For operand type Unit Opfield
Execution for .L1, .L2 and .S1, .S2 Opcodes
Pipeline StageE1 Read src2 Written dst Unit in use
Absolute Value With Saturation
ABS
Before instruction
ABSDP, Abssp
Cycle after instruction
Before instruction Cycle after instruction
Absdp
Absolute Value, Double-Precision Floating-Point
Pipeline Stage Read
ABS, Abssp
Written
Before instruction Cycles after instruction
Abssp
Absolute Value, Single-Precision Floating-Point
ABS, Absdp
ADD
Add Two Signed Integers Without Saturation
ADD
Unit in use Or .D
ADDDP, ADDK, ADDSP, ADDU, ADD2, SADD, SUB
Add Two Signed Integers Without Saturation ADD
ADD, ADDAD, ADDAH, Addaw
Add Using Byte Addressing Mode
Addab
Add Using Byte Addressing Mode Addab
Addad
Add Using Doubleword Addressing Mode
ADD, ADDAB, ADDAH, Addaw
ADD, ADDAB, ADDAD, Addaw
Add Using Halfword Addressing Mode
Addah
Add Using Halfword Addressing Mode Addah
ADD, ADDAB, ADDAD, Addah
Add Using Word Addressing Mode
Addaw
Add Using Word Addressing Mode Addaw
Adddp
Add Two Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
Add Two Double-Precision Floating-Point Values Adddp
Unit in use Or .S
ADD, ADDSP, ADDU, Subdp
Pipeline StageE1 Read cst16 Written dst Unit in use
Add Signed 16-Bit Constant to Register
Addk
Addsp
Add Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values
Add Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values Addsp
ADD, ADDDP, ADDU, Subsp
ADD, SADD, Subu
Add Two Unsigned Integers Without Saturation
Addu
Addu Add Two Unsigned Integers Without Saturation
ADD2
Add Two 16-Bit Integers on Upper and Lower Register Halves
ADD, ADDU, SUB2
Bitwise
OR, XOR
S1, .S2
Branch Using a Displacement
Opcode map field used For operand type Unit
Cycle Program Counter Value Action
Delay Slots Example
Xuint
Branch Using a Register
Written Branch Taken Unit in use
Target Instruction Pipeline Stage Read
Xsint
Branch Using an Interrupt Return Pointer
IRP
−15. Program Counter Values for B IRP Instruction
NRP
Branch Using NMI Return Pointer
−16. Program Counter Values for B NRP Instruction
CLR
Clear a Bit Field
SET
Execution Pipeline
Clear a Bit Field CLR
Cmpeq
Compare for Equality, Signed Integers
CMPEQDP, CMPEQSP, CMPGT, Cmplt
Cmpeqdp
Compare for Equality, Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
Cmpeqdp .S1
Cmpeqsp
Compare for Equality, Single-Precision Floating-Point Values
CMPEQ, CMPEQDP, CMPGTSP, Cmpltsp
Cmpgt
Compare for Greater Than, Signed Integers
CMPEQ, CMPGTDP, CMPGTSP, CMPGTU, Cmplt
Cmpgt .L1X
Cmpgtdp
Delay Slots Functional Unit Latency See Also Example
Cmpgtsp
CMPEQSP, CMPGT, CMPGTDP, CMPGTU, Cmpltsp
Cmpgtu
Compare for Greater Than, Unsigned Integers
CMPGT, CMPGTDP, CMPGTSP, Cmpltu
Cmplt
Compare for Less Than, Signed Integers
Cmplt Compare for Less Than, Signed Integers
Compare for Less Than, Signed Integers Cmplt
Wise, 0 is written to dst
CMPEQDP, CMPGTDP, CMPLT, CMPLTSP, Cmpltu
Cmpltsp
Cmpltsp .S1 A1,A2,A3
Cmpltu
Compare for Less Than, Unsigned Integers
Instruction Type Single-cycle Delay Slots See Also Example
Dpint
Convert Double-Precision Floating-Point Value to Integer
Example
Dpint
Floating-Point Value
Dpsp
DPINT, DPTRUNC, INTSP, Spdp
With Truncation
Dptrunc
DPINT, DPSP, Sptrunc
Dptrunc
EXT
Extract and Sign-Extend a Bit Field
If cond src2 ext csta, cstb → dst else nop
Extu
Extu
Extract and Zero-Extend a Bit Field
If cond src2 extu csta, cstb → dst else nop
EXT
Idle
Multicycle NOP With No Termination Until Interrupt
Idle
DPINT, INTDPU, INTSP, Intspu
Intdp
Intdp
INTDP, INTSP, Intspu
Intdpu
Intdpu
INTDP, INTDPU, Intspu
Intsp
INTDP, INTDPU, Intsp
Intspu
Register Offset
Ldbu
−17. Data Types Supported by Ldbu Instruction
Left Shift
LDH, LDW
Cycles after LDB
Before LDB
Cycle after LDB
−18. Data Types Supported by Ldbu Instruction 15-Bit Offset
Load Byte From Memory With a 15-Bit Unsigned Constant Offset
Before LDB Cycle after LDB
Pipeline Stage Read B14 / B15 Written
Or Register Offset
Lddw
Execution Pipeline Instruction Type
LDB, LDH, LDW
−19. Data Types Supported by Ldhu Instruction
Ldhu
LDB, LDW
Cycles after LDH
Before LDH
Cycle after LDH
Tion operates only on the .D2 unit
−20. Data Types Supported by Ldhu Instruction 15-Bit Offset
LDW
LDB, LDDW, LDH
Cycle after LDW
LDW
LDB, LDH
Leftmost Bit Detection
Lmbd
→ dst
MPY
Multiply Signed 16 LSB y Signed 16 LSB
MPYU, MPYSU, MPYUS, Smpy
Pipeline StageE1 E2 Read
MPY Multiply Signed 16 LSB x Signed 16 LSB
Mpydp
Multiply Two Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
Pipeline E10 Stage Read
MPY, Mpysp
MPYHU, MPYHSU, MPYHUS, Smpyh
Multiply Signed 16 MSB y Signed 16 MSB
Mpyh Multiply Signed 16 MSB x Signed 16 MSB
MPYHLU, MPYHSLU, MPYHULS, Smpyhl
Multiply Signed 16 MSB y Signed 16 LSB
Mpyhl
Mpyhl Multiply Signed 16 MSB x Signed 16 LSB
MPYHL, MPYHSLU, Mpyhuls
Multiply Unsigned 16 MSB y Unsigned 16 LSB
MPYHL, MPYHLU, Mpyhuls
Mpyhslu
Multiply Signed 16 MSB y Unsigned 16 LSB
MPYH, MPYHU, Mpyhus
Multiply Signed 16 MSB y Unsigned 16 MSB
MPYH, MPYHSU, Mpyhus
Mpyhu
Multiply Unsigned 16 MSB y Unsigned 16 MSB
MPYHL, MPYHLU, Mpyhslu
Multiply Unsigned 16 MSB y Signed 16 LSB
Mpyhuls
MPYH, MPYHU, Mpyhsu
Multiply Unsigned 16 MSB y Signed 16 MSB
Mpyi
Multiply 32-Bit y 32-Bit Into 32-Bit Result
Mpyi
Mpyid
Mpyid
Multiply 32-Bit y 32-Bit Into 64-Bit Result
Mpyid Multiply 32-Bit x 32-Bit Into 64-Bit Result
MPYLHU, MPYLSHU, MPYLUHS, Smpylh
Multiply Signed 16 LSB y Signed 16 MSB
Mpylh
Mpylh Multiply Signed 16 LSB x Signed 16 MSB
MPYLH, MPYLSHU, Mpyluhs
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB y Unsigned 16 MSB
MPYLH, MPYLHU, Mpyluhs
Mpylshu
Multiply Signed 16 LSB y Unsigned 16 MSB
MPYLH, MPYLHU, Mpylshu
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB y Signed 16 MSB
Mpyluhs
Mpysp
Multiply Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values
MPY, MPYDP, MPYSP2DP
Mpysp
Mpyspdp
MPY, MPYDP, MPYSP, MPYSP2DP
Mpyspdp
Double-Precision Result
Multiply Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values for
MPYSP2DP
MPYSP2DP
Multiply Signed 16 LSB y Unsigned 16 LSB
Mpysu
MPY, MPYU, Mpyus
MPY, MPYSU, Mpyus
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB y Unsigned 16 LSB
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB x Unsigned 16 LSB Mpyu
MPY, MPYU, Mpysu
Mpyus
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB y Signed 16 LSB
Multiply Unsigned 16 LSB x Signed 16 LSB Mpyus
Move From Register to Register
If cond 0 + src2 → dst
MVC
Move Between Control File and Register File
Src2 → dst
−21. Register Addresses for Accessing the Control Registers
Pipeline StageE1 Read Written dst Unit in use
Move Signed Constant Into Register and Sign Extend
MVK
MVKH, MVKL, Mvklh
MVKH/MVKLH
Move 16-Bit Constant Into Upper Bits of Register
If you are loading the address of a label, use
Mvkl
Pipeline Stage Read Written
MVK, MVKH, Mvklh
NEG
Negate
Ucst4 None
No Operation
NOP
Cycle after NOP
Before NOP
No operation Executes
Cycle after ADD
Norm
Normalize Integer
Execution If cond Norm src → dst Else nop Pipeline
Not
Bitwise not
Bitwise or
AND, XOR
Src1 or src2 → dst
Rcpdp
Double-Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Approximation
RCPSP, Rsqrdp
Rcpsp
Single-Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Approximation
RCPDP, Rsqrsp
Rsqrdp
If src2 is positive infinity, positive 0 is placed in dst
Rsqrsp
Rsqrsp .S1
Sadd
Add Two Signed Integers With Saturation
ADD, Ssub
Add Two Signed Integers With Saturation Sadd
SAT
Saturate a 40-Bit Integer to a 32-Bit Integer
SAT .L2
SET
Set a Bit Field
CLR
If cond src2 SET csta, cstb → dst else nop
SET .S1
SHL
Arithmetic Shift Left
SHR, Sshl
SHR
Arithmetic Shift Right
SHL, Shru
Shru
Logical Shift Right
SHL, SHR
MPY, SMPYH, SMPYHL, Smpylh
Smpy
CSR
MPYH, SMPY, SMPYHL, Smpylh
Smpyh
MPYHL, SMPY, SMPYH, Smpylh
Smpyhl
Instruction Set 223
MPYLH, SMPY, SMPYH, Smpyhl
Smpylh
Instruction Set 225
Spdp
DPSP, INTDP, SPINT, Sptrunc
Spint
Convert Single-Precision Floating-Point Value to Integer
DPINT, INTSP, SPDP, Sptrunc
Spint
Sptrunc
DPTRUNC, SPDP, Spint
Sptrunc
Sshl
Shift Left With Saturation
Sshl .S1
Ssub
Subtract Two Signed Integers With Saturation
SUB
STB
Before Cycle after Instruction
STH, STW
Store Byte to Memory With a 15-Bit Unsigned Constant Offset
Pipeline Stage Read B14 /B15 , src Written Unit in use
STH
Before
STB, STW
Instruction Cycles after
STH
Instruction Type Store Delay Slots See Also
STW
STB, STH
Store Word to Memory With a 15-Bit Unsigned Constant Offset
248
SUB
Subtract Two Signed Integers Without Saturation
Src1 − src2 → dst else nop
Src2 − src1 → dst
ADD, SSUB, SUBC, SUBDP, SUBSP, SUBU, SUB2
SUB, SUBAH, Subaw
Subtract Using Byte Addressing Mode
Subab
BK0 = 3 → size = A5 in circular addressing mode using BK0
SUB, SUBAB, Subaw
Subtract Using Halfword Addressing Mode
Subah
SUB, SUBAB, Subah
Subtract Using Word Addressing Mode
Subaw
Subtract Using Word Addressing Mode Subaw
ADD, SSUB, SUB, SUBDP, SUBSP, SUBU, SUB2
Subtract Conditionally and Shift-Used for Division
Subc
Subtract Conditionally and Shift−Used for Division Subc
Subdp
Subtract Two Double-Precision Floating-Point Values
Subtract Two Double-Precision Floating-Point Values Subdp
ADDDP, SUB, SUBSP, Subu
Subsp
Subtract Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values
Subsp Subtract Two Single-Precision Floating-Point Values
ADDSP, SUB, SUBDP, Subu
ADDU, SSUB, SUB, SUBC, SUBDP, SUBSP, SUB2
Subtract Two Unsigned Integers Without Saturation
Subu
Subtract Two Unsigned Integers Without Saturation Subu
Src1 and placed in the lower-half of dst
SUB2
ADD2, SSUB, SUB, SUBC, Subu
XOR
Bitwise Exclusive or
AND, or
Zero
Zero a Register
Pipeline
Fetch
Pipeline Operation Overview
Decode
−2. Fetch Phases of the Pipeline
−3. Decode Phases of the Pipeline
Execute
−4. Execute Phases of the Pipeline
Clock cycle Fetch
Pipeline Operation Summary
−1. Operations Occurring During Pipeline Phases
Stage Phase Symbol During This Phase Completed
Adddp
−7. Pipeline Phases Block Diagram
Example 4−1. Execute Packet in −7
Pipeline Execution of Instruction Types
Delay slots Functional Unit latency
DP Compare
Instruction Type Execution Phases Cycle DP
ADDDP/SUBDP Mpyi Mpyid Mpydp
Instruction Type Execution Phases
Instruction Type
Execution Phases
Unit in use M, or .D
Single-Cycle Instructions
−3. Single-Cycle Instruction Execution
−4 y 16-Bit Multiply Instruction Execution
2 16 y 16-Bit Multiply Instructions
−5. Store Instruction Execution
Store Instructions
−13. Store Instruction Execution Block Diagram
−6. Load Instruction Execution
Load Instructions
−15. Load Instruction Execution Block Diagram
−7. Branch Instruction Execution
Branch Instructions
−17. Branch Instruction Execution Block Diagram
−8. Two-Cycle DP Instruction Execution
Two-Cycle DP Instructions
Unit in use Or .M
Four-Cycle Instructions
−9. Four-Cycle Instruction Execution
−10. Intdp Instruction Execution
Intdp Instruction
−11. DP Compare Instruction Execution
DP Compare Instructions
−12. ADDDP/SUBDP Instruction Execution
ADDDP/SUBDP Instructions
−13. Mpyi Instruction Execution
Mpyi Instruction
Pipeline Stage E4 E5 E6 E7 E8 E9 E10 Read
Mpyid Instruction
−14. Mpyid Instruction Execution
−15. Mpydp Instruction Execution
Mpydp Instruction
−16. Mpyspdp Instruction Execution
Mpyspdp Instruction
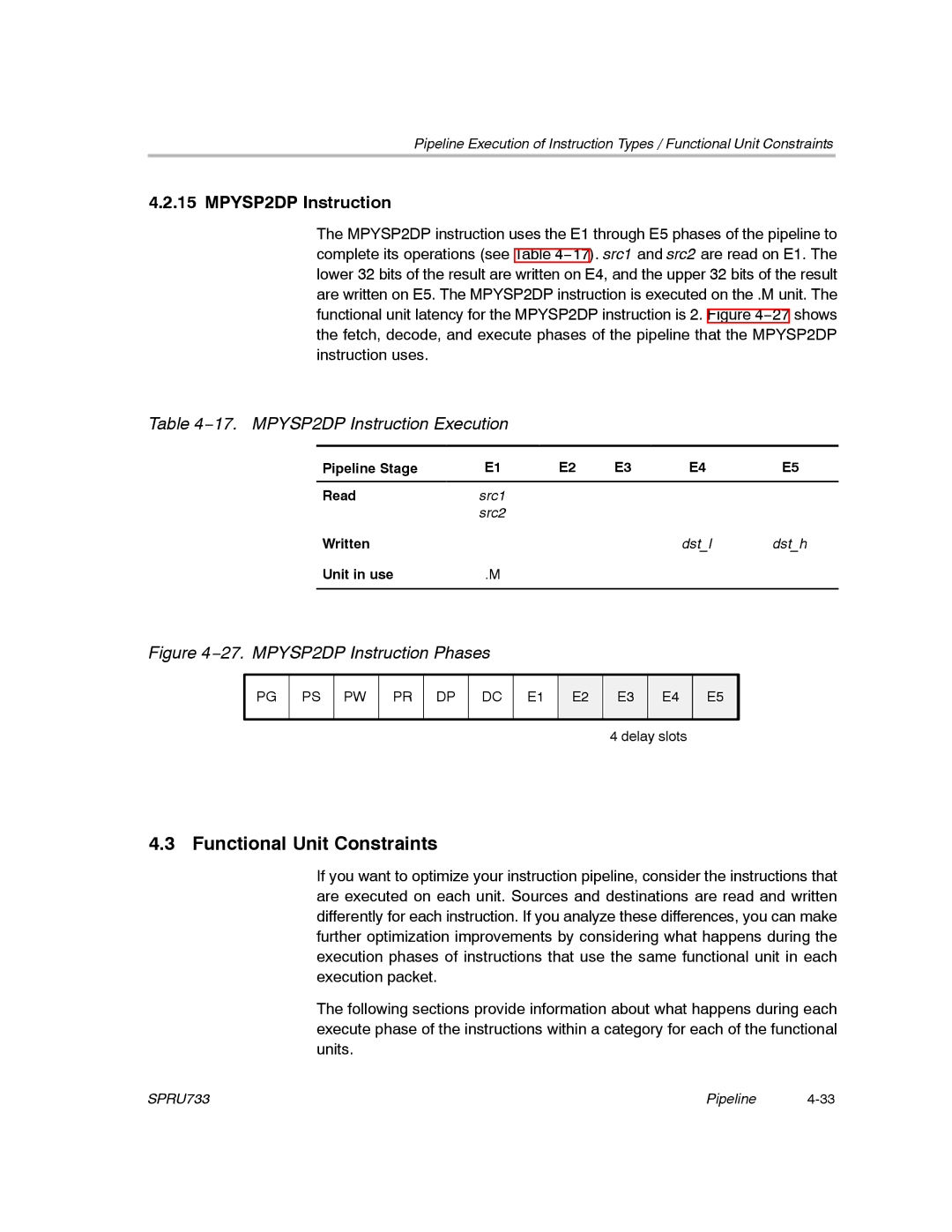
−17. MPYSP2DP Instruction Execution
Functional Unit Constraints
MPYSP2DP Instruction
Instruction Execution
Unit Constraints
−18. Single-Cycle .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−19. DP Compare .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−20 -Cycle DP .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−21. ADDSP/SUBSP .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−22. ADDDP/SUBDP .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−23. Branch .S-Unit Instruction Constraints
−24 y 16 Multiply .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−25 -Cycle .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−26. Mpyi .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−27. Mpyid .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−28. Mpydp .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−29. Mpysp .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−30. Mpyspdp .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−31. MPYSP2DP .M-Unit Instruction Constraints
−32. Single-Cycle .L-Unit Instruction Constraints
−33 -Cycle .L-Unit Instruction Constraints
−34. Intdp .L-Unit Instruction Constraints
−35. ADDDP/SUBDP .L-Unit Instruction Constraints
−36. Load .D-Unit Instruction Constraints
Unit Instruction Constraints
−37. Store .D-Unit Instruction Constraints
−38. Single-Cycle .D-Unit Instruction Constraints
Lddw
Performance Considerations
Pipeline Stall
−29. Multicycle NOP in an Execute Packet
Multicycle NOPs
Cycle #
Pipeline Phase Branch Target
Memory Considerations
−40. Program Memory Accesses Versus Data Load Accesses
Data Load
Operation
+10
−32. Program and Data Memory Stalls
Example 4−2. Load From Memory Banks
−33 -Bank Interleaved Memory
−34 -Bank Interleaved Memory With Two Memory Spaces
−41. Loads in Pipeline from Example 4−2
Interrupts
Overview
Types of Interrupts and Signals Used
Priority Interrupt Name Interrupt Type
−1. Interrupt Priorities
Nonmaskable Interrupt NMI
Interrupt Acknowledgment Iack and Interrupt Number INUMn
−1. Interrupt Service Table
Interrupt Service Table IST
−2. Interrupt Service Fetch Packet
1238h
Interrupt Service Table Pointer Istp
Example 5−1. Relocation of Interrupt Service Table
Acronym Register Name Description
Summary of Interrupt Control Registers
−2. Interrupt Control Registers
Globally Enabling and Disabling Interrupts
MVC CSR,B0
Enabling and Disabling Interrupts
Individual Interrupt Control
Status of Interrupts
Setting and Clearing Interrupts
Example 5−9. Code to Return from a Maskable Interrupt
Returning From Interrupt Servicing
Example 5−8. Code to Return From NMI
Interrupt Detection and Processing
Setting the Nonreset Interrupt Flag
Conditions for Processing a Nonreset Interrupt
Isfp
Actions Taken During Nonreset Interrupt Processing
PS PW PR DP DC
Setting the Reset Interrupt Flag
Actions Taken During Reset Interrupt Processing
Pipeline Interaction
General Performance
Single Assignment Programming
Programming Considerations
Nested Interrupts
Example 5−11. Code Using Single Assignment
STW
Example 5−14. Manual Interrupt Processing
Manual Interrupt Processing
Example 5−16. Code Sequence for Trap Return
Traps
Example 5−15. Code Sequence to Invoke a Trap
Instruction C62x DSP C64x DSP C67x DSP C67x+ DSP
Instruction Compatibility
Cmpltu
Intsp
Mpylh
Rsqrdp
Subab
Functional Unit Instruction
Table B−1. Functional Unit to Instruction Mapping
Displacement Register
Intdp Intdpu Intsp Intspu
N n n n n n n n n n n n n
STB memory
SUB Subab Subah Subaw Subc Subdp Subsp Subu SUB2 XOR Zero
Unit Instructions and Opcode Maps
Table C−1. Instructions Executing in the .D Functional Unit
Instructions Executing in the .D Functional Unit
Table C−2. .D Unit Opcode Map Symbol Definitions
Opcode Map Symbols and Meanings
Syntax Modification Performed
Table C−3. Address Generator Options for Load/Store
Figure C−1 or 2 Sources Instruction Format
32-Bit Opcode Maps
Appendix D
Table D−1. Instructions Executing in the .L Functional Unit
Instructions Executing in the .L Functional Unit
Table D−2. .L Unit Opcode Map Symbol Definitions
Figure D−1 or 2 Sources Instruction Format
Appendix E
Table E−1. Instructions Executing in the .M Functional Unit
Instructions Executing in the .M Functional Unit
Table E−2. .M Unit Opcode Map Symbol Definitions
Figure E−1. Extended M-Unit with Compound Operations
Appendix F
Table F−1. Instructions Executing in the .S Functional Unit
Instructions Executing in the .S Functional Unit
Table F−2. .S Unit Opcode Map Symbol Definitions
Figure F−1 or 2 Sources Instruction Format
Figure F−7. Branch with NOP Constant Instruction Format
No Unit Specified Instructions and Opcode Maps
Table G−1. Instructions Executing With No Unit Specified
Instructions Executing With No Unit Specified
Figure G−1. Loop Buffer Instruction Format
Index
Cmpeqdp
Dpsp
Index-4
Reset
Index-6
Mpysu
Unit No unit instructions
Rsqrdp
To memory with a 15-bit unsigned constant offset STB
260 Single-precision Subsp 263