Appendix A IP Addresses and Subnetting
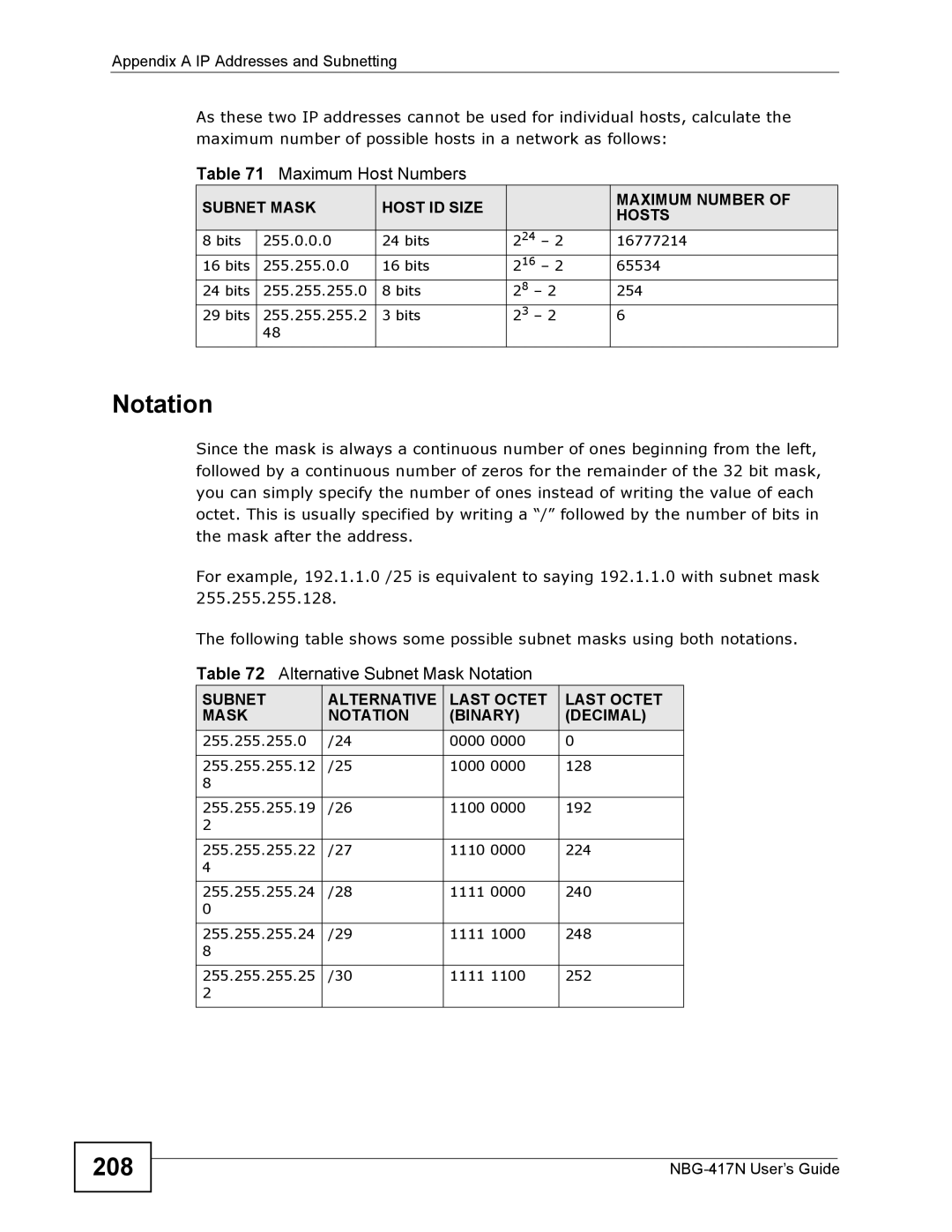
As these two IP addresses cannot be used for individual hosts, calculate the maximum number of possible hosts in a network as follows:
Table 71 Maximum Host Numbers
SUBNET MASK | HOST ID SIZE |
| MAXIMUM NUMBER OF | |
| HOSTS | |||
|
|
|
| |
8 bits | 255.0.0.0 | 24 bits | 224 – 2 | 16777214 |
16 bits | 255.255.0.0 | 16 bits | 216 – 2 | 65534 |
24 bits | 255.255.255.0 | 8 bits | 28 – 2 | 254 |
29 bits | 255.255.255.2 | 3 bits | 23 – 2 | 6 |
| 48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notation
Since the mask is always a continuous number of ones beginning from the left, followed by a continuous number of zeros for the remainder of the 32 bit mask, you can simply specify the number of ones instead of writing the value of each octet. This is usually specified by writing a “/” followed by the number of bits in the mask after the address.
For example, 192.1.1.0 /25 is equivalent to saying 192.1.1.0 with subnet mask 255.255.255.128.
The following table shows some possible subnet masks using both notations.
Table 72 Alternative Subnet Mask Notation
SUBNET | ALTERNATIVE | LAST OCTET | LAST OCTET |
MASK | NOTATION | (BINARY) | (DECIMAL) |
255.255.255.0 | /24 | 0000 0000 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.12 | /25 | 1000 0000 | 128 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.19 | /26 | 1100 0000 | 192 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.22 | /27 | 1110 0000 | 224 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.24 | /28 | 1111 0000 | 240 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.24 | /29 | 1111 1000 | 248 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
255.255.255.25 | /30 | 1111 1100 | 252 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|