Managing Zones, Neighbors and Alternates
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATION SERVER ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Configuring Zones - All Types
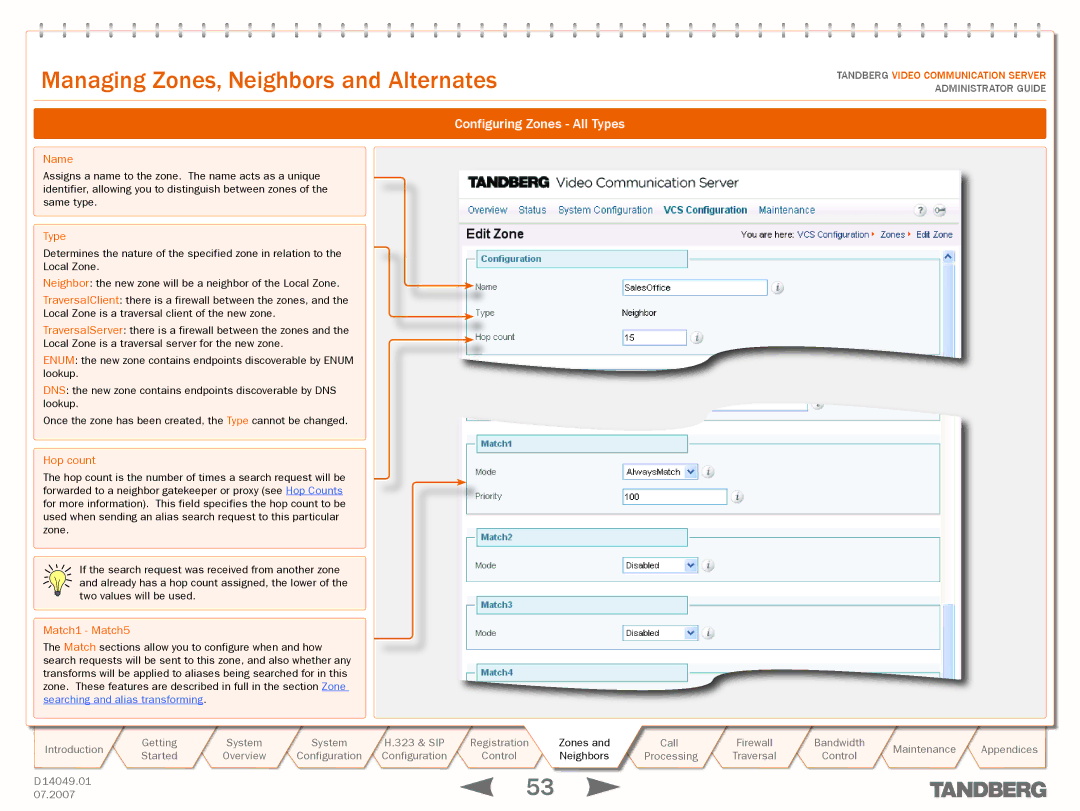
Name
Assigns a name to the zone. The name acts as a unique identifier, allowing you to distinguish between zones of the same type.
Type
Determines the nature of the specified zone in relation to the Local Zone.
Neighbor: the new zone will be a neighbor of the Local Zone.
TraversalClient: there is a firewall between the zones, and the Local Zone is a traversal client of the new zone.
TraversalServer: there is a firewall between the zones and the Local Zone is a traversal server for the new zone.
ENUM: the new zone contains endpoints discoverable by ENUM lookup.
DNS: the new zone contains endpoints discoverable by DNS lookup.
Once the zone has been created, the Type cannot be changed.
Hop count
The hop count is the number of times a search request will be forwarded to a neighbor gatekeeper or proxy (see Hop Counts for more information). This field specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to this particular zone.
If the search request was received from another zone and already has a hop count assigned, the lower of the two values will be used.
Match1 - Match5
The Match sections allow you to configure when and how search requests will be sent to this zone, and also whether any transforms will be applied to aliases being searched for in this zone. These features are described in full in the section Zone searching and alias transforming.
Introduction | Getting | System | System | H.323 & SIP | Registration | Zones and | Call | Firewall | Bandwidth | Maintenance | Appendices | |
Started | Overview | Configuration | Configuration | Control | Neighbors | Processing | Traversal | Control | ||||
|
|
| ||||||||||
D 14049.01 |
|
|
|
| 53 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
07.2007 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|