Shortest Path Tree
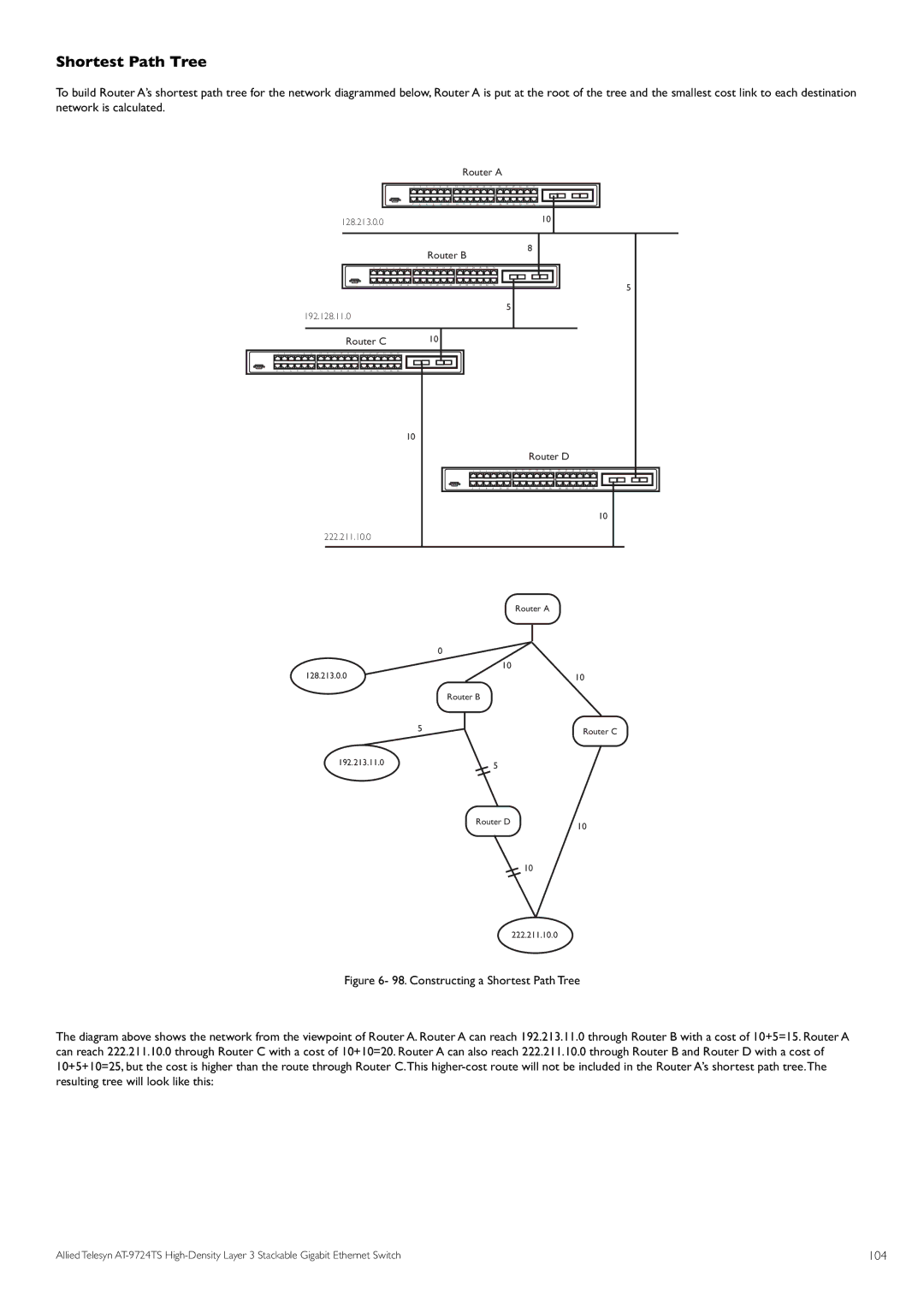
To build Router A’s shortest path tree for the network diagrammed below, Router A is put at the root of the tree and the smallest cost link to each destination network is calculated.
Router A
1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 29 | 31 | 33 | 35 |
2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 |
128.213.0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Router B
8
1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 29 | 31 | 33 | 35 |
2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 |
5
192.128.11.0
Router C | 10 |
5
1 |
| 3 |
| 5 |
| 7 |
| 9 |
| 11 |
| 13 |
| 15 |
| 17 |
| 19 |
| 21 |
| 23 |
| 25 |
| 27 |
| 29 |
| 31 |
| 33 |
| 35 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
| 4 |
| 6 |
| 8 |
| 10 | 12 |
| 14 | 16 |
| 18 |
| 20 |
| 22 |
| 24 |
| 26 | 28 |
| 30 |
| 32 |
| 34 |
| 36 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10
Router D
1 |
| 3 |
| 5 |
| 7 |
| 9 |
| 11 |
| 13 |
| 15 |
| 17 |
| 19 |
| 21 |
| 23 |
| 25 |
| 27 |
| 29 |
| 31 |
| 33 |
| 35 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
| 4 |
| 6 |
| 8 |
| 10 | 12 |
| 14 | 16 |
| 18 |
| 20 |
| 22 |
| 24 |
| 26 | 28 |
| 30 |
| 32 |
| 34 |
| 36 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10
222.211.10.0
|
|
| Router A |
|
| 0 |
|
128.213.0.0 |
| 10 |
|
|
| 10 | |
|
| Router B |
|
| 5 |
| Router C |
|
|
| |
192.213.11.0 |
| 5 |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Router D | 10 |
|
|
|
10
222.211.10.0
Figure 6- 98. Constructing a Shortest Path Tree
The diagram above shows the network from the viewpoint of Router A. Router A can reach 192.213.11.0 through Router B with a cost of 10+5=15. Router A can reach 222.211.10.0 through Router C with a cost of 10+10=20. Router A can also reach 222.211.10.0 through Router B and Router D with a cost of 10+5+10=25, but the cost is higher than the route through Router C.This higher-cost route will not be included in the Router A’s shortest path tree.The resulting tree will look like this:
Allied Telesyn | 104 |