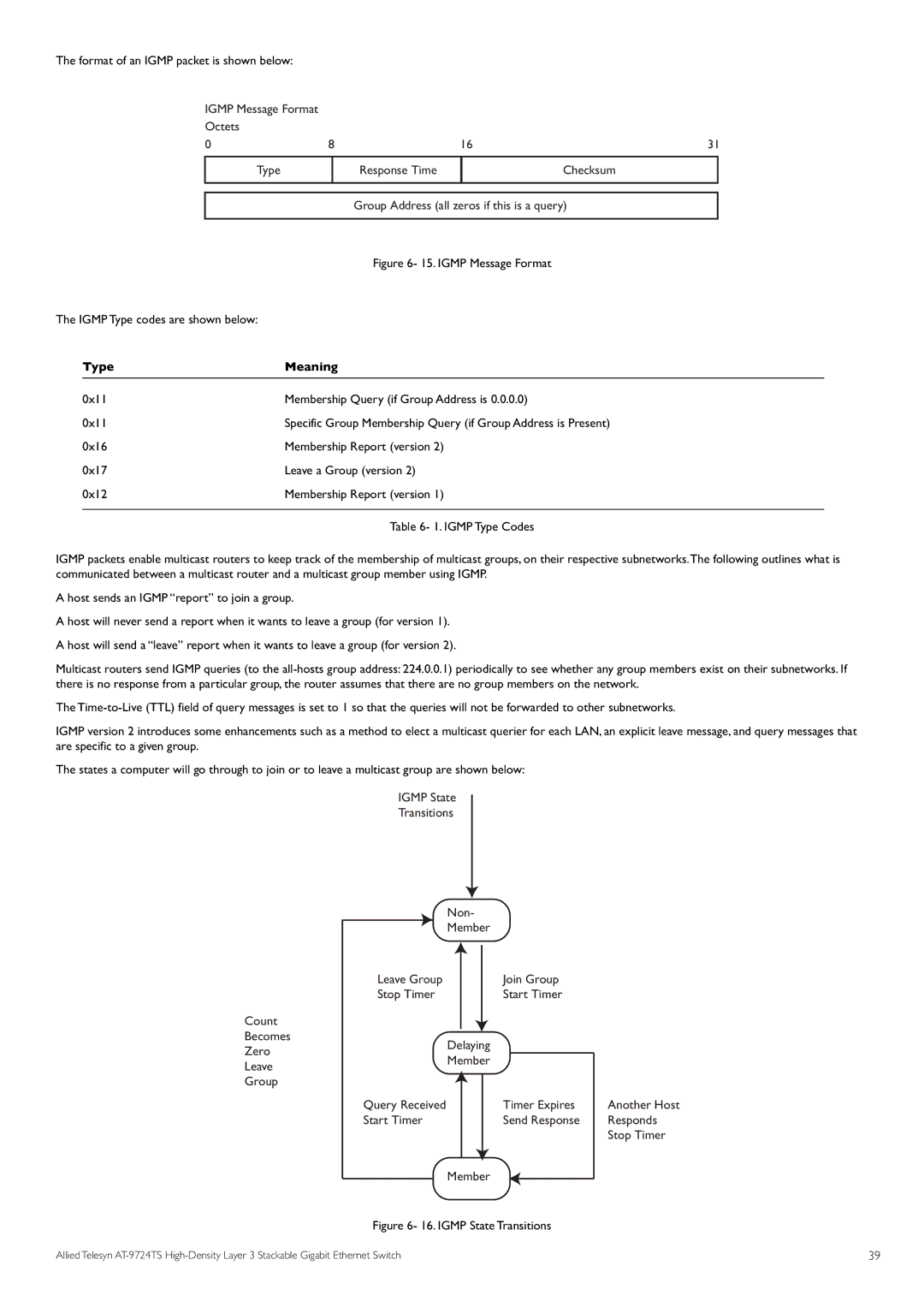
The format of an IGMP packet is shown below: |
|
|
|
IGMP Message Format |
|
|
|
Octets |
|
|
|
0 | 8 | 16 | 31 |
Type |
| Response Time | Checksum |
Group Address (all zeros if this is a query)
|
| Figure 6- 15. IGMP Message Format |
The IGMP Type codes are shown below: |
| |
| Type | Meaning |
| 0x11 | Membership Query (if Group Address is 0.0.0.0) |
| 0x11 | Specific Group Membership Query (if Group Address is Present) |
| 0x16 | Membership Report (version 2) |
| 0x17 | Leave a Group (version 2) |
| 0x12 | Membership Report (version 1) |
Table 6- 1. IGMP Type Codes
IGMP packets enable multicast routers to keep track of the membership of multicast groups, on their respective subnetworks.The following outlines what is communicated between a multicast router and a multicast group member using IGMP.
A host sends an IGMP “report” to join a group.
A host will never send a report when it wants to leave a group (for version 1). A host will send a “leave” report when it wants to leave a group (for version 2).
Multicast routers send IGMP queries (to the
The
IGMP version 2 introduces some enhancements such as a method to elect a multicast querier for each LAN, an explicit leave message, and query messages that are specific to a given group.
The states a computer will go through to join or to leave a multicast group are shown below:
IGMP State
Transitions
| Non- | ||||
| Member | ||||
Leave Group |
|
| Join Group | ||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
Stop Timer |
|
| Start Timer | ||
Count |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
Becomes | Delaying |
| |||
Zero | |||||
Member | |||||
Leave | |||||
|
|
|
| ||
Group |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
Query Received |
|
| Timer Expires | ||
Start Timer |
|
| Send Response | ||
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Member
Figure 6- 16. IGMP State Transitions
Another Host
Responds
Stop Timer
Allied Telesyn | 39 |