6-18 QoS
The
The Advantages of QoS
QoS is an implementation of the IEEE 802.1p standard that allows network administrators a method of reserving bandwidth for important functions that require a large bandwidth or have a high priority, such as VoIP
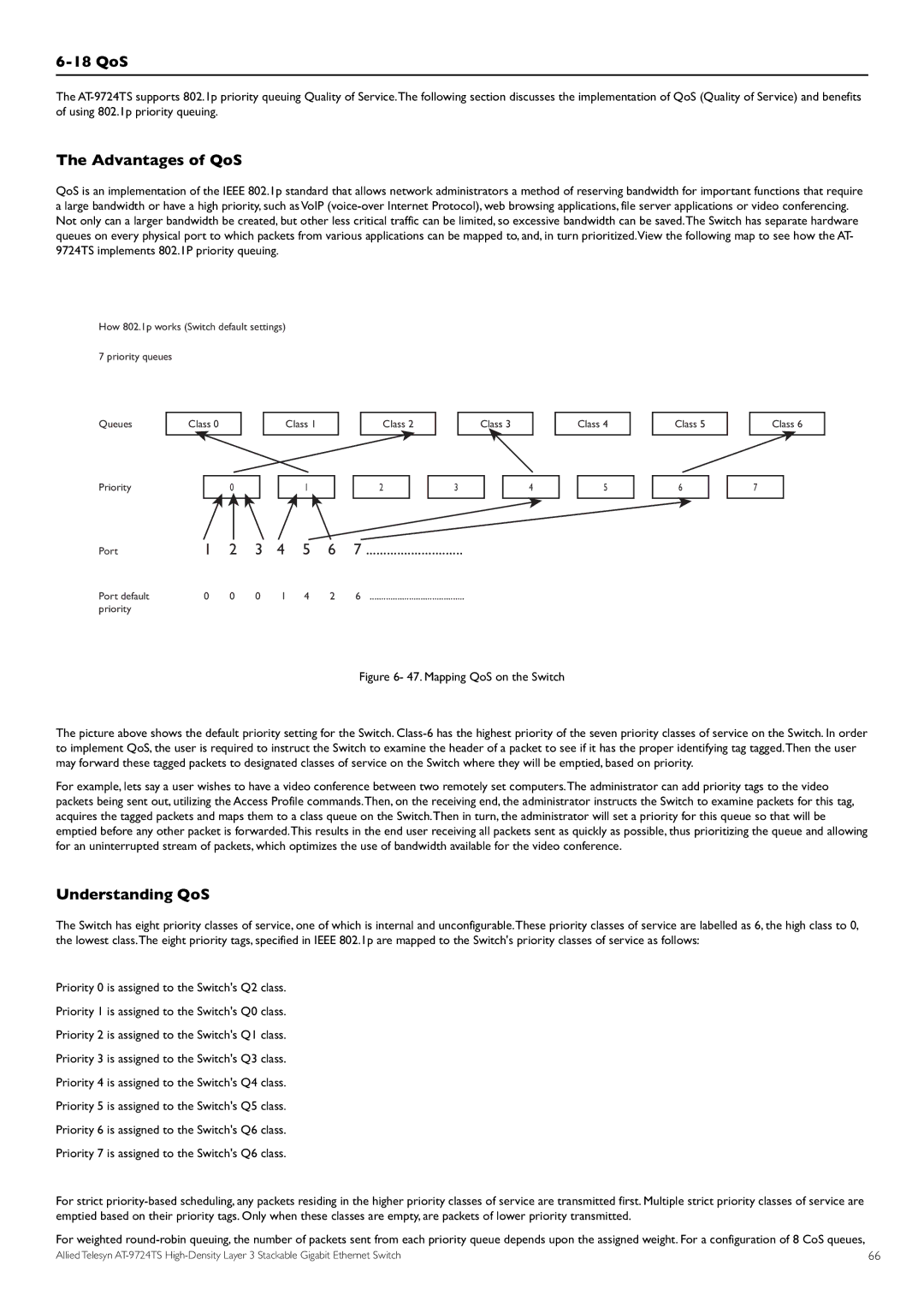
How 802.1p works (Switch default settings)
7 priority queues
Queues
Priority
Port
Port default priority
Class 0 |
|
|
|
|
| Class 1 |
|
|
|
| Class 2 |
| Class 3 |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| 6 | ......................................... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
Class 4
5
Class 5
6
Class 6
7
Figure 6- 47. Mapping QoS on the Switch |
|
The picture above shows the default priority setting for the Switch. |
|
to implement QoS, the user is required to instruct the Switch to examine the header of a packet to see if it has the proper identifying tag tagged.Then the user |
|
may forward these tagged packets to designated classes of service on the Switch where they will be emptied, based on priority. |
|
For example, lets say a user wishes to have a video conference between two remotely set computers.The administrator can add priority tags to the video |
|
packets being sent out, utilizing the Access Profile commands.Then, on the receiving end, the administrator instructs the Switch to examine packets for this tag, |
|
acquires the tagged packets and maps them to a class queue on the Switch.Then in turn, the administrator will set a priority for this queue so that will be |
|
emptied before any other packet is forwarded.This results in the end user receiving all packets sent as quickly as possible, thus prioritizing the queue and allowing |
|
for an uninterrupted stream of packets, which optimizes the use of bandwidth available for the video conference. |
|
Understanding QoS |
|
The Switch has eight priority classes of service, one of which is internal and unconfigurable.These priority classes of service are labelled as 6, the high class to 0, |
|
the lowest class.The eight priority tags, specified in IEEE 802.1p are mapped to the Switch's priority classes of service as follows: |
|
Priority 0 is assigned to the Switch's Q2 class. |
|
Priority 1 is assigned to the Switch's Q0 class. |
|
Priority 2 is assigned to the Switch's Q1 class. |
|
Priority 3 is assigned to the Switch's Q3 class. |
|
Priority 4 is assigned to the Switch's Q4 class. |
|
Priority 5 is assigned to the Switch's Q5 class. |
|
Priority 6 is assigned to the Switch's Q6 class. |
|
Priority 7 is assigned to the Switch's Q6 class. |
|
For strict |
|
emptied based on their priority tags. Only when these classes are empty, are packets of lower priority transmitted. |
|
For weighted | 66 |
Allied Telesyn |