The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
•Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering.
•Assumes the presence of a single global spanning tree.
•Uses an explicit tagging scheme with
•802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
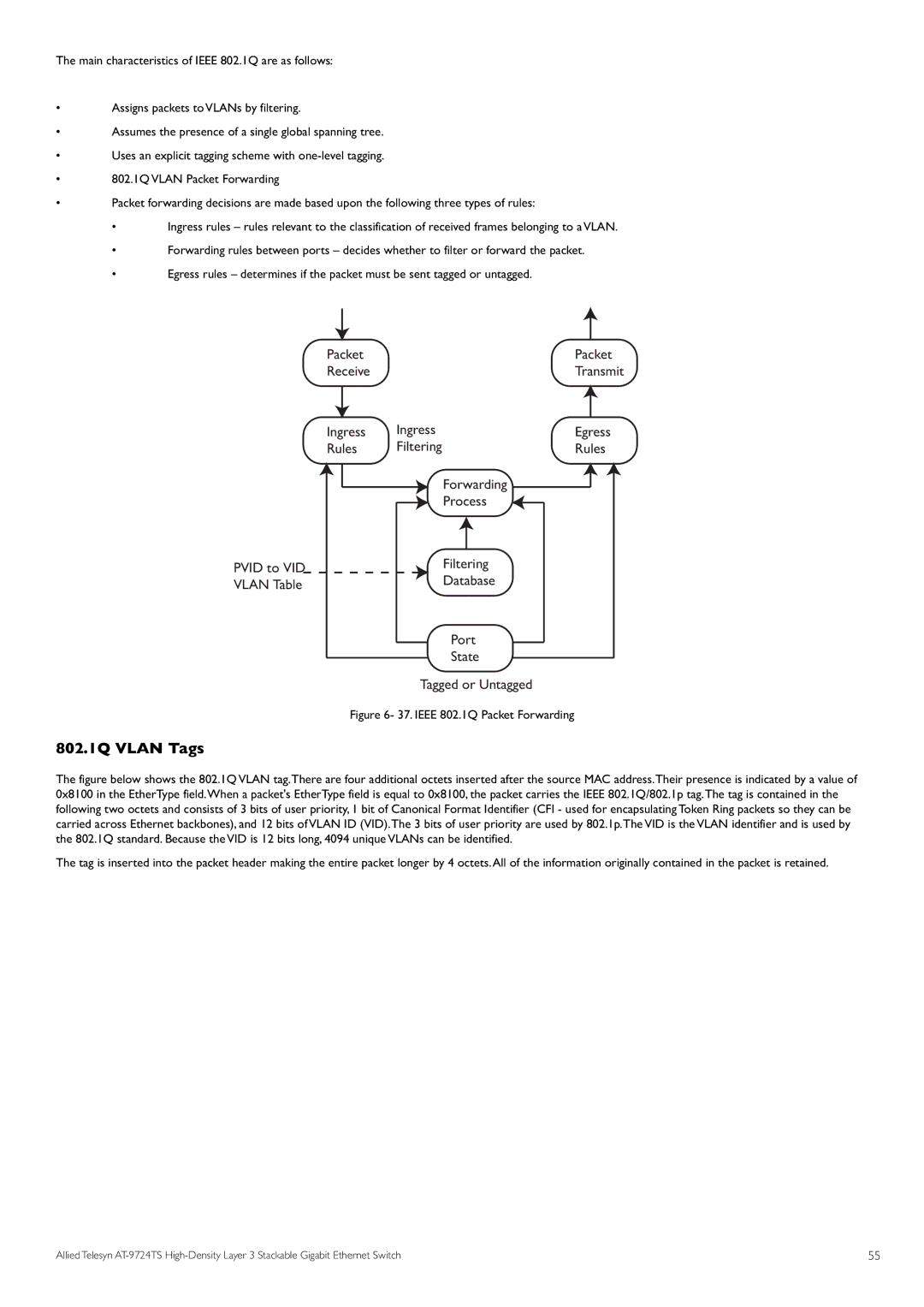
•Packet forwarding decisions are made based upon the following three types of rules:
• | Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of received frames belonging to a VLAN. |
•Forwarding rules between ports – decides whether to filter or forward the packet.
•Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
PVID to VID VLAN Table
Packet |
|
Receive |
|
Ingress | Ingress |
Rules | Filtering |
Packet |
Transmit |
Egress |
Rules |
Forwarding |
Process |
Filtering |
Database |
Port |
State |
Tagged or Untagged
Figure 6- 37. IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag.There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC address.Their presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the EtherType field.When a packet's EtherType field is equal to 0x8100, the packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag.The tag is contained in the following two octets and consists of 3 bits of user priority, 1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier (CFI - used for encapsulating Token Ring packets so they can be carried across Ethernet backbones), and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID).The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p.The VID is the VLAN identifier and is used by the 802.1Q standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLANs can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets.All of the information originally contained in the packet is retained.
Allied Telesyn | 55 |