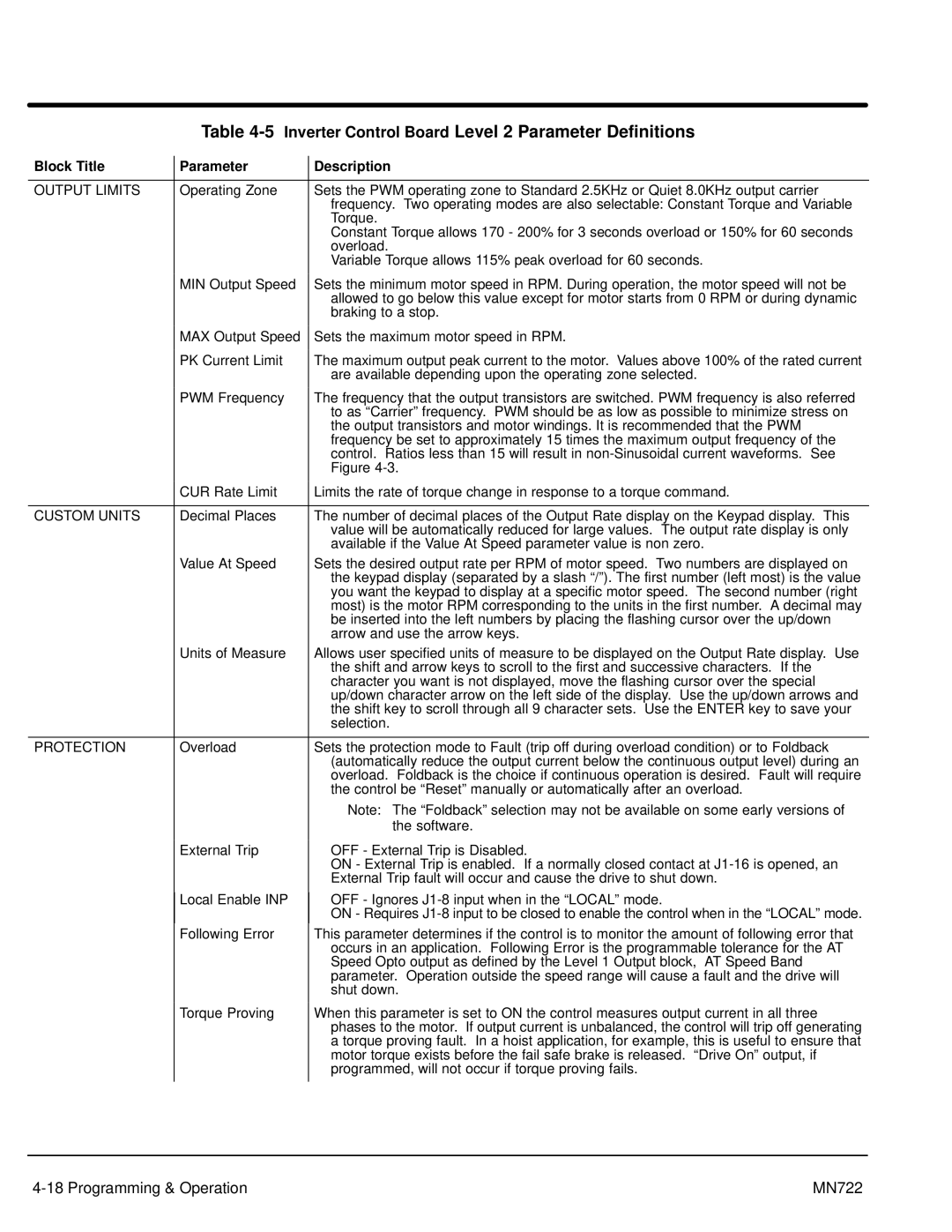
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions
Block Title | Parameter | Description |
|
|
|
OUTPUT LIMITS | Operating Zone | Sets the PWM operating zone to Standard 2.5KHz or Quiet 8.0KHz output carrier |
|
| frequency. Two operating modes are also selectable: Constant Torque and Variable |
|
| Torque. |
|
| Constant Torque allows 170 - 200% for 3 seconds overload or 150% for 60 seconds |
|
| overload. |
|
| Variable Torque allows 115% peak overload for 60 seconds. |
| MIN Output Speed | Sets the minimum motor speed in RPM. During operation, the motor speed will not be |
|
| allowed to go below this value except for motor starts from 0 RPM or during dynamic |
|
| braking to a stop. |
| MAX Output Speed | Sets the maximum motor speed in RPM. |
| PK Current Limit | The maximum output peak current to the motor. Values above 100% of the rated current |
|
| are available depending upon the operating zone selected. |
| PWM Frequency | The frequency that the output transistors are switched. PWM frequency is also referred |
|
| to as “Carrier” frequency. PWM should be as low as possible to minimize stress on |
|
| the output transistors and motor windings. It is recommended that the PWM |
|
| frequency be set to approximately 15 times the maximum output frequency of the |
|
| control. Ratios less than 15 will result in |
|
| Figure |
| CUR Rate Limit | Limits the rate of torque change in response to a torque command. |
|
|
|
CUSTOM UNITS | Decimal Places | The number of decimal places of the Output Rate display on the Keypad display. This |
|
| value will be automatically reduced for large values. The output rate display is only |
|
| available if the Value At Speed parameter value is non zero. |
| Value At Speed | Sets the desired output rate per RPM of motor speed. Two numbers are displayed on |
|
| the keypad display (separated by a slash “/”). The first number (left most) is the value |
|
| you want the keypad to display at a specific motor speed. The second number (right |
|
| most) is the motor RPM corresponding to the units in the first number. A decimal may |
|
| be inserted into the left numbers by placing the flashing cursor over the up/down |
|
| arrow and use the arrow keys. |
| Units of Measure | Allows user specified units of measure to be displayed on the Output Rate display. Use |
|
| the shift and arrow keys to scroll to the first and successive characters. If the |
|
| character you want is not displayed, move the flashing cursor over the special |
|
| up/down character arrow on the left side of the display. Use the up/down arrows and |
|
| the shift key to scroll through all 9 character sets. Use the ENTER key to save your |
|
| selection. |
|
|
|
PROTECTION | Overload | Sets the protection mode to Fault (trip off during overload condition) or to Foldback |
|
| (automatically reduce the output current below the continuous output level) during an |
|
| overload. Foldback is the choice if continuous operation is desired. Fault will require |
|
| the control be “Reset” manually or automatically after an overload. |
|
| Note: The “Foldback” selection may not be available on some early versions of |
|
| the software. |
| External Trip | OFF - External Trip is Disabled. |
|
| ON - External Trip is enabled. If a normally closed contact at |
|
| External Trip fault will occur and cause the drive to shut down. |
|
|
|
Local Enable INP
Following Error
Torque Proving
OFF - Ignores
ON - Requires
This parameter determines if the control is to monitor the amount of following error that occurs in an application. Following Error is the programmable tolerance for the AT Speed Opto output as defined by the Level 1 Output block, AT Speed Band parameter. Operation outside the speed range will cause a fault and the drive will shut down.
When this parameter is set to ON the control measures output current in all three phases to the motor. If output current is unbalanced, the control will trip off generating a torque proving fault. In a hoist application, for example, this is useful to ensure that motor torque exists before the fail safe brake is released. “Drive On” output, if programmed, will not occur if torque proving fails.
MN722 |