26Chapter 1: Introduction to the EIU
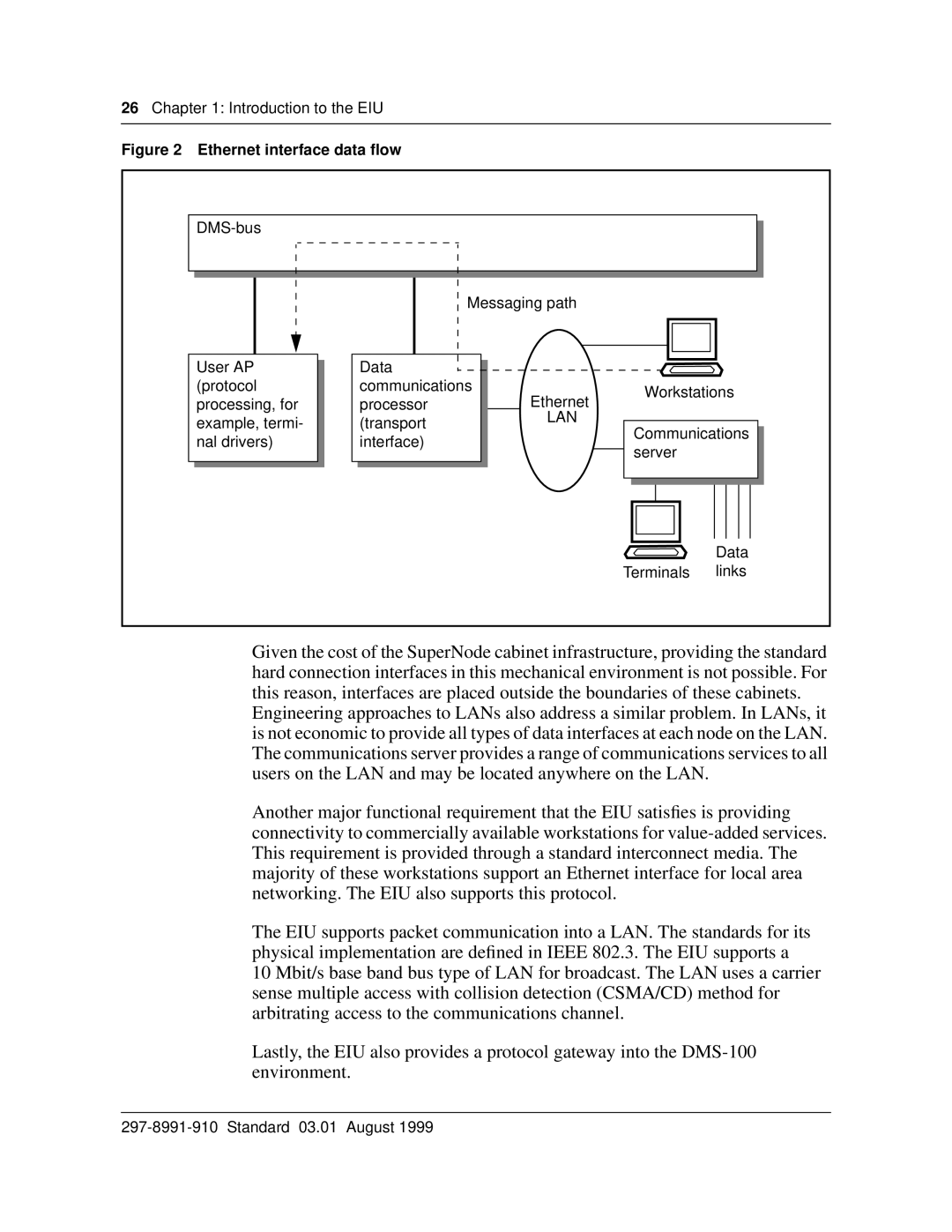
Figure 2 Ethernet interface data flow
|
|
|
| ||
|
| Messaging path |
|
| |
User AP | Data |
|
|
| |
(protocol | communications | Workstations | |||
processing, for | processor | Ethernet | |||
|
| ||||
example, termi- | (transport | LAN | Communications | ||
| |||||
nal drivers) | interface) |
| |||
| server |
| |||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| Data | |
|
|
| Terminals | links | |
Given the cost of the SuperNode cabinet infrastructure, providing the standard hard connection interfaces in this mechanical environment is not possible. For this reason, interfaces are placed outside the boundaries of these cabinets.
Engineering approaches to LANs also address a similar problem. In LANs, it is not economic to provide all types of data interfaces at each node on the LAN. The communications server provides a range of communications services to all users on the LAN and may be located anywhere on the LAN.
Another major functional requirement that the EIU satisfies is providing connectivity to commercially available workstations for
The EIU supports packet communication into a LAN. The standards for its physical implementation are defined in IEEE 802.3. The EIU supports a
10 Mbit/s base band bus type of LAN for broadcast. The LAN uses a carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) method for arbitrating access to the communications channel.
Lastly, the EIU also provides a protocol gateway into the