150Appendix E: Understanding IP and IP addressing
not recommended. If connection to public networks is needed later, all the addressing work must be repeated.
IP addresses
IP uses a
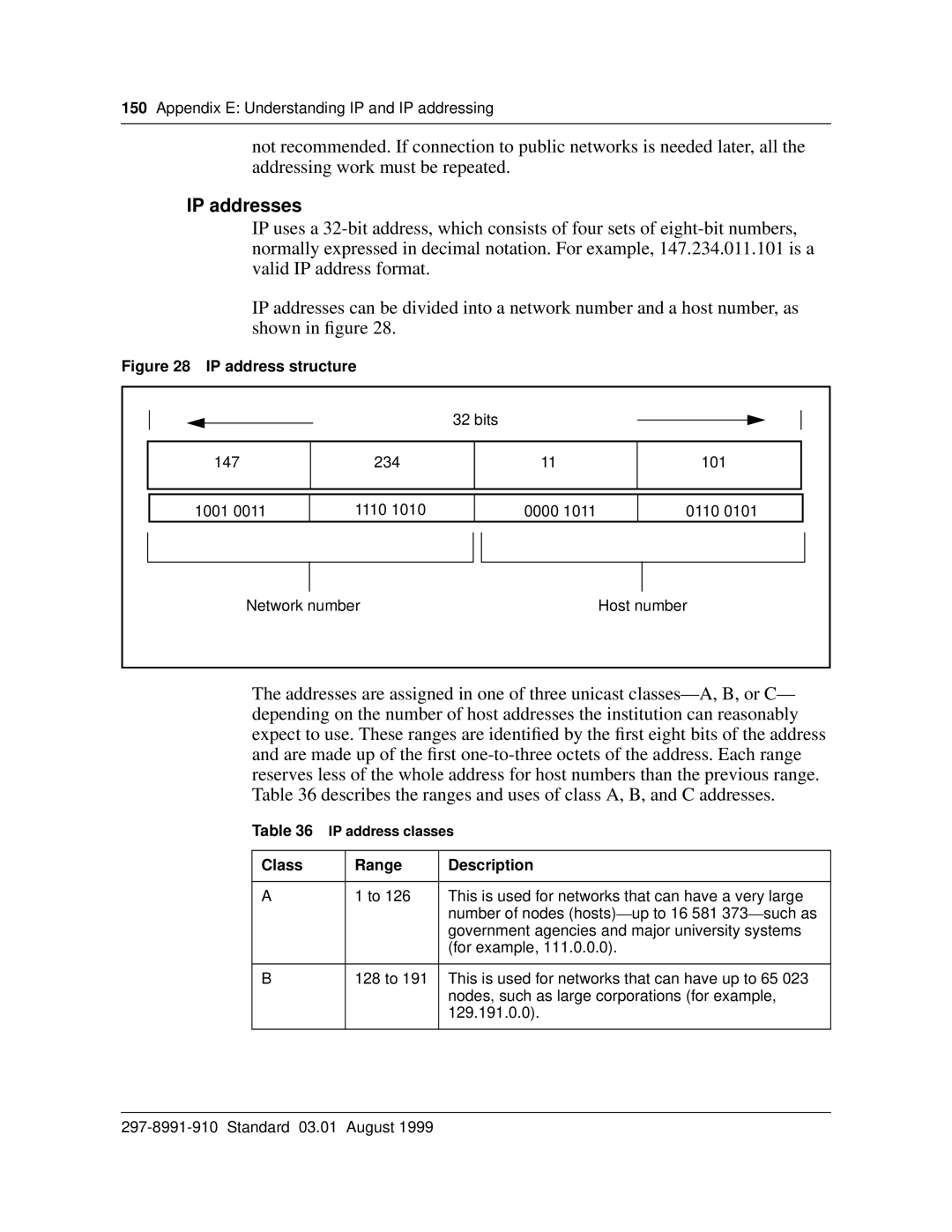
IP addresses can be divided into a network number and a host number, as shown in figure 28.
Figure 28 IP address structure
|
| 32 bits |
|
147 | 234 | 11 | 101 |
1001 0011 | 1110 1010 | 0000 1011 | 0110 0101 |
Network number |
| Host number | |
The addresses are assigned in one of three unicast
Table 36 IP address classes
Class | Range | Description |
|
|
|
A | 1 to 126 | This is used for networks that can have a very large |
|
| number of nodes (hosts)— up to 16 581 373— such as |
|
| government agencies and major university systems |
|
| (for example, 111.0.0.0). |
|
|
|
B | 128 to 191 | This is used for networks that can have up to 65 023 |
|
| nodes, such as large corporations (for example, |
|
| 129.191.0.0). |
|
|
|