Control Modules
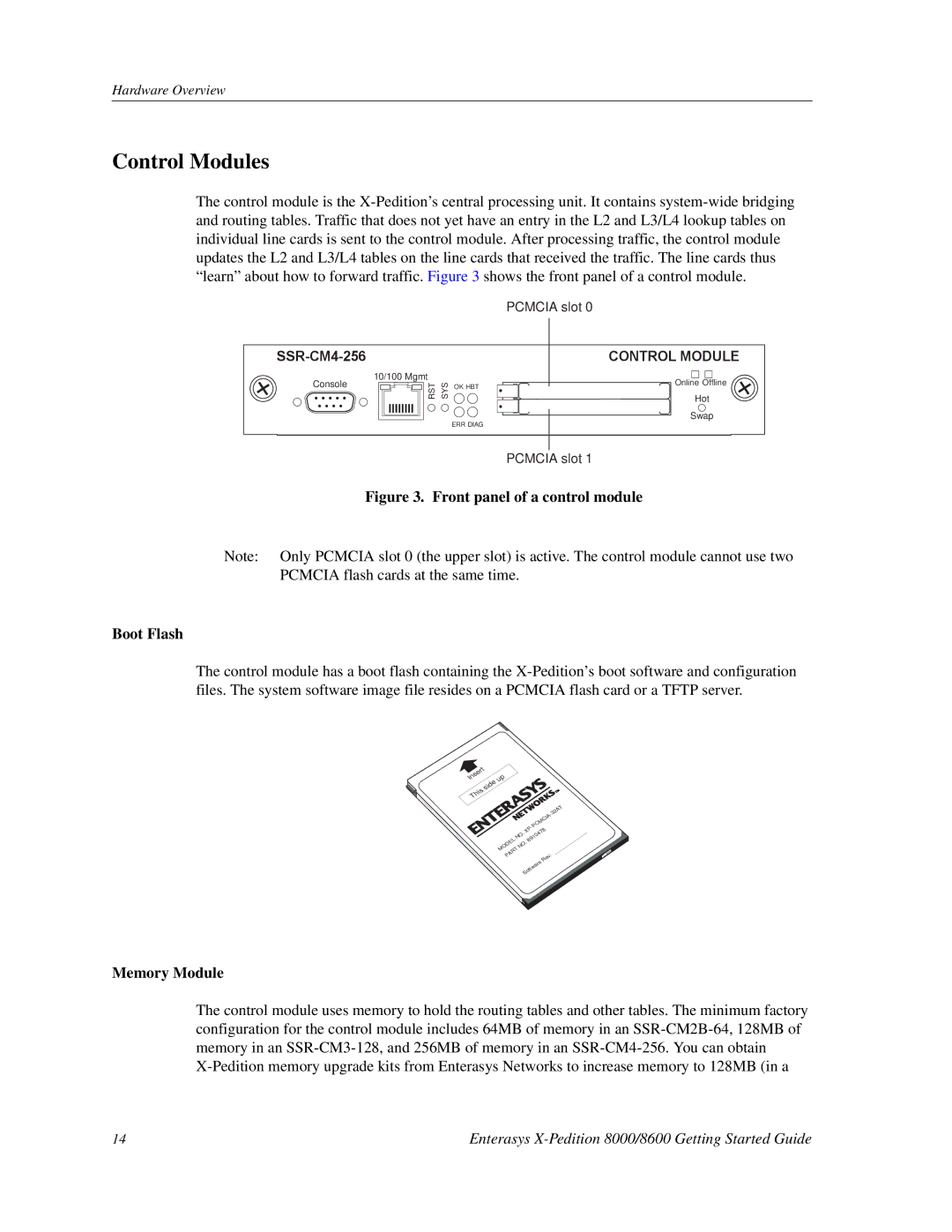
The control module is the X-Pedition’s central processing unit. It contains system-wide bridging and routing tables. Traffic that does not yet have an entry in the L2 and L3/L4 lookup tables on individual line cards is sent to the control module. After processing traffic, the control module updates the L2 and L3/L4 tables on the line cards that received the traffic. The line cards thus “learn” about how to forward traffic. Figure 3 shows the front panel of a control module.
PCMCIA slot 0
SSR-CM4-256 | | | CONTROL MODULE |
Console | 10/100 Mgmt | | Online Offline |
RST SYS | OK HBT |
| | Hot |
| | |
| | ERR DIAG | Swap |
| | |
PCMCIA slot 1
Figure 3. Front panel of a control module
Note: Only PCMCIA slot 0 (the upper slot) is active. The control module cannot use two PCMCIA flash cards at the same time.
Boot Flash
The control module has a boot flash containing the X-Pedition’s boot software and configuration files. The system software image file resides on a PCMCIA flash card or a TFTP server.
| | | | -32AT |
| | | -PCMCIA |
| | .XP | |
MODEL | NO | .8910478 |
| NO | |
PART | | | Rev: |
| | Software |
| | |
Memory Module
The control module uses memory to hold the routing tables and other tables. The minimum factory configuration for the control module includes 64MB of memory in an SSR-CM2B-64, 128MB of memory in an SSR-CM3-128, and 256MB of memory in an SSR-CM4-256. You can obtain X-Pedition memory upgrade kits from Enterasys Networks to increase memory to 128MB (in a
14 | Enterasys X-Pedition 8000/8600 Getting Started Guide |