As with RAID 3, in the event of disk failure, the information can be rebuilt from the remaining drives. RAID level 5 array also uses parity information, though it is still important to make regular backups of the data in the array. RAID level 5 stripes data across all of the drives in the array, one segment at a time (a segment can contain multiple blocks). In an array with n drives, a stripe consists of data segments written to
The advantages and disadvantages of the various RAID levels are summarized in the following table:
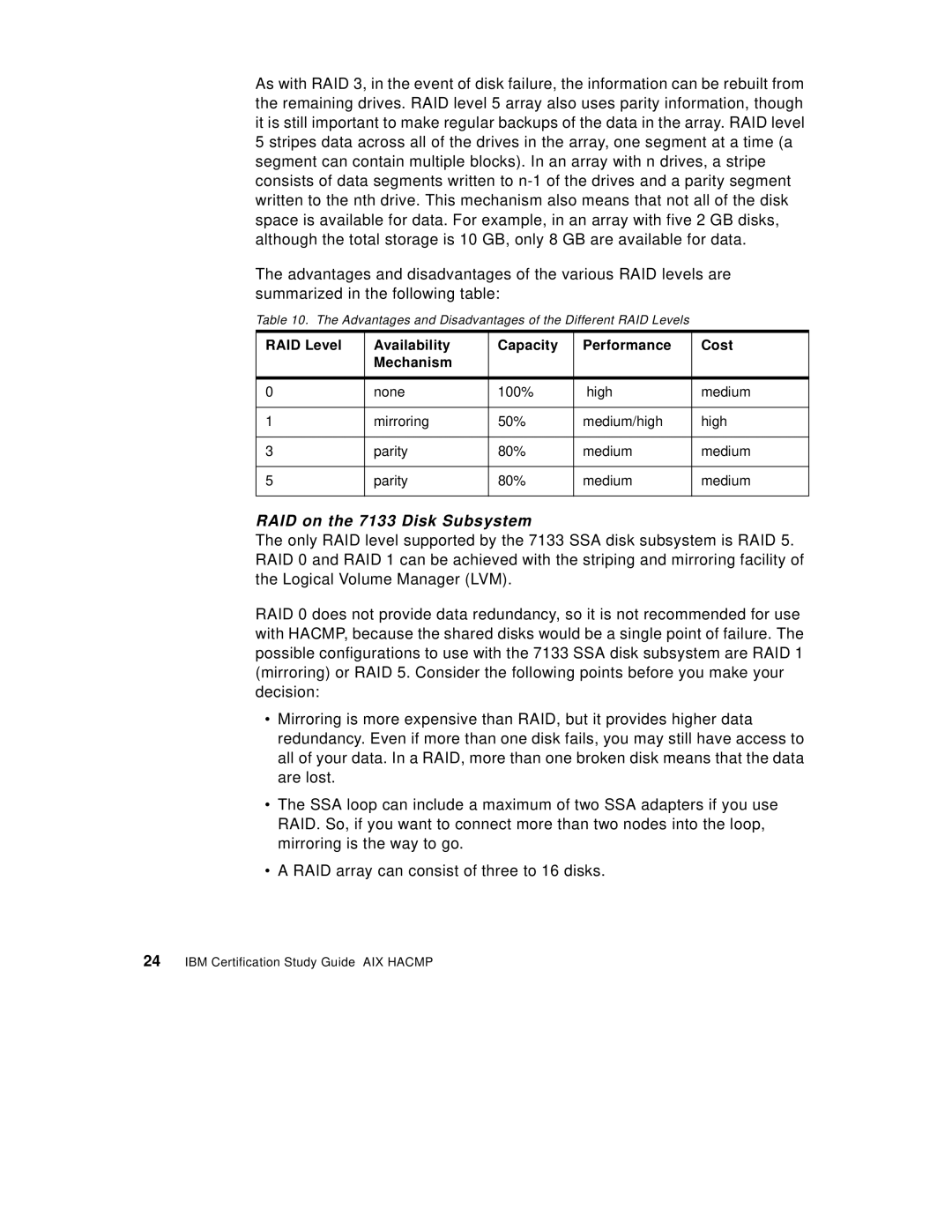
Table 10. The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Different RAID Levels
RAID Level | Availability | Capacity | Performance | Cost |
| Mechanism |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 | none | 100% | high | medium |
|
|
|
|
|
1 | mirroring | 50% | medium/high | high |
|
|
|
|
|
3 | parity | 80% | medium | medium |
|
|
|
|
|
5 | parity | 80% | medium | medium |
|
|
|
|
|
RAID on the 7133 Disk Subsystem
The only RAID level supported by the 7133 SSA disk subsystem is RAID 5. RAID 0 and RAID 1 can be achieved with the striping and mirroring facility of the Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
RAID 0 does not provide data redundancy, so it is not recommended for use with HACMP, because the shared disks would be a single point of failure. The possible configurations to use with the 7133 SSA disk subsystem are RAID 1 (mirroring) or RAID 5. Consider the following points before you make your decision:
•Mirroring is more expensive than RAID, but it provides higher data redundancy. Even if more than one disk fails, you may still have access to all of your data. In a RAID, more than one broken disk means that the data are lost.
•The SSA loop can include a maximum of two SSA adapters if you use RAID. So, if you want to connect more than two nodes into the loop, mirroring is the way to go.
•A RAID array can consist of three to 16 disks.