operation that was in progress, as well as new I/O operations against rvsd_X, are suspended until failover is complete. When Node X is repaired and rebooted, RVSD switches the rvsd_X back to its primary, Node X.
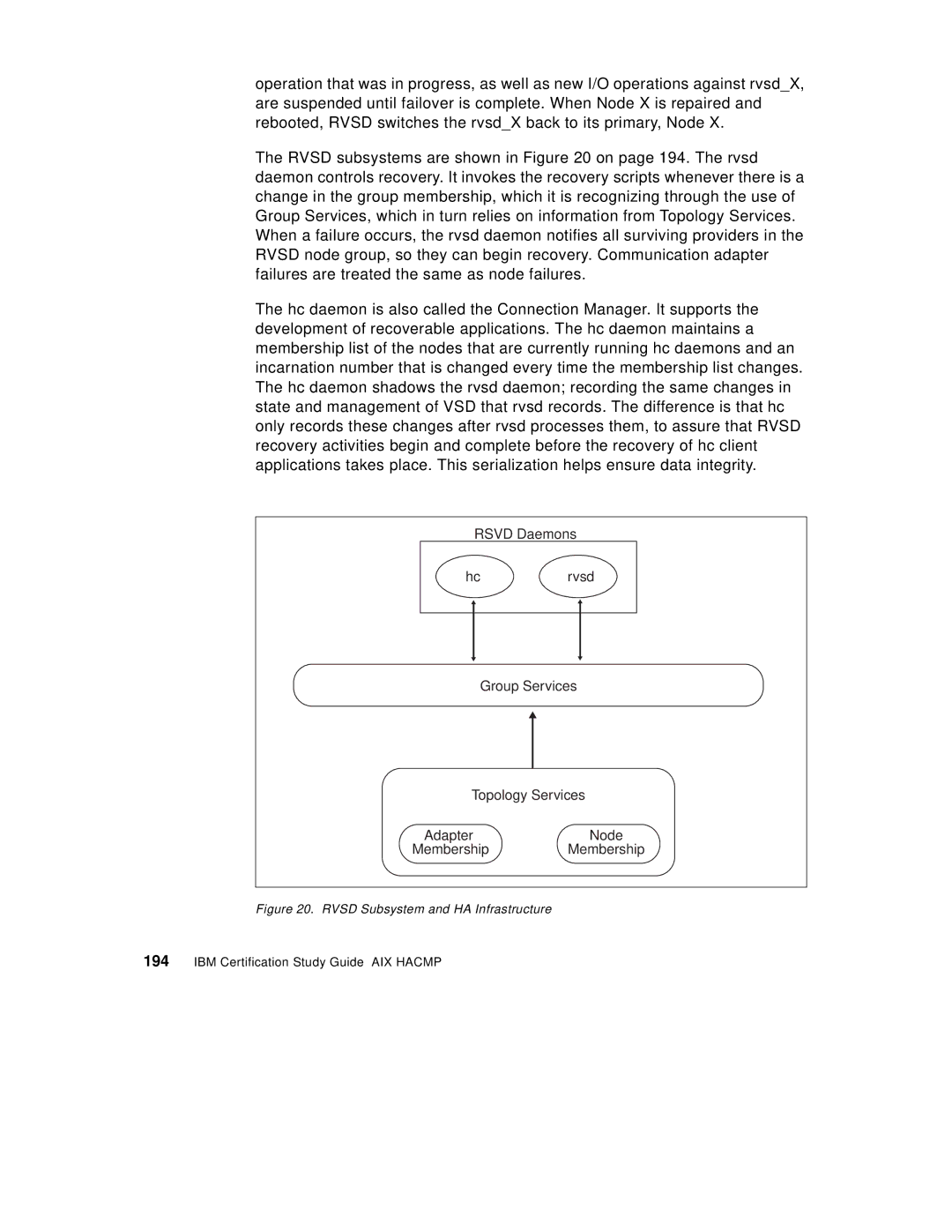
The RVSD subsystems are shown in Figure 20 on page 194. The rvsd daemon controls recovery. It invokes the recovery scripts whenever there is a change in the group membership, which it is recognizing through the use of Group Services, which in turn relies on information from Topology Services. When a failure occurs, the rvsd daemon notifies all surviving providers in the RVSD node group, so they can begin recovery. Communication adapter failures are treated the same as node failures.
The hc daemon is also called the Connection Manager. It supports the development of recoverable applications. The hc daemon maintains a membership list of the nodes that are currently running hc daemons and an incarnation number that is changed every time the membership list changes. The hc daemon shadows the rvsd daemon; recording the same changes in state and management of VSD that rvsd records. The difference is that hc only records these changes after rvsd processes them, to assure that RVSD recovery activities begin and complete before the recovery of hc client applications takes place. This serialization helps ensure data integrity.
RSVD Daemons | |
hc | rvsd |
Group Services | |
Topology Services | |
Adapter | Node |
Membership | Membership |