16 Automatic Geometric Calculations
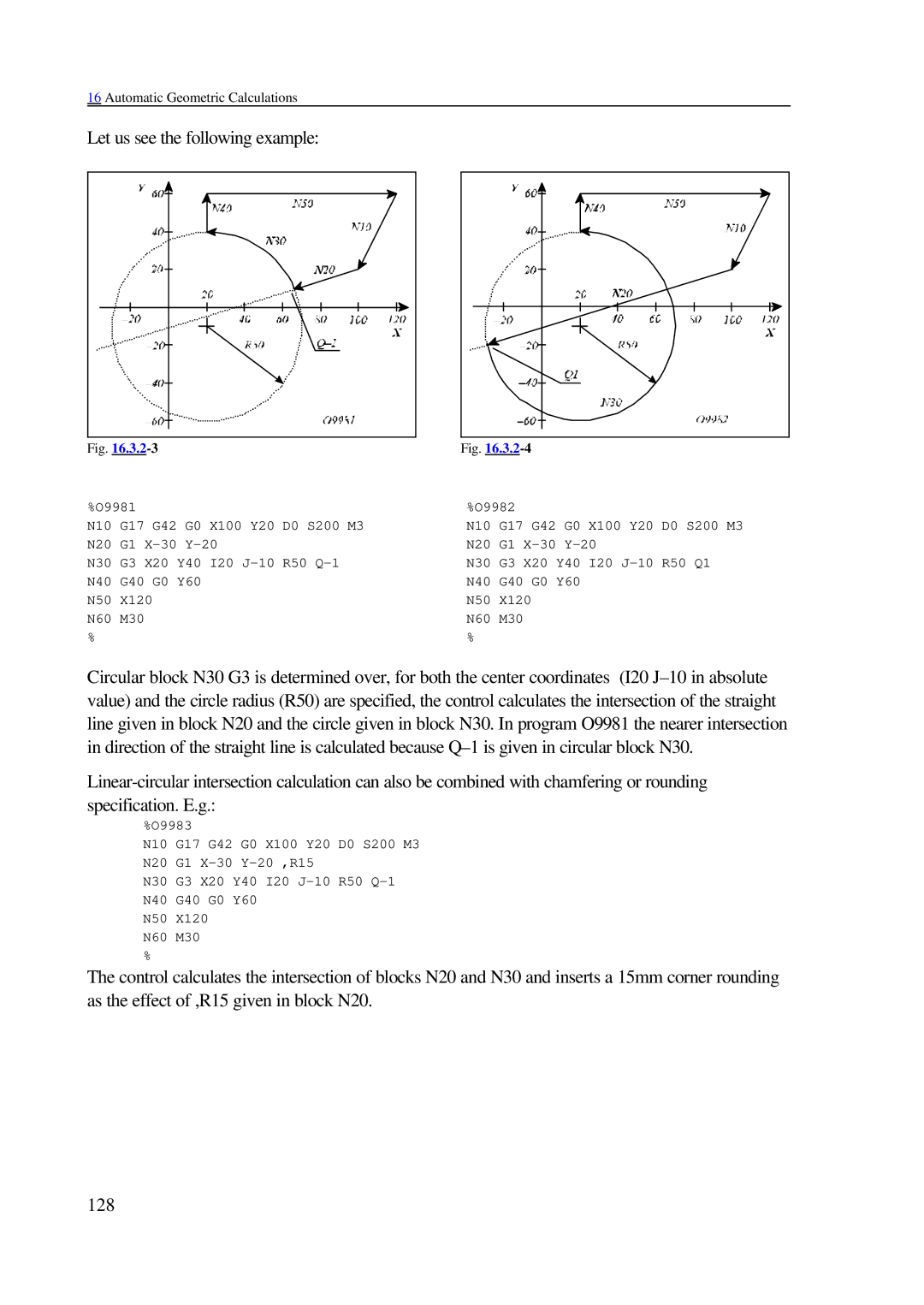
Let us see the following example:
Fig. |
Fig. |
%O9981 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| %O9982 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
N10 | G17 | G42 | G0 | X100 Y20 | D0 S200 | M3 | N10 | G17 | G42 | G0 | X100 Y20 | D0 S200 M3 | ||||
N20 | G1 |
|
| N20 | G1 |
| ||||||||||
N30 | G3 | X20 | Y40 | I20 | R50 |
| N30 | G3 | X20 | Y40 | I20 | R50 Q1 | ||||
N40 | G40 | G0 | Y60 |
|
|
| N40 | G40 | G0 | Y60 |
|
| ||||
N50 | X120 |
|
|
|
|
| N50 | X120 |
|
|
|
| ||||
N60 | M30 |
|
|
|
|
|
| N60 | M30 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Circular block N30 G3 is determined over, for both the center coordinates (I20
%O9983
N10 G17 G42 G0 X100 Y20 D0 S200 M3
N20 G1
N30 G3 X20 Y40 I20
N50 X120
N60 M30
%
The control calculates the intersection of blocks N20 and N30 and inserts a 15mm corner rounding as the effect of ,R15 given in block N20.
128