Page
Important Safety Instructions
Page
Using the Unit Safely
Important Notes
How to Use This Manual
How to Use This Manual
Contents
Creating Performances
Contents
Adding Effects
Using the XV-88 as a GM Sound Module GM Mode 192
Appendices 213
Main Features
Front Panel
Front and Rear Panel
Front and Rear Panel
Effects Section
Numeric Keys
Group Section
Bank Section
INC/+, DEC
Rear Panel
Individual 1-4 Jacks
Wave Expansion Board Installation Slot
Output a MIX Jacks L MONO, R
Output B Jacks L, R
Overview
How the XV-88 Is Organized
Basic Structure
Classification of XV-88 Sound Types
Tones
Patches
Part
Rhythm Sets
Parts
Generator
Keys are played
Overview Setting the Midi Connection Zone and Part
Overview Voice Reserve
Number of Voices
Calculating the Number of Voices Being Used
How a Patch Sounds
Basic Operations on
Switching Modes
System Mode
Utility Mode
GM Mode Edit Indicator is Extinguished
Performance Mode Edit Indicator is Extinguished
Overview Patch Mode Edit Indicator is Extinguished
Rhythm Set Mode Edit Indicator is Extinguished
Moving Between Display Pages
Overview When Edit Indicator is Lit
Remote Control of External Sequencers
About the Cursor Buttons
Numeric Keys
Modifying a Value
Value Dial
INC/+ and DEC
Convenient Functions
Using the Numeric Keys
Available characters/symbols
Assigning a Name
Playing in Patch Mode
Playing
Selecting a Patch
Express Patch Select Digit Hold
Selecting Patches by Category Patch Finder
Following categories can be selected
Selecting Favorite Patches from Favorite List
Using Phrase Preview to Play Patches
Preview Mode Preview Sound Mode
Making a Patch Sound Thick or Thin Turning a Tone On/Off
Creating Smooth Pitch Changes Portamento
Playing Single Notes Solo
About the Midi Connection Settings Zone and Part
Playing in Performance Mode
Using the Sliders to Modify the Sound in Realtime
Changing the Volume of Each Tone
Single Performance
PR-A, B Preset A, B
Selecting a Performance
Layer Performance
Playing Fatter and Richer Sounds by Combining Patches Layer
Selecting a Part You Want to Play on the Keyboard
Assigning a Different Patch to a Part
Playing Muting a Specific Part Turning Receive Switch On/Off
Selecting a Rhythm Set
Playing in Rhythm Set Mode
Adjusting the Volume Balance Between Parts
PR-A-F Presets A-F
Selecting Favorite Rhythm Sets from the Favorite List
Playing Percussion Instruments
Patch/Rhythm Set/GM Mode
Performance Mode
Playing Arpeggios Arpeggiator
Playing a Keyboard Instrument
Playing a Glissando
Playing a Bass Part
Playing a Guitar
Playing an Arpeggio Over a Preset Keyboard Area
When Using a Hold Pedal
Holding an Arpeggio
Simulating a Rhythm Guitar
Playing an Arpeggio from an External Midi Device
Creating an Arpeggio Pattern
Assign parameter SYSTEM/D BEAM/D Beam Control p
Output parameter SYSTEM/D BEAM/D Beam Control p
Convenient Functions for Performance
Transposing the Keyboard in Octave Units Octave Shift
Effective range of the D Beam Controller
When Sounds from the XV-88 Do Not Stop Playing
Transposing the Keyboard in Semitone Steps Transpose
If Stuck Notes Occur Panic
How to Make Performance Settings
Creating Performances
How a Performance Is Organized
Copying the Settings of Another Part Part Copy
Making Settings While Comparing Parts Palette Edit
KEY Rang Key Range
Settings Common to the Entire Performance Common
Functions of Performance Parameters
Perform Name Performance Name
Midi
Setting Effects for a Performance Effects
Making Settings for Receiving Midi Midi
RxSWITCH Receive Switch
Patch
Making Settings for Each Part Part
Setting
Velo CRV Velocity Curve
Pitch
Modify
Creating Performances MONO/POL Mono/Poly
Confirming Midi Information for Each Part Info
Info Part Information
Vo Voice Information
How to Make the Zone Settings
Zone Settings
Functions of Zone Parameters
Making Settings While Comparing Zones Palette Edit
Settings Common to the Entire Zone Common
Key Mode
Lower Key Range Lower
Setting the Keyboard Range KEY Range
Making Settings for Transmitting Midi Midi
Tx Transmit Switch
Controlling External Sound Module EXT Control
EXT P.C External Program Change
EXT Ctrl External Control
Octave Range
Arpeggiator Settings Arpeggio
Arpeggio
Style Arpeggio Style
Shuffle Rate
Motif
Beat Pattern
Accent Rate
Beam Control
Setting the D Beam Controller D Beam
Info Zone Information
Confirming the Settings for Each Zone Info
Beam Range
Beam Sens
Creating Patches
How a Patch Is Organized
How a Tone Is Organized
Decide which Tones will sound p , p
How to Make the Patch Settings
Check the Structure setting p
Four Tips for Editing Patches
Making Settings While Comparing Tones Palette Edit
Copying the Settings of Another Tone Tone Copy
Patch Name
Settings Common to the Entire Patch Common
Functions of Patch Parameters
Waveform
Creating Patches Patch LVL&PAN Patch level & Pan
Patch OCT&TUNE Patch Octave & Tune
Patch Common
Patch Modify
Patch Tempo
TMT VEL Rang TMT Velocity Range
TMT Velo Control TMT Velocity Control
TMT KEY Rang TMT Key Range
Creating Patches Struct Structure
Type Structure Type
Creating Patches
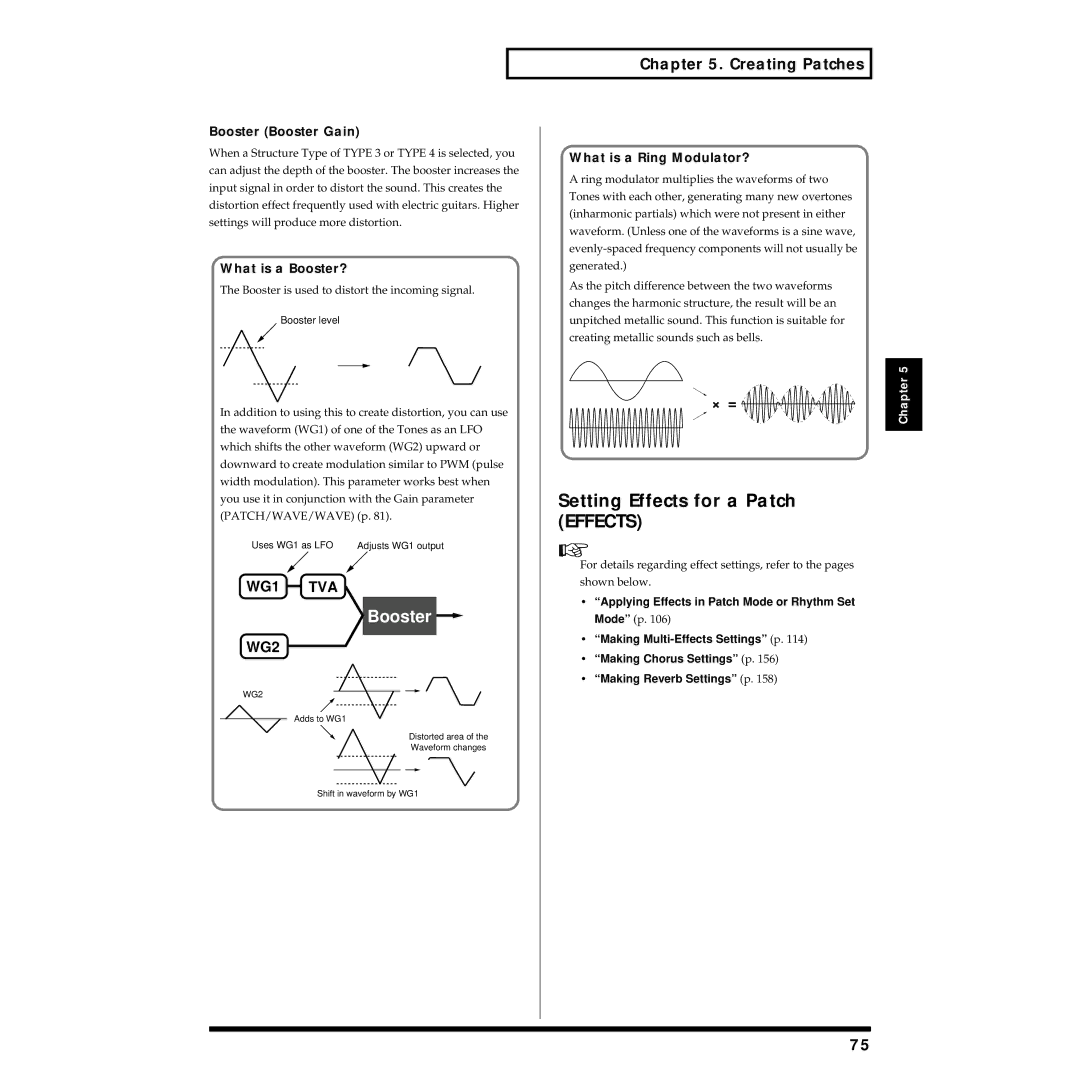
Booster Booster Gain
Setting Effects for a Patch Effects
What is a Booster?
What is a Ring Modulator?
Using Controllers to Change How Sounds Are Played Control
Patch KEY Mode Patch Key Assign Mode
Patch Portamnt Patch Portamento
Start Portamento Start Pitch
Bender Receive Pitch Bend Switch
Hold-1 Receive Hold 1 Switch
Ctrl Rx Midi Control Receive Midi
Matrix Ctrl SRC Matrix Control Source
TMT CTRL&BENDER TMT Control & Bender
Opening and Closing the Filter
Changing the Volume, Pan, and Pitch
Matrix Control
Dest Matrix Control Destination
Changing the TVF Envelope
Changing How the Effects Are Applied
Applying LFO to Modulate Sounds
Changing the Pitch Envelope
Modifying Waveforms Wave
Wave
FXM Frequency Cross Modulation
Mode Tone Delay Mode
Tone Delay
LFO1/LFO2 Wave
Modulating Sounds LFO
LFO1/LFO2 Delay
How to Apply the LFO
LFO1/LFO2 Fade
TVF TVF LFO Depth 1
LFO Depth
LFO is gradually added after the key is released
Pitch Pitch LFO Depth 1
PCH Envelope Pitch Envelope
Modifying Pitch Pitch
Modifying the Brightness of a
Sound with a Filter TVF
TVF Filter
Cutoff Cutoff Frequency
Resonance
Keyfollow Cutoff Frequency Keyfollow
TVF Envelope
TVF Velocity
TVA
Adjusting the Volume and Pan TVA
PAN Modulate
Bias
TVA Envelope
Creating Patches TVA Time ENV TVA Time Envelope
How to Make the Rhythm Set Settings
Creating Rhythm Sets
How a Rhythm Set Is Organized
Copying the Settings of Another Rhythm Tone Rhythm Tone Copy
Making Settings While Comparing Waveforms Palette Edit
Waveform to create a decay that is longer than the original
Rhythm Common Rhythm Set Common
Settings Common to the Entire Rhythm Set Common
Functions of Rhythm Set Parameters
Rhythm Name Rhythm Set Name
Setting Effects for a Rhythm Set Effects
Control
Rx Midi Receive Midi
Modifying Waveform of a Rhythm Tone Wave
Tone Name Rhythm Tone Name
WMT Wave
WMT VEL Rang WMT Velocity Range
Creating Rhythm Sets Velo Control Velocity Control
WMT PAN
WMT Frequency Cross Modulation
Modifying Pitch of a Rhythm Tone Pitch
Creating Rhythm Sets WMT Tune WMT Tune
WMT FXM
101
Changing the Tone Filter of a Rhythm Tone TVF
102
Pan Rhythm Tone Pan
Adjusting the Volume and Pan of a Rhythm Tone TVA
103
Level Rhythm Tone Level
Velocity Curve TVA Envelope Velocity Curve
TVA Velocity
104
Velocity Sens TVA Envelope Velocity Sensitivity
Turning Effects On/Off
Adding Effects
About the Onboard Effects
Effect Types
Applying Effects in Patch Mode or Rhythm Set Mode
Basic Process of Making Effects Settings
106
REV
Adding Effects Audio Signal Flow
107
Tone MFX
Selecting the Way the Direct Sound is Output
108
About the Output Jacks
109
Settings for Each Tone/ Rhythm Tone
When Selecting a Tone
When Selecting a Rhythm Tone
110
Chorus Chorus Send Level
Reverb Reverb Send Level
111
Applying Effects Performance Mode
REV Main
112
113
MFX Type
Making Multi-Effects Settings
Setting Procedure
Functions of Parameters
115
What is the Multi-Effects Controller?
MFX PRM MFX Parameter
MFX Ctrl MFX Control
116
MFX OUT MFX Output
117
Multi-Effects Types
118
Adding Effects Selecting Multi-Effects by Category
Stereo EQ Stereo Equalizer
Overdrive
119
Phaser
Distortion
120
Spectrum
Enhancer
121
Auto WAH
Rotary
122
Compressor
Limiter
123
HEXA-CHORUS
Tremolo Chorus
124
125
Phase
SPACE-D
Stereo Chorus
Stereo Flanger
Step Flanger
126
127
Stereo Delay
Modulation Delay
128
Fbk Feedback Level
129
Triple TAP Delay
130
Quadruple TAP Delay
Time Control Delay
22 2VOICE Pitch Shifter
131
Coarse Coarse Pitch #1
FBK Pitch Shifter Feedback Pitch Shifter
132
Lvl Bal Level Balance
Reverb
Gated Reverb
133
OVERDRIVE→ Chorus
OVERDRIVE→ Flanger
134
DISTORTION→ Flanger
OVERDRIVE→ Delay
DISTORTION→ Delay
DISTORTION→ Chorus
Enhancer Sens Enhancer Sensitivity #
ENHANCER→ Chorus
ENHANCER→ Flanger
136
137
ENHANCER→ Delay
CHORUS→ Delay
Delay Balance #
Flg Bal Flanger Balance #
FLANGER→ Delay
CHORUS→ Flanger
138
CHORUS/FLANGER
CHORUS/DELAY
FLANGER/DELAY
Stereo Phaser
140
Keysync Flanger
141
Formant Filter
Mod Modulator
Ring Modulator
142
Freq Frequency #
143
Multi TAP Delay
144
Reverse Delay
145
Shuffle Delay
146
Adding Effects 48 3D Delay
Pitch Shifter
Lofi Compress
147
Lofi Noise
Speaker Simulator
148
Amp Type Amp Simulator Switch/Type
149
Tone
Attack Attack Time
Stereo Compressor
Stereo Limiter
150
Gate
Slicer
151
Isolator
60 3D Chorus
152
153
61 3D Flanger
Tremolo
154
Mod Wave Modulation Wave
When Using 3D Effects
Auto PAN
155
Type Chorus Type
Making Chorus Settings
CHO Type
156
157
CHO PRM CHO Parameter
Making Reverb Settings
Adding Effects CHO OUT Chorus Output
158
REV Type
Adding Effects REV PRM REV Parameter
159
160
REV OUT REV Output
161
Copying Another Effect Setting Effects Copy
Saving Sounds
About Memory
162
Temporary Memory
Rewritable Memory
Non-Rewritable Memory
Saving to Internal Memory
Comparing with the Save Destination Patch Compare Function
164
Registering Data Without Displaying the Favorite List
165
166
When Saving a Performance
When Saving a Patch When Saving a Rhythm Set
Saving to an External Midi Device
167
Saving a Group of Tones to a Memory Card
Functions of System Parameters
How to Make the System Function Settings
Display Screen Contrast and Clock Settings Setup
System Setup
Midi Settings Midi
Perform Midi Performance Midi
169
170
Patch Midi
GM Midi
Receive Midi
Keyboard
Settings Control
Keyboard and Controllers
Transmit Midi
172
Hold Pedal
Control Pedal 1
C1-C4 Assign C1-C4 Slider Assign
Patch Scale
Adjusting Tuning Tune
SYS Ctrl Assign 1, 2 System Control Assign 1
System Tune
Just Temperament Tonic of C
KEY Scale
174
Equal Temperament
Getting More Familiar with the XV-88 System Functions
175
176
Preview Velocity
Phrase Preview Settings Preview
System Preview
Preview KEY
Battery Check
Info EXP
Transmit P.C
Memory Settings Utility Mode
About Utility Mode
Basic Procedure in Utility Mode
Internal Write Protect
Storing Sound Data in User Memory Write
Saving a Performance
180
Compare Function
Saving a Patch
Saving a Rhythm Set
181
Copying a Performance
Copying Sound Generator Settings Copy
Patch Name Copy
Copying a Patch
Patch Tone Copy
Patch Effects Copy
Rhythm Set Name Copy
Copying a Rhythm Set
Rhythm Tone Copy
Rhythm Set Effects Copy
Transmitting Sound Settings Xfer
Initializing Sound Generator Settings Init
Block Source Block
Transmitting Data to
186
Type Data Type
187
188
Memory Card-Related Settings Card
Before Using a Memory Card
Protecting the Internal Memory Protect
Copying Files Between Memory Cards File Copy
Formatting the Memory Card for the XV-88 Format
Renaming a File Rename
Deleting Unwanted Files Delete
Checking the Contents of a Memory Card Info
Loading a File from Memory Card into the XV-88 Load
Saving Data to Memory Card Save
191
Recalling Factory Default Settings Factory Reset
General MIDI/General Midi 2 System On Message
Entering GM Mode
Playing Back GM Scores
192
Modifying GM Mode Settings
Using the XV-88 as a GM Sound Module GM Mode
193
Making Effects Settings in GM Mode Effects
Output
194
Making Settings for Receiving
GM Chorus GM Reverb
195
196
Confirming Midi Information for
Each Part Info
197
Basic Procedure
Convenient Functions in GM Mode GM Utility
Initializing GM Mode Init
Transmitting GM Mode Settings Xfer
199
Techniques for Using Patches
Reinforcing Filter Characteristics
Using the Slider to Change the Pan in Realtime
Changing the Tone Produced with the Modulation Lever
Syncing the LFO Cycle to System Tempo
200
Multi-effects Type Parameter synchronized To tempo
Modifying Multi-Effects to Match the System’s Tempo
Playing Phrase Loops in Sync with the System Tempo
201
202
Using the XV-88 to Play Live
Playing an External Midi Sound Module from
Using External Midi Devices
Changing Sounds with a Pedal Switch
Patch/Rhythm Set Mode
204
Controlling an External Midi Sequencer from
GM Mode
205
Generator from an External Midi Device p
Group Number Bank Select
Selecting XV-88 Sounds from an External Midi Device
Selecting Performances
206
Number Bank Select
Realizing the Potential Selecting Patches
Selecting Rhythm Sets
207
Two Connection Methods
Connecting to Your Computer
Connecting with Computer Connector
Enjoying Desktop Music
209
Connecting with Midi Connectors
USB
210
211
Turn on the Midi Thru Function of Your Sequencer Software
212
When the Computer Switch Is Set to Mac or PC
When the Computer Switch Is Set to
How Midi Messages Are Exchanged with a Computer
213
Appendices
214
Troubleshooting
Cannot Turn the Power On
No Sound
Specific Keyboard Area Does Not Sound
Song Data Does Not Play Back Correctly
Specific Part Does Not Sound
No Sound from Connected Midi Device
Effects Do Not Apply
When You Play the Keyboard, Notes Do Not Stop
Sound Is Distorted
Pitch Is Incorrect
Cannot Use Memory Cards
217
Is the memory card SmartMedia formatted?
218
Error Messages
219
Error Messages
Quick Reference of Procedures
Performance Mode
220
Patch Mode
Quick Reference of Procedures
221
222
Rhythm Set Mode
223
Controller Settings
224
225
Saving and Loading Data
226
227
Controlling External Midi Devices
228
Controlling the XV-88 from an External Midi Device
229
Others
Effects Group p
Parameter List
Performance Parameters
Common Group p
231
Parameter List Midi Group p
Part Group p
Information Group p
Zone Parameters
233
Patch Parameters
Parameter List Beam Group p
Info Group p
234
Parameter List Effects Group p
Parameter List Control Group p
Wave Group p
235
Parameter List LFO Group p
Pitch Group p
236
237
Rhythm Set Parameters
Parameter List TVF Group p
TVA Group p
238
Parameter List Pitch Group p
239
TVA Velocity
240
GM Mode Parameters
Multi-Effects Parameters
Tremolo Chorus p
Stereo Delay p
Parameter List Limiter p
HEXA-CHORUS p
Parameter List Time Control Delay p
Modulation Delay p
Triple TAP Delay p
Quadruple TAP Delay p
CHORUS→ Delay p
OVERDRIVE→ Delay p
DISTORTION→ Delay p
ENHANSER→ Delay p
Stereo Phaser p
FLANGER→ Delay p
CHORUS/DELAY p
FLANGER/DELAY p
48 3D Delay p
Parameter List Multi TAP Delay p
Reverse Delay p
Shuffle Delay p
Distortion 2 p
Lofi Noise p
Speaker Simulator p
Overdrive 2 p
Chorus Parameters
249
DELAY, PAN-DLY
Reverb Parameters
SRV ROOM/SRV HALL/SRV Plate p
Setup Group p
System Parameters
250
Parameter List Tune Group p
Preview Group p
251
252
User Group Preset a Group Preset B Group
Performance List
User PR-A PR-B
No. Name Voice Key Assign
User User Group PR-A Preset a Group
Patch List
253
254
Patch List PR-B Preset B Group PR-C Preset C Group
PR-D Preset D Group PR-E Preset E Group
Patch List
255
Patch List PR-F Preset F Group
256
Name Voice Key Assign
Name Voice LSB
Patch List PR-H GM2 Group
257
Name Voice
User User Group PR-A Preset a Group
Rhythm Set List
258
PR-B Preset B Group PR-C Preset C Group PR-D Preset D Group
Rhythm Set List
259
PR-E Preset E Group PR-F Preset F Group
260
001 002 XV Pop Kit XV Rock Kit XV Jazz Kit XV Rust Kit
261
PR-H GM2 Group
001 002 003 004 005 006
007 008 009
262
Waveform List
263
Wave Name
Waveform List
264
PWM
MMM VOX
265
266
REV 909 Nzhh
267
Arpeggio Style List
268
Style Motif Beat Pattern Accent Rate
About Midi Connectors
About Midi
Midi Channels and Multi-timbral Sound Generators
Control Change
Midi Implementation
270
Polyphonic Key Pressure
271
Midi Implementation
Pitch Bend Change
272
Program Change
Channel Pressure
273
274
Universal Realtime System Exclusive Messages
Global Parameter Control
Data Transmission
275
Data set 1DT1 12H
276
277
278
279
Performance Common MFX
280
System Keyboard
Performance Common
281
Performance Common Chorus
Performance Common Reverb
Performance Keyboard
282
Performance Midi
Performance Part
Patch Common
283
Patch Common MFX
284
Patch TMT Tone Mix Table
285
Patch Common Chorus
Patch Common Reverb
Patch Tone
286
287
Rhythm Common
Rhythm Common MFX
Rhythm Tone
288
Rhythm Common Chorus
Rhythm Common Reverb
289
Part Parameter
290
System Parameter
Common Parameter
291
Drum Setup Parameter
Arpeggio Beat Pattern
292
Arpeggio Style
Arpeggio Motif
Examples of Actual Midi Messages
293
Example of an Exclusive Message Calculating a Checksum
294
Arabian Scale
295
Equal Temperament
Just Temperament Tonic of C
296
Midi Implementation Chart
RPN LSB, MSB
297
298
Specifications
299
Computer Cable Wiring Diagrams
300
Index
301
Index
Expression
302
Info
303
Lower
304
Output
305
PCH Envelope
306
258
307
308
Setting
TVF Envelope
309
310
Avis
Africa
Information