www.ti.com | EMAC Functional Architecture |
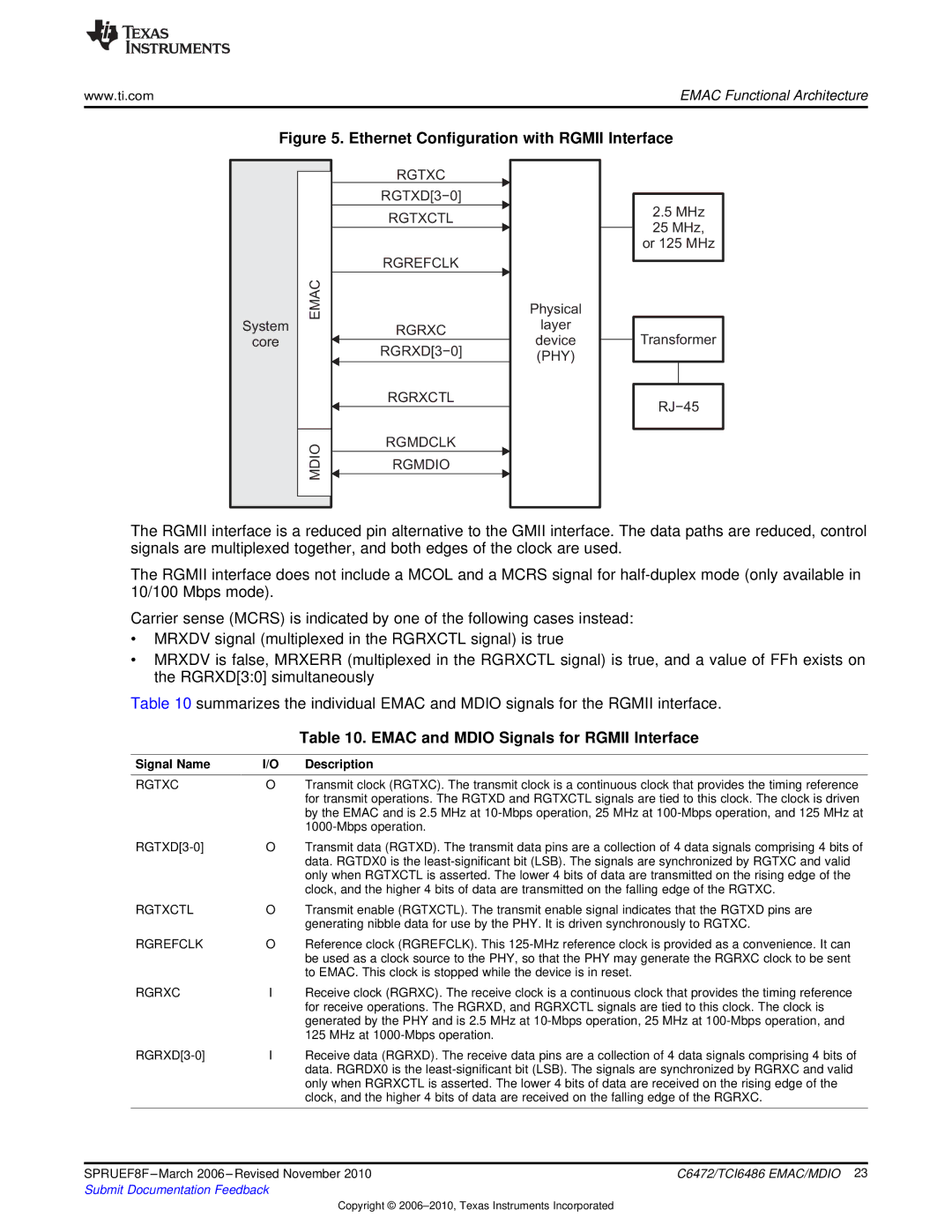
Figure 5. Ethernet Configuration with RGMII Interface
System
core
EMAC
MDIO
RGTXC
RGTXD[3−0]
RGTXCTL
RGREFCLK
RGRXC
RGRXD[3−0]
RGRXCTL
RGMDCLK
RGMDIO
Physical
layer
device (PHY)
2.5MHz 25 MHz,
or 125 MHz
Transformer
RJ−45
The RGMII interface is a reduced pin alternative to the GMII interface. The data paths are reduced, control signals are multiplexed together, and both edges of the clock are used.
The RGMII interface does not include a MCOL and a MCRS signal for
Carrier sense (MCRS) is indicated by one of the following cases instead:
•MRXDV signal (multiplexed in the RGRXCTL signal) is true
•MRXDV is false, MRXERR (multiplexed in the RGRXCTL signal) is true, and a value of FFh exists on the RGRXD[3:0] simultaneously
Table 10 summarizes the individual EMAC and MDIO signals for the RGMII interface.
|
| Table 10. EMAC and MDIO Signals for RGMII Interface |
|
|
|
Signal Name | I/O | Description |
|
|
|
RGTXC | O | Transmit clock (RGTXC). The transmit clock is a continuous clock that provides the timing reference |
|
| for transmit operations. The RGTXD and RGTXCTL signals are tied to this clock. The clock is driven |
|
| by the EMAC and is 2.5 MHz at |
|
| |
O | Transmit data (RGTXD). The transmit data pins are a collection of 4 data signals comprising 4 bits of | |
|
| data. RGTDX0 is the |
|
| only when RGTXCTL is asserted. The lower 4 bits of data are transmitted on the rising edge of the |
|
| clock, and the higher 4 bits of data are transmitted on the falling edge of the RGTXC. |
RGTXCTL | O | Transmit enable (RGTXCTL). The transmit enable signal indicates that the RGTXD pins are |
|
| generating nibble data for use by the PHY. It is driven synchronously to RGTXC. |
RGREFCLK | O | Reference clock (RGREFCLK). This |
|
| be used as a clock source to the PHY, so that the PHY may generate the RGRXC clock to be sent |
|
| to EMAC. This clock is stopped while the device is in reset. |
RGRXC | I | Receive clock (RGRXC). The receive clock is a continuous clock that provides the timing reference |
|
| for receive operations. The RGRXD, and RGRXCTL signals are tied to this clock. The clock is |
|
| generated by the PHY and is 2.5 MHz at |
|
| 125 MHz at |
I | Receive data (RGRXD). The receive data pins are a collection of 4 data signals comprising 4 bits of | |
|
| data. RGRDX0 is the |
|
| only when RGRXCTL is asserted. The lower 4 bits of data are received on the rising edge of the |
|
| clock, and the higher 4 bits of data are received on the falling edge of the RGRXC. |
|
|
|
SPRUEF8F | C6472/TCI6486 EMAC/MDIO 23 |
Submit Documentation Feedback |
|
Copyright ©