www.ti.com | MDIO Registers |
4.12 MDIO User Access Register 0 (USERACCESS0)
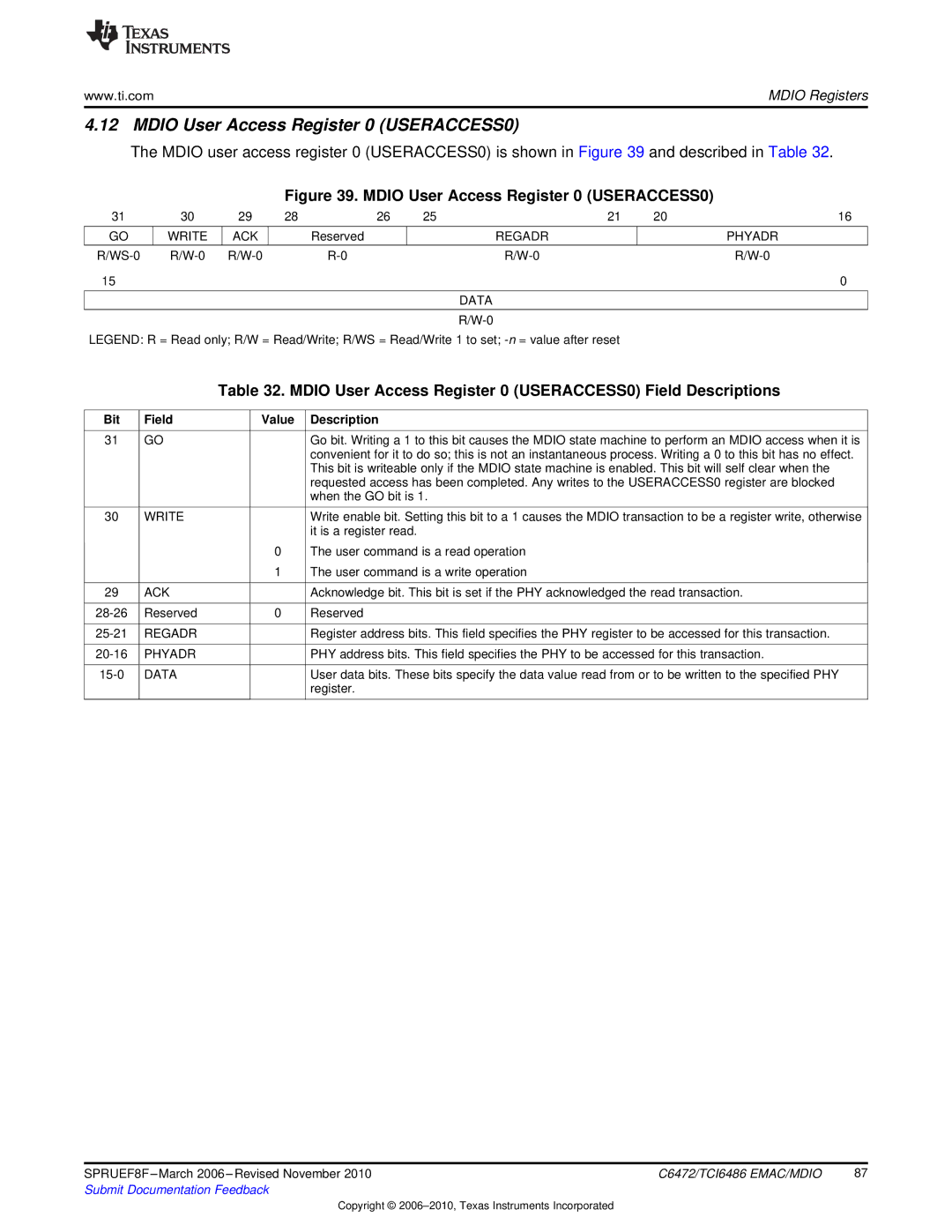
The MDIO user access register 0 (USERACCESS0) is shown in Figure 39 and described in Table 32.
Figure 39. MDIO User Access Register 0 (USERACCESS0)
31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 26 | 25 | 21 | 20 | 16 |
GO | WRITE | ACK |
| Reserved |
| REGADR |
| PHYADR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LEGEND: R = Read only; R/W = Read/Write; R/WS = Read/Write 1 to set; |
|
| ||||||
Table 32. MDIO User Access Register 0 (USERACCESS0) Field Descriptions
Bit | Field | Value | Description |
|
|
|
|
31 | GO |
| Go bit. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the MDIO state machine to perform an MDIO access when it is |
|
|
| convenient for it to do so; this is not an instantaneous process. Writing a 0 to this bit has no effect. |
|
|
| This bit is writeable only if the MDIO state machine is enabled. This bit will self clear when the |
|
|
| requested access has been completed. Any writes to the USERACCESS0 register are blocked |
|
|
| when the GO bit is 1. |
|
|
|
|
30 | WRITE |
| Write enable bit. Setting this bit to a 1 causes the MDIO transaction to be a register write, otherwise |
|
|
| it is a register read. |
|
| 0 | The user command is a read operation |
|
| 1 | The user command is a write operation |
|
|
|
|
29 | ACK |
| Acknowledge bit. This bit is set if the PHY acknowledged the read transaction. |
|
|
|
|
Reserved | 0 | Reserved | |
|
|
|
|
REGADR |
| Register address bits. This field specifies the PHY register to be accessed for this transaction. | |
|
|
|
|
PHYADR |
| PHY address bits. This field specifies the PHY to be accessed for this transaction. | |
|
|
|
|
DATA |
| User data bits. These bits specify the data value read from or to be written to the specified PHY | |
|
|
| register. |
|
|
|
|
SPRUEF8F | C6472/TCI6486 EMAC/MDIO | 87 |
Submit Documentation Feedback |
|
|
Copyright ©