Revision Firmware Version
External RAID Controller & Subsystem
Disclaimer
Copyright This Edition First Published
Supported Models
Iii
RMA Policy
Table of Contents
LCD Keypad Operation
LCD Screen Messages
Viewing and Editing Scsi Drives
Viewing and Editing Logical Drives and Drive Members
Vii
Terminal Screen Messages
Terminal Operation
Viii
Fibre Operation
Host-side and Drive-side Scsi Parameters
Advanced Configuration
Multi-Host Access Control LUN Filtering
10-19
Redundant Controller
10-1
10-14
Array Expansion
Record of Settings
Xii
Appendix C System Functions Upgrading Firmware
Appendix D Event Messages
Functional Table of Contents
7.8
Xiv
Chapter Fibre Operation
Chapter Advanced Configurations
Xvi
Chapter Redundant Controller Configuration
Chapter Array Expansion
Xvii
Appendix C Controller Maintenance
Chapter
Xviii
Xix
Optimization Setting
About This Manual
Xxi
Revision History
Xxii
Chapter
Logical Volume
What is a logical volume?
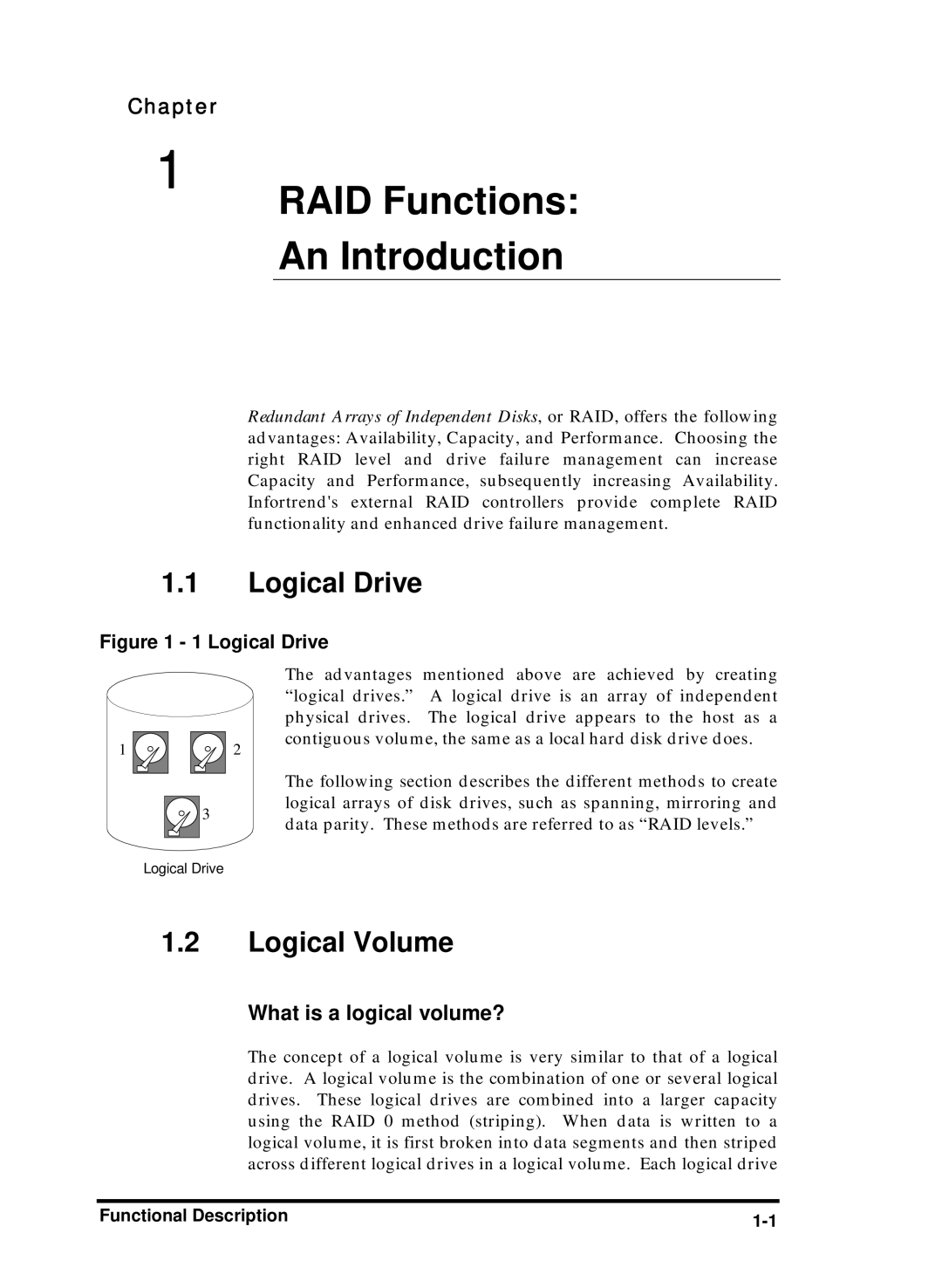
Logical Drive
Infortrend
RAID Levels
What are the RAID levels?
RAID Levels
LogicalDrive
RAID 0+1
RAID 0+1
Disk Striping with Dedicated Parity Disk
Spare
Spare Drives
Global and Local Spare Drives
Local
12 Mixing Local and Global Spares
Flash All but Selected Drives
Identifying Drives
Flash Selected Scsi Drive
Flash All Scsi Drives
Automatic Rebuild and Manual Rebuild
Rebuild
14 Manual Rebuild
Manual Rebuild
Concurrent Rebuild in RAID 0+1
15 Logical Volume
Logical Volume Multi-Level RAID
16 Logical Drive Composed of 24 Drives
18 Logical Volume with Drives on Different Channels
Spare drives assigned to a logical volume?
Limitations
Different controller settings using logical volume?
Different write policies within a logical volume?
RAID expansion with logical volume?
Multi-level RAID systems
Logical volume with logical drives of different levels?
RAID Planning
How many physical drives do you have?
How many drives on each drive channel?
What kind of host application?
Dual loop, hub, or switch?
What RAID level?
Optimization Mode
Limitations?
Any spare drives?
Starting a RAID System
Array Configuration Process
Infortrend
Grouping Drives into an Array
1 I/O Channel, Scsi ID, and LUN
Physical locations of drive members
Mapping Partitions to Host ID/LUNs
Making Arrays Available to Hosts
Tunable Parameters
Controller Parameter Settings
Optimization Mode
Array Configuration
Out-of-Band via Serial Port and Ethernet
Following are guidelines on using the serial port
RS-232C Serial Port
Configuring RS-232C Connection via Front Panel
Starting RS-232C Terminal Emulation
Keys used when operating via the terminal are as follows
Connecting Terminal
Out-of-Band via Ethernet
What Is the Disk Reserved Space?
Requirements
Connecting Ethernet Port
Other Concerns
Use a Terminal Emulator to Begin Configuration
Configuring the Controller
Assign an IP Address to Ethernet Port
Starting the Manager
Snmptrap
NPC Onboard
Snmptrap section
LCD Screen Messages
Quick Installation Screen
Initial Screen
Drive numbers
Logical Drive Status
Logical Drive
RAID level
Logical Volume Status
Logical Volume Status
Scsi Drive Status
Primary Controller Scsi ID Mapping
Channel Mode
Default Scsi Bus Sync Clock
Scsi Channel Status
Controller Voltage and Temperature
View and Edit Event Logs
UPS Power Failure Detected Press 2 Seconds to Clear Events
Cache Dirty Percentage
View and Edit Event Logs
Front Panel Operation
Power on RAID Enclosure
Caching Parameters
Optimization Modes
Database and Transaction-based Applications
Optimization Mode and Stripe Size
Optimization for Random or Sequential I/O
Write-Back/Write-Through Cache Enable/Disable
Write-Back Cache Enabled Disable Write
Infortrend
View Drive Information
View Connected Drives
View and Edit Scsi Drives
=2 I=0 1010MB New DRV Seagate
Logical Drive Preferences
Creating a Logical Drive
Choosing a RAID Level
Choosing Member Drives
Disk Reserved Space
Initialization Mode
Maximum Drive Capacity
Spare Drive Assignments
Beginning Initialization
Stripe size Default ?
On-Line Mode
Stripe Size
Off-Line Mode
Creating a Logical Volume
Logical Volume Assignment
Partitioning a Logical Drive/Logical Volume
View Edit Host Luns
Mapping a Logical Volume/Logical Drive to Host LUN
View and Edit Scsi Drives =2 I=4 1010MB
Assigning Spare Drive and Rebuild Settings
Adding a Local Spare Drive
MAP to LV=0 PRT=0?
Add Global Spare Drive Add Global Spare Drive Successful
Rebuild Settings
Adding a Global Spare Drive
Deleting a Logical Drive
Viewing and Editing Logical Drives and Drive Members
Drive Space Allocated to the Last Partition
Deleting a Partition of a Logical Drive
Rebuild Logical Drive Drive? Rebuilding 25% Please Wait
Assigning a Name to a Logical Drive
Rebuilding a Logical Drive
View and Edit Logical Drives LG0 RAID5 DRV=3 2012MB FL SB=0
LG0 RAID5 DRV=3 2012MB RB SB=0 Rebuild Progress
Regenerating Logical Drive Parity
View and Edit Logical Drives LG0 RAID5 DRV=3 4095MB GD SB=0
Media Scan
Write Policy
Viewing and Deleting LUN Mappings
Pass-through Scsi Commands
Viewing and Editing Host LUNs
Scan Channel=1 ID=1 Scan Fail
Viewing and Editing Scsi Drives
Scanning New Scsi Drive
=1 I=1 Absent
Identifying a Drive
Deleting Spare Drive Global / Local Spare Drive
Redefining Channel Mode
Viewing and Editing Scsi Channels
Primary Controller ? Add CHL=0 ID=2 Primary Ctlr ?
Setting a Scsi Channel’s ID Host Channel Viewing IDs
Adding a Channel ID
Add Channel
Delete ID=2 Primary Ctlr ?
Setting a Scsi Channel’s Primary ID Drive Channel
Deleting a Channel ID
Delete Channel
Setting Channel Bus Terminator
Setting a Scsi Channel’s Secondary ID Drive Channel
Scsi Terminator Enabled CHL=0 Disable Terminator ?
Setting Transfer Speed
View and Edit Scsi Target
Setting Transfer Width
Viewing and Editing Scsi Target Drive Channel
View and Edit Scsi Channels CH1=Drive PID=7
Maximum Transfer Width
Slot Number
Maximum Synchronous Transfer Clock
Max Xfer Narrow Only?
Disconnecting Support
Parity Check
Maximum Tag Count
Restore to Default Setting
Mute Beeper
Change Password
Changing Password
System Functions
Shutdown Controller
Disabling Password
Reset Controller
Restore Nvram From Disks
Restore Nvram from Disks
ShutdownComplete Reset Ctlr?
Controller Maintenance Save Nvram To Disks
LCD Title Display Controller Name
Password Validation Timeout
Controller Parameters
Controller Name
Time Zone
Controller Date and Time
Time Zone
Date and Time MMDDhhmmYYYY
Date and Time
GMT +0800
Scsi Drives Utilities Drive Read/Write Test
Scsi Drive Utilities
Scsi Drive Low-level Format
View and Edit Scsi Drives =1 I=1 8683MB
Scsi Drive Read/Write Test
Cursor Bar
Transfer Rate Indicator
PC Graphic Ansi Mode
Terminal VT-100 Mode
Main Menu
Quick Installation
Terminal Screen Messages
Status
SizeMB
Name
Column C
Speed
Slot
Chl
Size MB
PID
Scsi Channel’s Status
CurWid
Term
CurSynClk
Controller voltage and temperature monitoring
Viewing Event Logs on the Screen
Terminal Operation
Terminal Operation
Limitations
Optimization Mode and Stripe Size
Viewing the Connected Drives
Creating a Logical Drive
Choosing a RAID Level
Logical Drive Assignments
Assign Spare Drives
Initialization Mode
Terminal Operation
Creating a Logical Volume
Partitioning a Logical Drive/Logical Volume
Infortrend
Mapping a Logical Volume to Host LUN
Infortrend
Adding Local Spare Drive
Assigning Spare Drive, Rebuild Settings
Viewing and Editing Logical Drive and Drive Members
1000MB
Rebuilding a Logical Drive
Applies to RAID1, 3,
Iteration Count
Edit Host-ID/WWN Name List
Viewing or Deleting LUN Mappings
Scanning New Drive
Identifying Drive
Slot Number Drive Entry
Terminal Operation
Viewing and Editing Scsi Channels
Viewing and Editing Scsi IDs Host Channel
Deleting an ID
Setting a Primary Controller’s Scsi ID Drive Channel
Drive Channel
Setting a Secondary Controller’s Scsi ID Drive Channel
Setting Channel Terminator
Setting a Transfer Speed
Host Channel
Setting the Transfer Width
Viewing and Editing Scsi Target / Drive Channel
Maximum Synchronous Transfer Clock
Data Rate
Infortrend
System Functions
Setting a New Password
Changing the Password
Disabling the Password
Controller Parameters
Saving Nvram to Disks
Password Validation Timeout
Terminal Operation
Set Controller Date and Time
View Drive Information
Drive Information
Scsi Drive Utilities
Scsi Drive Low-level Format
Scsi Drive Read/Write Test
Fibre Operation
Overview
Major Concerns
Fibre Operation
Multiple Target IDs
Supported Features
Fibre Chip
In-band Fibre and S.E.S. Support
Drive IDs
Primary and Secondary Controller IDs
Configuration Host and Drive Parameters
Channel Mode
Limitation
Redundant Controller Cache Coherency Channel RCC Channel
View Channel WWN
User-Assigned ID Scan Scsi Drive
View Device Port Name List Wwpn
View and Edit Fibre Drive
View and Edit Host-Side Parameters
View and Edit Drive-Side Parameters Drive-Side Dual Loop
Fibre Channel Connection Type
Controller Unique Identifier
Controller Communications over Fibre Loops
Fibre Operation
Storage Pool
Multi-Host Access Control LUN Filtering
Host-LUN Mapping
Creating LUN Masks
WWN Name List
Logical Unit to Host LUN Mapping
Infortrend
Filter Type Include or Exclude
LUN Mask ID Range Configuration
Access Mode Read Only or Read/Write
Sample Configuration
Configuration Procedure
Infortrend
A.R.T
Fault Prevention
Advanced Configurations
Replace after Clone
Clone Failing Drive
Perpetual Clone
Advanced Configurations
Introduction
Clone + Replace
Disable
Detect Only
Perpetual Clone
Examining Whether Your Drives Support S.M.A.R.T
Configuration Procedure
Enabling the S.M.A.R.T. Feature
Detect Only Setting
Using S.M.A.R.T. Functions
Detect, Perpetual Clone Setting
Detect, Clone+Replace Function
Foreword Scsi Channel, Scsi ID and LUN
Host-side and Drive-side Scsi Parameters
Host-side Scsi Parameters
Number of Tags Reserved for each Host-LUN Connection
LUN Applicability
Maximum Queued I/O Count
LUNs per Host Scsi ID
In-band Scsi or Fibre
What is In-band?
Peripheral Device Type
SCO
Peripheral Device Type Parameters
Cylinder/Head/Sector Mapping under Sun Solaris
Peripheral Device Type Settings
Device Type Setting
Cylinder/Head/Sector Mapping
Configuring Sector Ranges/Head Ranges/Cylinder Ranges
Scsi Motor Spin-Up
Drive-side Parameters
Scsi Reset at Power-Up
Scsi I/O Timeout
Disk Access Delay Time
Maximum Tag Count Tag Command Queuing
Periodic Drive Check Time
Detection of Drive Hot Swap Followed by Auto Rebuild
SAF-TE and S.E.S. Enclosure Monitoring
Periodic Auto-Detect Failure Drive Swap Check Time
Idle Drive Failure Detection
Advanced Configurations
View Peripheral Device Status
Monitoring and Safety Mechanisms
Dynamic Switch Write-Policy
Controller Auto-Shutdown Event Trigger Option
Rebuild Priority
Disk Array Parameters
Verification on Writes
Redundant Controller 10-1
Operation Theory
10-2 Infortrend
Setup Flowchart
Considerations Related to Physical Connection
SCSI-Based Controllers
Redundant Controller 10-3
Fibre-Based Controllers
10-4 Infortrend
Grouping Hard Drives and LUN Mapping
Redundant Controller 10-5
Logical Drive, Logical Volume, and Logical Partitions
10-6 Infortrend
System Drive Mapping
Primary and Secondary IDs
Redundant Controller 10-7
Mapping
10-8 Infortrend
Fault-Tolerance
What Is a Redundant Controller Configuration?
Redundant Controller 10-9
How does Failover and Failback Work? Channel Bus
10-10 Infortrend
ID Mapping Status Normal Operation
ID Mapping Status Controller Failed
Auto-Failback
Active-to-Active Configuration
Controller Failover and Failback
Replacing a Failed Unit
Redundant Controller 10-12
Traffic Distribution and Failover Process
10-13 Infortrend
Symptoms
Controller Failure
Connection
Controller RCC cable
Preparing Controllers
Requirements
Cabling Requirements
Redundant Controller 10-15
Controller Settings
10-16 Infortrend
Configurable Parameters
Limitations
Primary or Secondary
Redundant Controller 10-17
Active-to-Standby Configuration
Battery Support
Cache Synchronization
10-18 Infortrend
Redundant Controller 10-19
Configuration
Via Front Panel Keypad
Redundant Configuration Using Automatic Setting
Enable Redundant Controller
Autoconfig
Redundant Controller 10-21
Redundant Configuration Using Manual Setting
View and Edit Peripheral Dev
10-22 Infortrend
RC connecting ENT to cancel
Starting the Redundant Controllers
Creating Primary and Secondary ID
Redundant Controller 10-23
Set Sec. Ctlr Idna to ID 6?
CHL=0 ID=0 Primary Ctlr Add Channel
View and Edit Logical Drives
10-24 Infortrend
Mapping a Logical Drive/Logical Volume to the Host LUNs
Redundant Ctlr Failure Detected
What will happen when one of the controllers fails?
When and how is the failed controller replaced?
Front Panel View of Controller Failure
10-26 Infortrend
Via Terminal Emulation
Redundant Controller 10-27
10-28 Infortrend
Redundant Controller 10-29
Assigning Logical Drives to the Secondary Controller
10-30 Infortrend
Redundant Controller 10-31
When and How Is the Failed Controller Replaced?
Terminal Interface View of Controller Failure
10-32 Infortrend
Redundant Controller 10-33
Forcing Controller Failover for Testing
Cache Synchronization on Write-Through
RCC Status Redundant Controller Communications Channel
Secondary Controller RS-232
Remote Redundant Controller
View and Edit Logical Drives
Record of Settings 11-1
11-2 Infortrend
Record of Settings 11-3
View and Edit Logical Volumes
11-4 Infortrend
View and Edit Host LUN’s
Record of Settings 11-5
11-6 Infortrend
View and Edit Scsi Drives
View and Edit Scsi Channels
Record of Settings 11-7
11-8 Infortrend
View and Edit Configuration Parameters
Communication Parameters
Host Side Scsi Parameters
Record of Settings 11-9
11-10 Infortrend
Disk Array Parameters
View and Edit Peripheral Devices
Record of Settings 11-11
11-12 Infortrend
Save Nvram to Disk, Restore from Disk
RAID Security Password
Array Expansion
What is it and how does it work?
Added Capacity
Array Expansion
Expand Logical Drive Re-Striping
Add-Drive Procedure
Mode 1 Expansion Adding Drives to a Logical Drive
12-5
12-6
Expansion by Copy & Replace
Copy and Replace Procedure
12-8
12-9
Making Use of the Added Capacity Expand Logical Drive
12-10
Expand Logical Volume
Example
Limitations When Using Windows
12-13
12-14
12-15
12-16
12-17
Start
Navigation Map
Create
View and Edit Scsi Drives
View and Edit Scsi Channels
View and Edit Configuration Parameters
View and Edit Peripheral Device
End
Appendix
Basic RAID Management
Advanced Features
128
Caching Operation
Caching Optimization
RAID Expansion
Fibre Channel Support
Redundant Controller
A.R.T. Support
Data Safety
System Security
Environment Management
Remote Manageability
User Interface
Others
JBOD-Specific
System Functions Upgrading Firmware
Redundant Controller Rolling Firmware Upgrade
Upgrading Firmware
Establish the In-band Scsi connection in RAIDWatch Manager
Redundant Controller Firmware Sync-version
Upgrade Both Boot Record and Firmware Binaries
Upgrade the Firmware Binary Only
Upgrading Firmware Using RS-232C Terminal Emulation
Upgrading Both Boot Record and Firmware Binaries
Upgrading the Firmware Binary Only
Event Messages
Event Index
Controller Event
Notification
Drive Scsi Channel/Drive Error
General Target Events
Logical Drive Event
I2C Device
Notification SAF-TE Device
3fa2 Notice Controller FAN Back On-Line RPM
Happens?
Controller Event
Happens? What to Do?
Happens? What to Do?
Drive Scsi Channel/Drive Error
Received Sensekey Sensecode
Happens? What to Do? Line LCD
= I= Unexpected Sense Rec
What to Do?
What to Press ESC to clear the message
Red Path for C Failure Detected
Logical Drive Event
Infortrend
Happens?
Infortrend
Event Type
General Target Events
Controller On-board
Event Type
Check I 2C cable connection and contact your system supplier
3F22 Peripheral Device Alert high/low threshold Fan Speed
Event Messages
SES Device
Line LCD . Temp Sensor Device Unknown Status
What Happens? What to
Line LCD . Current Sensor Device Not Supported
Infortrend
What Happens?
Temperature back to non-critical level
Controller Self Diagnostics
Contlr FAN Back On-Line
Happens?
SES Device Alert
Alert Notification What UPS device failure detected
Index-1
Index
Index-2 Infortrend
Index-3
Index-4 Infortrend
Index-5
Nvram
Index-6 Infortrend
RCC
Index-7
Index-8 Infortrend
Zmodem