Submerged Probe Flow Meter
Page
Foreword
Page
Understood. While specific hazards may vary according to
These three levels are described in the sample alerts below
Hazard Symbols
Symboles de sécurité
Important Please Read
Flow Meter Safety
Flow Meter
Submerged Probe Installation
Options and Accessories
Maintenance and Service
Iii
Appendix D General Safety Procedures
Appendix E Material Safety Data Sheets
List of Illustrations
List of Tables
Page
Introduction
Description Compatible Equipment
Manual Organization
Flow Meter Introduction
Submerged Probe
Software Upgrades Controls, Indicators, and Connectors
Submerged Probe Level Sensor with Standard Tip
4220 Controls and Indicators
Pin Function
Rain Gauge Input 12V Ground Sense Line
Controls, Indicators, and Connectors
Controls Settings Function
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications for the 4220 Flow Meter
Technical Specifications for the 3222 Submerged Probe
Flowlink Data Storage and Retrieval System
Chart Longevity
Battery Life Expectancy1
How to Make Battery Calculations
000 ÷ 15 = 266.67 hours
Hours ÷ 24 = 11.1 days
11.1 1.1 = 10 days
Current Draw
00I5
Flow Meter Introduction
Normal, programming, and messages. In the normal mode
Programming
Getting Started
Operation
Flow Meter Programming
Programming Procedure
Flow Meter Programming
Operating Mode
Description of Program Steps
Conversion Type
Data POINTS, and Equation
= k1HP1+ k2HP2
270 D.O. module is no longer available from Teledyne Isco
YSI 600 Sonde
Sampler
Pacing
Enable
Mode
Printer
Step
Reports/History
Interpreting the Program Screens
Year Month DAY Hour MIN
Level Reading Interval
Following will appear if you are measuring temperature
Interrogator connector
Optional Outputs
Analog Output
Output Range
Ascii Output Codes
Code Parameter Units
YCO
Periodic Serial Output
Report Setup Report a Report B
Temperature in Report
Setup Options Exit to Quit Status Report Setup LCD Backlight
Program
Flow Rate Units of Measure
Rain Gauge Inches MM not Measured
Temperature Units
Sured
Flow Conversion Level-to-Flow Rate
If you select V-NOTCH, the following will appear
If you select LEOPOLD-LAGCO, this will appear
For Example
Then
Enter Maximum Head All Models
Programming the 4-20 mA Outputs
Adjust
= h level
Dissolved Oxygen Calibration Standardabs Barometric Pressure
Then the display will advance to the following
Returning to the YSI menu, if you select D.O
Place Probe in X.XX PPT Press Enter When Stable X.XX MS/CM
YSI 600 Sonde Calibration Flow Chart
This step determines how the flow meter will signal an asso
Condition
Sampler
Sampler Enable Mode Disable Enable Conditional Storm
Time Since Last Rainfall
As described previously for sampler enabling
Alarm Dial OUT Disable Conditional Storm Flowlink
Alarm Dialout Numbers
Printer
Printer Line a Bottom Scale
Step
Report B Duration to be Hours Days Months
Flow Meter History Contents
Installation
Installing
Desiccant Canister
Flow Meter Installation
Connection to a Power Source
Low Power Indication
Isco Sampler
Battery
Attaching
Nickel-Cadmium
Lead-Acid Battery
Attaching the Isco
Power
Supply
Flow Meter Mounting and Installation Procedures
Carrying Handle
Meter
Flow Stream
Quick-Disconnect Box for the Submerged Probe Cover Removed
Extension Cables
Flow Meter Installation
Flow Meter Installation
Submerged Probe Installation
General Mounting Considerations
Submerged Probe Nose Sections
Solids
Minimum Reliable Detection Level
Mounting Rings
Spring Rings
Flow Meter Submerged Probe Installation
Spring Ring Preparation
Rings
Isco’s Four-Foot Probe Extension only. Do not attempt to
Flow
Mounting
Gun
Other Mounting Techniques
Locating the Head-Measuring Point
Device Head-Measuring Point
Submerged Probe Dimensions
Typical Primary Device Installations
Weighted Plate
Options and Accessories
4200T Modem
How it Works
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
4-20 mA Output Interface Specifications
4-20 mA Output Interface Specifications
Internal Multiple
Analog Output Board
Multiple Analog Output Board Specifications
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
Isco Flowlink Software High-Low Alarm Relay Box
674 Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
Wiring to a 4200 Series Flow Meter
Installation of Parameter Probes
Parameter Sensing with Isco 4200 Series Flow Meters
Temperature Probe
PH Probe
PH Probe with protective cap
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
Guidelines Sensor and other parameter probes
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
PH Parameter Module
PH Probe Specifications
Dissolved Oxygen Probe
D.O. Probe
Steps for installing a new membrane
Works
Probe Preparation
10.4 Probe Installation
Precautions Frequency of service
10.3 Membrane
Thicknesses
Flow Meter Options and Accessories
D.O. Probe Specifications
Calibrating the D.O. Probe with a Flow Meter
Installation of Parameter Probes in Mounting Rings
YSI 600 Multiple Parameter Sonde
Mounting of Four Foot Probe Extension
YSI 600 Probe Specifications
Complete Unit
Dissolved Oxygen % Saturation
Maintenance and Service
Minor Service
Case
Damage
Reactivation of the Desiccators
Regenerating
Internal Case
Desiccant
Regenerating the External Desiccant Cartridge
To regenerate the desiccant cartridge
Low Maintenance
Care of the Submerged Probe and Cables
Probe for Cleaning
Disassembling
Mounting hole must be aligned with the grounding point
Cable Inspection
Maintenance of the Printer
Changing the Roll of Paper
To remove the used roll
To install the new chart paper
Replacement
Ink Ribbon
To replace the ribbon
Servicing And Troubleshooting
Do Not Disassemble or Lubricate the Printer
Disassembling the Flow Meter
Fuse Replacement
F1 5 amp., fast blow
F2 5 amp., fast blow
F3 2 1/ 2 amp., fast blow
System Reset
Display Warnings
Preliminary Troubleshooting Steps
To reset the 4220 software
Occur
Department. Contact information can be found on the War
Flow Meter Maintenance and Service
Precautions for Servicing Cmos Circuitry
Hazard of Static Electricity
Getting Started Following instructions assume that
Recommends using it to update 4200 Series Flow
Updating your instrument erases the data stored
If you have Flowlink, Teledyne Isco strongly
Running Flash Update
This window
Options Menu
Minimum DOS and Computer Hardware Requirements
DOS
Appendix a Replacement Parts
Teledyne Isco, Inc
Flow Meter Appendix a Replacement Parts
Flow Meter Appendix a Replacement Parts
Table A-1 Replacement Parts List
Part Number Complete Part Description
Flow Meter
Flow Meter Appendix a Replacement Parts
Appendix B Accessories List
Accessories
Flow Meter Basic Unit
YSI 600 Accessories
Optional Equipment
Mounting Rings
Flow Meter Appendix B Accessories List
Setup
Appendix C Programming Worksheets
Flow Meter Appendix C Programming Worksheets
Flow Conversion Level-to-Flow Rate
Parameter to Adjust
Data Point Set
Enter Maximum Head
Reset Totalizer Sampler Pacing Sampler Enable
Alarm Dialout Mode Printer Reports/History
Additional table for Data Point Entry Data Point Set #2
Flow Meter Appendix C Programming Worksheets
Appendix D General Safety Procedures
Practical Safety Precautions
Flow Meter Appendix D General Safety Procedures
Flow Meter Appendix D General Safety Procedures
Lethal Atmospheres in Sewers
Flow Meter Appendix D General Safety Procedures
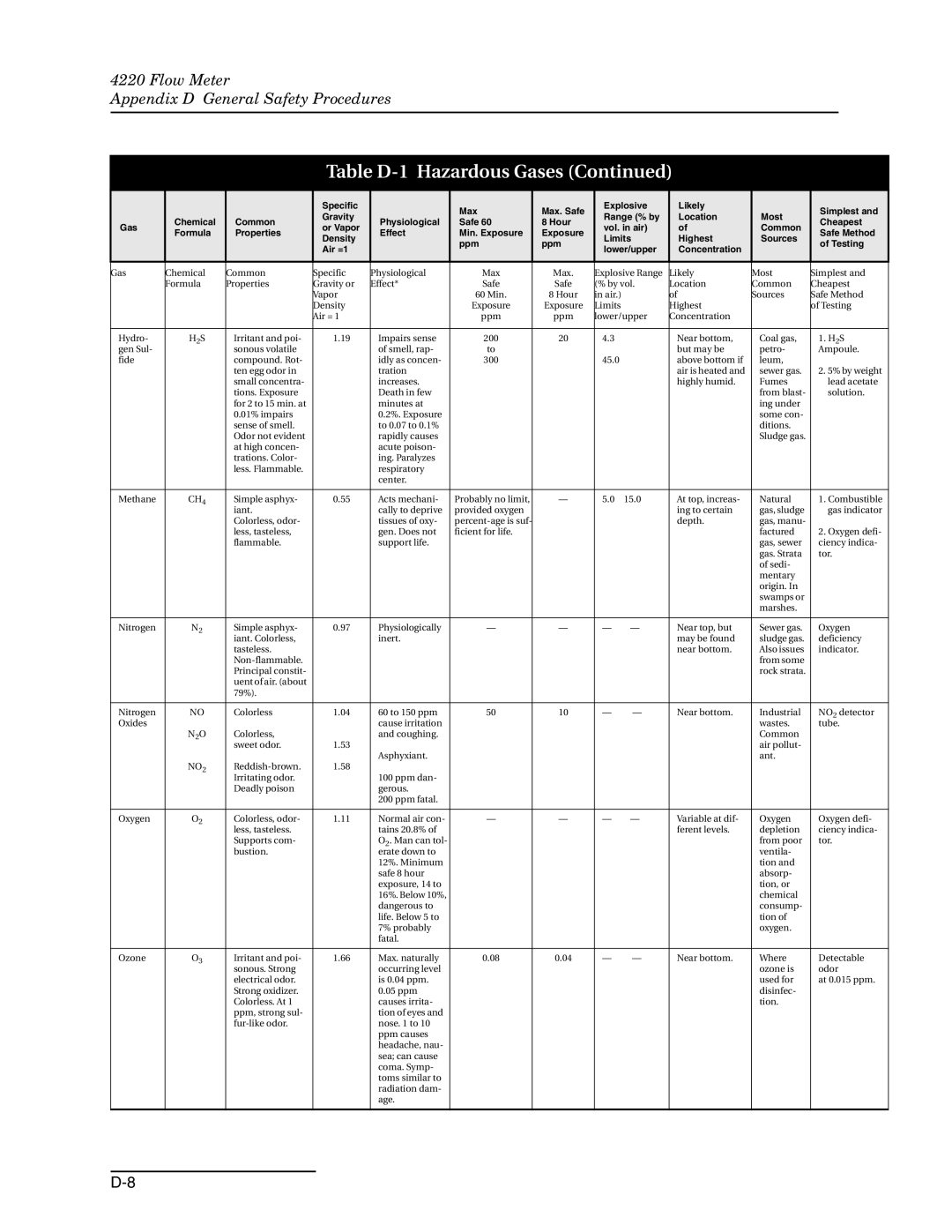
Hazardous Gases
Table D-1 Hazardous Gases
CH 2O
N2O
Sea, bad taste Lassitude Turpentine
Flow Meter Appendix D General Safety Procedures
Appendix E Material Safety Data Sheets
Overview
Material Safety Data Sheet
Health Hazard Data
Material Safety Data Sheet
First Aid Measures
Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Toxicological Information
Other Information
Index
Numerics
Index-2
Declaration of Conformity
Page
Standard Description Severity Applied Performance Criteria
Page
Teledyne Isco One Year Limited Factory Service Warranty