Debug and Trace
R
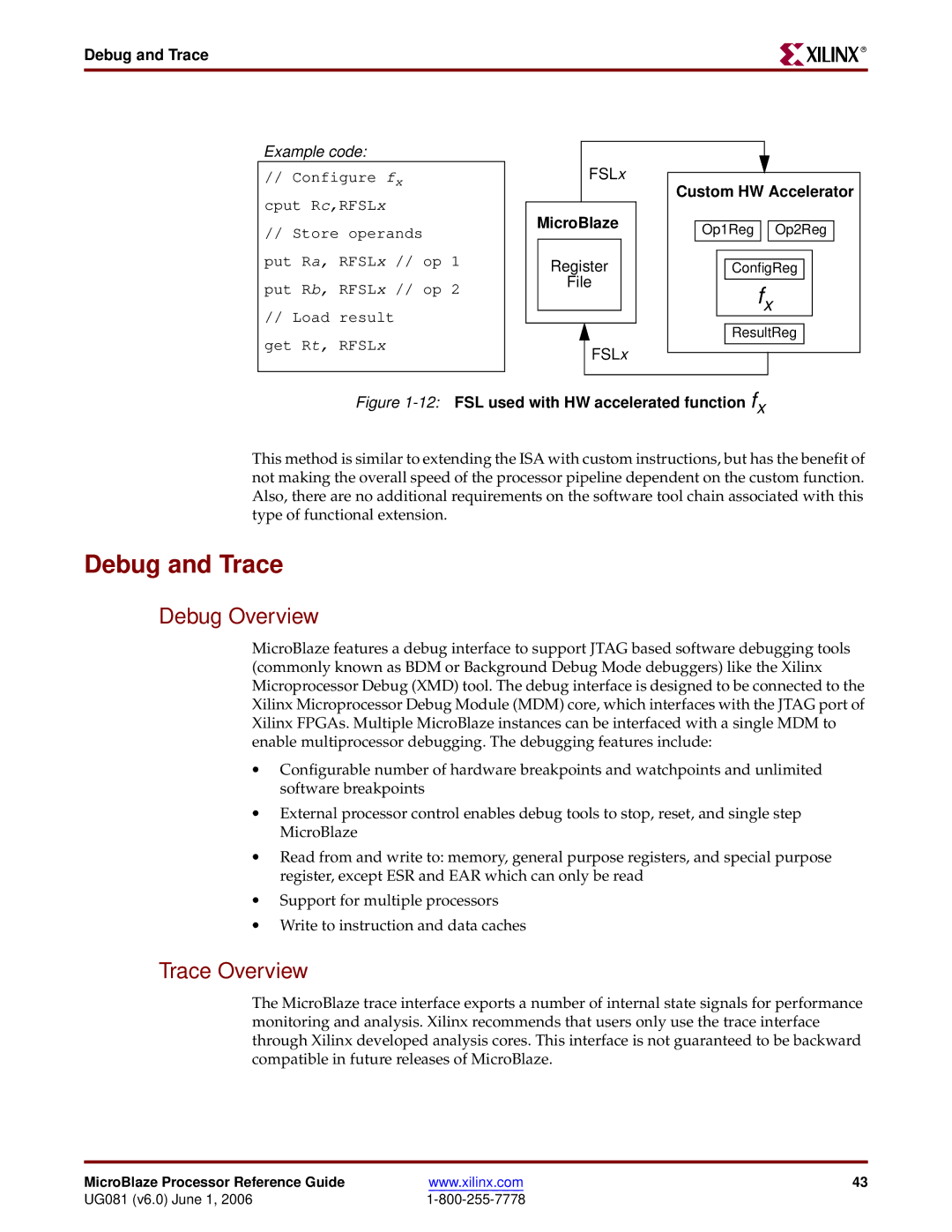
Example code:
// Configure fx cput Rc,RFSLx
//Store operands put Ra, RFSLx // op 1 put Rb, RFSLx // op 2
//Load result
get Rt, RFSLx
FSLx
MicroBlaze
Register
File
FSLx
Custom HW Accelerator
Op1Reg ![]()
![]() Op2Reg
Op2Reg
ConfigReg
fx
ResultReg
Figure 1-12: FSL used with HW accelerated function fx
This method is similar to extending the ISA with custom instructions, but has the benefit of not making the overall speed of the processor pipeline dependent on the custom function. Also, there are no additional requirements on the software tool chain associated with this type of functional extension.
Debug and Trace
Debug Overview
MicroBlaze features a debug interface to support JTAG based software debugging tools (commonly known as BDM or Background Debug Mode debuggers) like the Xilinx Microprocessor Debug (XMD) tool. The debug interface is designed to be connected to the Xilinx Microprocessor Debug Module (MDM) core, which interfaces with the JTAG port of Xilinx FPGAs. Multiple MicroBlaze instances can be interfaced with a single MDM to enable multiprocessor debugging. The debugging features include:
•Configurable number of hardware breakpoints and watchpoints and unlimited software breakpoints
•External processor control enables debug tools to stop, reset, and single step MicroBlaze
•Read from and write to: memory, general purpose registers, and special purpose register, except ESR and EAR which can only be read
•Support for multiple processors
•Write to instruction and data caches
Trace Overview
The MicroBlaze trace interface exports a number of internal state signals for performance monitoring and analysis. Xilinx recommends that users only use the trace interface through Xilinx developed analysis cores. This interface is not guaranteed to be backward compatible in future releases of MicroBlaze.
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide | www.xilinx.com | 43 |
UG081 (v6.0) June 1, 2006 |
|