MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide
UG081 v6.0 June 1
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide UG081 v6.0 June 1
Date Version Revision
UG081 v6.0 June 1
Preface About This Guide
MicroBlaze Application Binary Interface
Manual Contents
Additional Resources
Conventions
Typographical
Online Document
Conventions Meaning or Use Example
UG081 v6.0 June 1
Features
Overview
MicroBlaze Architecture
Version Status Deprecated Active
Data Types and Endianness
Instructions
EAR
MSR
ESR
FSR
Op1 if cond else op2
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide UG081 v6.0 June 1
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide UG081 v6.0 June 1
Registers
Program Counter PC
General Purpose Registers
Special Purpose Registers
Registers
9Machine Status Register MSR Bits Name Description
8Program Counter PC Bits Name Description Reset Value
Machine Status Register MSR
PVR
ICE
EIP
DCE
FSL
Buslock Enable
Exception Address Register EAR
Exception Status Register ESR
ESS
Branch Target Register BTR
Source/Destination Register
Floating Point Status Register FSR
Processor Version Register PVR
DIV
CFG
Cusebarrel
Cusediv
Unexec
Cdebugenabled
OP0EXEC
Cunalignedexception
Icbs
Icll
Cicachelinelen
Ccachebytesize
Arch
Cresetmsr
Pipeline Architecture
Rstmsr
Delay Slots
Memory Architecture
Branches
Reset, Interrupts, Exceptions, and Break
Reset, Interrupts, Exceptions, and Break
Equivalent Pseudocode
Reset
Hardware Exceptions
Exception Causes
Breaks
Hardware Breaks
Software Breaks
Interrupt
User Vector Exception
Latency
General Instruction Cache Functionality
Instruction Cache
Overview
Instruction Cache
Instruction Cache Software Support
Data Cache
Instruction Cache Operation
MSR Bit
General Data Cache Functionality
Data Cache Operation
Data Cache
Floating Point Unit FPU
Data Cache Software Support
WDC Instruction
Operations
Format
Rounding
Arithmetic
Exceptions
Hardware Acceleration using FSL
Fast Simplex Link FSL
Comparison
Debug and Trace
Debug Overview
Trace Overview
MicroBlaze Architecture
Ixcl
MicroBlaze I/O Overview
Ilmb
Dxcl
MicroBlaze Signal Interface Description
Dmrnw Dopb
IAS Ilmb
Imrnw Iopb
DAS Dlmb
Mfsl
Dxcls
On-Chip Peripheral Bus OPB Interface Description
Ixclm
Dxclm
Local Memory Bus LMB Interface Description
LMB Signal Interface
ByteEnable03
Addr031
WriteStrobe
DataWrite031
ReadStrobe
DataRead031
LMB Transactions
Generic Write Operation
Generic Read Operation
Back-to-Back Mixed Read/Write Operation
Back-to-Back Write Operation
Single Cycle Back-to-Back Read Operation
BE0 BE1 BE2
Read and Write Data Steering
RD1623 RD2431
RD07 RD815 RD1623 RD2431
Master FSL Signal Interface
Slave FSL Signal Interface
Fast Simplex Link FSL Interface Description
FSL BUS Write Operation
Xilinx CacheLink XCL Interface Description
FSL Transactions
FSL BUS Read Operation
CacheLink Signal Interface
CacheLink Transactions
Instruction Cache Read Miss
Data Cache Read Miss
Data Cache Write
Debug Interface Description
Debug Interface Description
Trace Interface Description
MDM
MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide
MicroBlaze Core Configurability
11 Type of Trace Exception TraceExceptionKind Description
Values Assigned Type
Pcmpne Cunalignedexception
Cusepcmpinstr
Cusemsrinstr
Cnumberofrdaddrbrk
Ffff
Cicacheusefsl
Cdcacheusefsl
Scope
Data Types
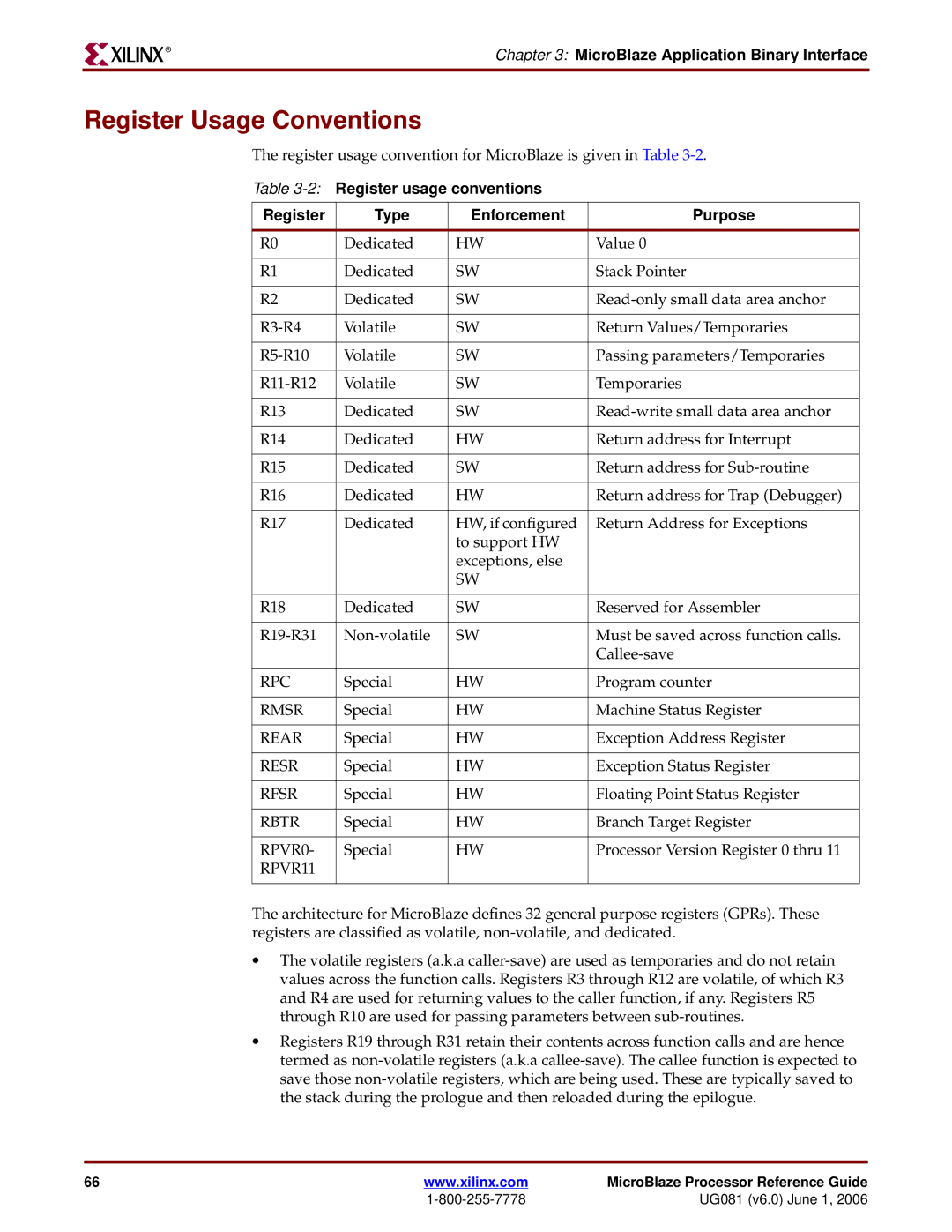
Register Usage Conventions
MicroBlaze Application Binary Interface
2Register usage conventions Type Enforcement Purpose
Stack Convention
Stack Convention
High Memory Low Memory Func
Memory Model
Interrupt and Exception Handling
1Symbol notation Meaning
Summary
Notation
Type B
Formats
Type a
Opcode Destination Reg Source Reg a Immediate Value
Add
Description
Registers Altered
Addi
Registers Altered Latency
RD, rA, rB
Andi
Logial and with Immediate Andi RD, rA, IMM
Andn
Logical and not
Andn RD, rA, rB
Andni
Logical and not with Immediate Andni RD, rA, IMM
Beq
Branch if Equal Beq
Beqd
Beqi
Branch Immediate if Equal Beqi
Beqid
Bge
Branch if Greater or Equal Bge
Bged
Bgei
Branch Immediate if Greater or Equal Bgei
Bgeid
Bgt
Branch if Greater Than Bgt
Bgtd
Bgti
Branch Immediate if Greater Than Bgti
Bgtid
Ble
Branch if Less or Equal Ble
Bled
Blei
Branch Immediate if Less or Equal Blei
Bleid
Blt
Branch if Less Than Blt
Blti
Blti
Bltid
Bne
Branch if Not Equal Bne
Bned
Bnei
Branch Immediate if Not Equal Bnei
Bneid
Brd
Instructions Unconditional Branch
Bra
Brad
MicroBlaze Instruction Set Architecture
Bri
MicroBlaze Instruction Set Architecture
Instructions BrkBreak RD, rB
Msrbip
Brki
Break Immediate Brki RD, IMM
Instructions Barrel Shift Bsrl
Bsra
Bsll
Bsrai
Bsi
Barrel Shift Immediate Bsrli
Bslli
Cmp
Integer Compare Cmp
Cmpu
Fadd
Floating Point Arithmetic Add Fadd
Esrec FSRIO,UF,OF,DO
Frsub
Reverse Floating Point Arithmetic Subtraction
Frsub RD, rA, rB Reverse subtract
Fmul
Floating Point Arithmetic Multiplication Fmul
Fdiv RD, rA, rB Divide
Fdiv
Floating Point Arithmetic Division
Esrec FSRIO,UF,OF,DO,DZ
Fcmp
Esrec FSRIO,DO
Nget
Get
Get from fsl interface
Cget
Idiv
Integer Divide Idiv
Idivu
Imm
Immediate ImmIMM
Lbu
Load Byte Unsigned
Lbu RD, rA, rB
Lbui
Load Byte Unsigned Immediate Lbui RD, rA, IMM
Lhu
Lhu RD, rA, rB
Lhui
Load Halfword Unsigned Immediate Lhui RD, rA, IMM
Load Word
Lwi
Load Word Immediate Lwi RD, rA, IMM
Mfs
Mfs RD, rS
Msrclr
Read MSR and clear bits in MSR Msrclr RD, Imm
Msrset
Msrset RD, Imm
Mts
Move To Special Purpose Register Mts RS, rA
Instructions Mul Multiply RD, rA, rB
Muli
Multiply Immediate Muli RD, rA, IMM
Logical or
Ori
Logical or with Immediate Ori RD, rA, IMM
Pcmpbf
Pattern Compare Byte Find Pcmpbf
Pcmpeq
Pattern Compare Equal Pcmpeq
Pcmpne
Pattern Compare Not Equal Pcmpne
Nput
Put
Put to fsl interface
Cput
Rsubc
Rsub
Arithmetic Reverse Subtract Rsub
Rsubk
Rsubic
Rsubi
Arithmetic Reverse Subtract Immediate Rsubi
Rsubik
Rtbd
Return from Break
Rtbd RA, IMM
Rtid
Return from Interrupt Rtid RA, IMM
Msrie
Rted
Return from Exception Rted RA, IMM
Msree Msreip ESR
Rtsd
Return from Subroutine Rtsd RA, IMM
None
Sbi
Store Byte Immediate Sbi RD, rA, IMM
Sext16
Sext16 RD, rA
Sext8
Sign Extend Byte
Sext8 RD, rA
Instructions Store Halfword RD, rA, rB
Shi
Store Halfword Immediate Shi RD, rA, IMM
Sra
Sra RD, rA
Src
Shift Right with Carry Src RD, rA
Srl
Shift Right Logical
Srl RD, rA
Addr ← rA + rB Addr3031 ← MemAddr ← rD031
Register Altered
Store Word Immediate Swi RD, rA, IMM
Wdc
Write to Data Cache
Wic
Xor
Logical Exclusive or Xor RD, rA, rB
Xori
Logical Exclusive or with Immediate
Xori RA, rD, IMM
148